![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The net products of glycolysis are: |
2 Pyruvate, 2 ATP and 2 NADH |
|
|
What is the role of oxygen in aerobic respiration |
electrons are combined with protons and oxygen to make water at the end of the electron transport chain |
|
|
Chlorophyll is found: |
embedded in the thylakoid membrane of a chloroplast |
|
|
in noncyclic photosynthetic electron transport: |
both photosystem 1 and 2 operate |
|
|
Describe the calