![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
129 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Physiological consequences of immobilization. |
Decreased ventilation! Dependent edema, negative nitrogen balance, renal calculi, osteoporosis, pressure ulcers. |
|
|
Does the nurse ever adjust the weights in traction? |
NEVER |
|
|
What is important about the ropes in traction? |
They need to be out of the child's reach; knots should be 6 inches away from pulleys/loops. |
|
|
How should the weights in traction be? |
Hanging freely; none on bed or floor. |
|
|
Purpose of traction. |
Alignment, relieve muscle spasm. |
|
|
Nursing care of a child in traction. |
Give activities - they're BORED. Monitor/ prevent skin breakdown. Watch the body's alignment (no slouching, tucked chin). |
|
|
What is the purpose of peddling a cast? |
Prevent skin breakdown from rubbing and from particles falling into cast. |
|
|
How often should a scoliosis patient wear their TLSO brace? |
23 hours a day, everyday. |
|
|
What is the most common fracture location in children? |
Clavicle (fall and try to catch self with arms out). |
|
|
What should the nurse suspect when a child has a spiral/twisted fracture? |
Child abuse. |
|
|
Who heals fractures fastest? |
Younger = faster |
|
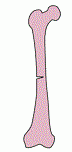
What type of fracture is this? |
Greenstick |
|
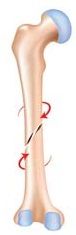
What type of fracture is this? |
Spiral |
|
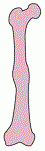
What type of fracture is this? |
Torus/Buckle |
|
|
Day 1 post-op scoliosis surgery: nursing care. |
Log roll q2 hrs; monitor neuro; monitor for ileus, NO WALKING/STANDING. |
|
|
Day 2 post-op scoliosis surgery: nursing care. |
Fitted for TLSO brace, NO WALKING/STANDING. |
|
|
Day 3 post-op scoliosis surgery: nursing care. |
Ambulate/physical therapy ONLY WITH BRACE. |
|
|
How can a child remove unwanted writing/markings from their plaster cast? |
White shoe polish (NO WATER) |
|
|
What does a nurse do when a child wants to keep their cast after removal? |
Remove all the padding from the inside and give them the hard outer layer. |
|
|
Nursing interventions for patients with halo traction. |
Skin care, pain, pin-site care (usually Chlorhexadine) |
|
|
Treatment for any limb fracture. |
RICE = Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation |
|
|
Does a child have to have a Harrington rod lifelong? |
No, it can be surgically removed after they stop growing. |
|
|
What bacteria causes impetigo? |
Group A Beta Hemolytic Strep |
|
|
What does impetigo look like? |
Honey crust. |
|
|
How long is impetigo contagious after initiating antibiotics? |
24 hours |
|
|
How long is bullous impetigo contagious after initiating antibiotics? |
48 hours |
|
|
One way to screen for hip dysplasia. |
Look for symmetrical gluteal folds. |
|
|
Hip dysplasia treatment |
Paulik harness |
|
|
How do you diaper a child in a Paulik harness? |
Under the harness. |
|
|
Can parents remove the Paulik harness at any time? |
Only VERY compliant parents can remove the harness temporarily for bathing. Usually, they much keep it on constantly. |
|
|
If you suspect a child has a Wilm's tumor, what should you NOT do? |
Palpate. |
|
|
What is important to tell a parent of a child with a Wilm's tumor? |
It's not their fault; the tumors grow very rapidly. |
|
|
What is the survival rate for children with leukemia? |
80% |
|
|
What is important about the leukemia child's room at the hospital? |
Reverse isolation: no fresh flowers, no outside toys, no standing water, visitors are minimal and must wear gown/gloves/mask. |
|
|
How low must the absolute neutrophil count be to initiate reverse isolation? |
< 500 |
|
|
What is important to teach parents and children about the side effect of 'moon face'? |
It's not permanent. |
|
|
Diabetic patients need _____ grams of carbohydrates for every 30 min. of extra physical exertion. |
10 |
|
|
Psychological consequences of immobility |
Diminished stimuli, no feedback, anxiety, depression, helplessness, regression. |
|
|
What is the major concern with epiphyseal plate injuries? |
May affect bone growth; e.g. different length limbs. |
|
|
What is an epiphyseal plate? |
Cartilage at the end of long bones (growth plates); weakest point. |
|
|
Assessment of fractures |
Five P's: Pain, Pulse, Pallor, Paresthesia, Paralysis. |
|
|
How do you handle a plaster cast in the 1st 24 hours of application? |
Use palms when touching; no fingers! |
|
|
How do you advise a patient that has an itch inside their cast? |
Scratch opposite limb; apply cool air. DO NOT insert anything inside to scratch. |
|
|
How do you clean a flaky skin from a limb that just had a cast removed? |
Soak arm in the tub; DO NOT scrub. Gently massage. |
|
|
What considerations are there for a young child with a cast? |
The child thinks it is a part of the body and that the cast saw will literally cut off their arm. |
|
|
What is distraction? |
Process of separating opposing bone to encourage regeneration of new bone in the created space. |
|
|
How do you cleanse the pin sites of external fixation? |
Clean with Chlorhexadine 2mg/mL q 6 hours x3 days, then q day (or hospital policy). |
|
|
What is the big concern when a fracture is not relieved by narcotic analgesics? |
It's a big sign of compartment syndrome. |
|
|
JRA Treatment |
Moist heat, splinting, warm waterbeds, NSAIDS, aspirin. |
|
|
What are the major goals in treating JRA? |
Promote mobility, control pain. |
|
|
What is used in children with JRA that do not respond well to NSAIDs/Aspirin? |
Methyltrexate in small doses. |
|
|
What is a major side effect of methyltrexate? |
Mucosal damage - mouth to anus. |
|
|
What is a concern when a child has a fracture in one location of the body, and a laceration in another part of the body? |
Infection; osteomyelitis. |
|
|
Treatment for osteomyelitis. |
High doses of antibiotics with PICC, no weight bearing, may need double-lumen tubes to flush out the infected bone, pain control. |
|
|
What side effects to look out for in high dosages of vancomycin and gentamicin? |
Hepatotoxicity, ototoxicity, renal toxicity. |
|
|
How often are casts changed in children with clubfoot? |
Every week to allow for growth. |
|
|
Who has a 20x greater risk of developing ALL? |
Those with Trisomy 21 (Downs) |
|
|
When can a child return to school after having chickenpox? |
When the lesions have scabbed over. |
|
|
What is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)? |
Slow progressive degeneration of muscle fibers. |
|
|
What type of gene is responsible for DMD? |
x-linked recessive (males have it) |
|
|
DMD S/S |
Waddling gait, lordosis, Gower's sign, contractures, weakness, pseudohypertrophy of calves. |
|
|
Pseudohypertrophy of calves. |
Large fatty deposits in place of the gastrocnemius muscles. |
|
|
When do most DMD children stop being able to walk? |
By 12 years. |
|
|
How long to DMD children usually live? |
Late teens. |
|
|
Gower's Sign |
Compensation of weak muscles: push self up with arms, climb own body with arms. |
|
|
DMD Treatment |
Steroids, prevent contractures, promote independence, C-PAP/Bi-PAP, counseling. |
|
|
What ultimately causes death in children with DMD? |
Respiratory/diaphragm failure (ventilator), then cardiac failure. |
|
|
What is phenylketonuria? |
Autosomal recessive; can't metabolize phenalalanine; can't convert it to Tyrosine, which is needed for epinephrine, melatonin, and thyroxine. |
|
|
PKU S/S |
Fair skin, blue eyes, musty mouse odor, mental retardation if untreated, FTT, irritable, vomiting, schizoid behavior, seizures. |
|
|
What is the most serious consequence of not treating PKU right away. |
Mental retardation |
|
|
PKU diagnostic test |
Guthrie test after ingesting protein, at 24 hours old. |
|
|
How much phenalanine can a PKU child get per day? |
30 kg |
|
|
What happens if the phenalanine level is <2? |
Catabolism |
|
|
What happens if the phenalanine level is >11? |
Brain damage |
|
|
How can you increase the calories of phenyl-free formula without adding any protein? |
Add polycose or MCT oil. |
|
|
PKU Treatment |
Restrict protein; supplement essential amino acid. |
|
|
Should pregnant women with PKU be on a special diet? |
Yes. |
|
|
Congenital hypothyroidism S/S in newborn |
Sleepy, low brow, large fontanel, poor feeding, prolonged jaundice, resp difficulty, cyanosis, bradycardia. |
|
|
Congenital hypothyroidism S/S after 6 weeks old |
Flat nasal bridge, low brow, puffy eyes, dry skin, coarse hair, large tongue, cold mottled skin, bradycardia, depressed reflexes, anemia, wide sutures. |
|
|
"She is SUCH a good baby! She never cries and sleeps through the night." |
Warning bells!!! Something isn't right!!! Possibly hypothyroid! |
|
|
Hypopituitarism S/S in infant |
Jaundice, hypoglycemic seizures, micropenis, undescended testicles, pale optic discs. |
|
|
How to diagnose hypopituitarism? |
Low 1GH-1 levels and bone age is younger than chronological age. |
|
|
What is very important to find out before initiating somatotrophin (growth hormone) treatment? |
Ensure the child has no tumors or cancer. GH wil accelerate their growth. |
|
|
How is somatotrophin (growth hormone) administered? |
SQ injection every day or every other day before bed. ROTATE INJECTION SITES. |
|
|
How should a child with hypopituitarism be encouraged to act? |
Dress age, participate in age appropriate activities. |
|
|
How to lessen the emotional trauma of daily injections with infants. |
Cuddle, love, distract. |
|
|
How to lessen the emotional trauma of daily injections with toddlers. |
Last minute; give choice. |
|
|
How to lessen the emotional trauma of daily injections with preschoolers. |
Tell them it's not their fault; play therapy. |
|
|
How to lessen the emotional trauma of daily injections with school age children. |
Educate them on how they body works; play therapy. |
|
|
What is IDDM? |
Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus; Type 1. |
|
|
What is NIDDM? |
Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus; Type 2 |
|
|
What type of DM do the majority of children have? |
IDDM/Type 2 |
|
|
Classic S/S DM |
Three P's: Polyuria, Polydipsia, Polyphagia |
|
|
What test monitors how the glucose level has been averaging over the prior 3 months? |
HbA1C |
|
|
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)? |
A condition that results when the body burns fat for energy; causes metabolic acidosis. |
|
|
DKA S/S |
Dehydration, Kussmaul breathing, wight loss, tachycardia, decreased LOC, hypotension, flushed cheeks and ears. |
|
|
If left untreated, how does DKA progress? |
Electrolyte disturbances, arrhythmias, and shock from dehydration. |
|
|
DKA labs. |
Hyperglycemia >300, glucosuria, ketonuria, pH <7.30, HCO1 < 15. |
|
|
Hypoglycemia S/S |
Irritability, shallow breathing, tachycardia, pallor, sweating, tremors, shaking, headaches, numb lips, confusion, seizure, unconsciousness, photophobia. |
|
|
Common causes for hypoglycemia |
Error in insulin dose, inadequate calories, exercise without corresponding caloric intake. |
|
|
Regular Insulin Onset, Peak, Duration |
Onset: 30 min, Peak: 2-3 hrs, Duration: 4-6 hours |
|
|
NPH Onset, Peak, Duration |
Onset: 2 hrs, Peak: 6-8 hrs, Duration: 12-16 hrs |
|
|
What do you advise parents of a diabetic child who has another illness. |
Keep insulin dose the same; give 8 oz. of liquid per hour, check urine for ketones. |
|
|
What is an autologous bone marrow transfusion? |
A transfusion using the patient's own disease-free tissue. |
|
|
What is the biggest problem with Hematopoietic Stem Cells Transplantation (HSCT)? |
Least desirable treatment: Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD); significant risk of mortality and morbidity; risk of overwhelming infection, severe organ damage. |
|
|
Cure rate after HSCT. |
60-70% |
|
|
Cancer S/S |
Pain, fever (FUO), skin changes, anemia, abdominal mass, lymphadenopathy. |
|
|
Neupogen Use |
Increase Leukocytes |
|
|
Neumega Use |
Increase neutrolphils and platelets |
|
|
Epo Alpha Use |
Increase RBCs |
|
|
Cytoxan major SE |
Hemhorragic Cystitis |
|
|
Adriamycin major SE |
Arrhythmia |
|
|
Vincritine Major SE |
nerVe damage; ileus |
|
|
Chemo drugs SEs, generally |
GI signs, Decrease WBCs, Decreased RBCs, Decreased platelets |
|
|
How should IV chemo be administered? |
Through a central line; they are vesicants. |
|
|
First sign of DMD? |
Muscle weakness at 3-7 years old. |
|
|
What is one of the risks of intrathecal cancer treatment? |
Developmental delay, some have personality change. |
|
|
Parents of child with cancer; when should they call the hospital/MD? |
Fever >38 C, port gets infected, exposure to illness, oral ulcer, vomiting, diarrhea, pain with elimination |
|
|
What is leukemia? |
An unrestricted proliferation of immature WBCs in the blood-forming tissues of the body. Liver and spleen are most severely effected. |
|
|
How is HIV diagnosed in children >18 months? |
ELISA and Western Blot |
|
|
How is HIV diagnosed in children <18 months? |
PCR |
|
|
How do you determine whether the child is responding well to the antiretroviral drugs for HIV? |
CD4 lymphocyte counts and viral loads. |
|
|
What prophylactic treatment do infants born to HIV+ mothers receive and why? |
Bactrim and Septra for 1 year to prevent Pneumocystitis Carinii |
|
|
Who is at high risk for latex allergy? |
Spina bifida patients (80%), urogenital abdnormalities, VADER, TEF, pts with multiple surgeries, healthcare workers. |
|
|
Cross reactions to latex allergy. |
Milk, kiwi, bananas, avocado, chestnuts, pineapple. |
|
|
Best pain reliever for otitis media. |
Tylenol |
|
|
Are antibiotic ear drops effective for otitis media? |
No, they are not effective. |
|
|
Are pain relief ear drops effective for otitis media? |
Yes, they are effective. |
|
|
What does 5ths disease look like? |
"Slapped cheek" |

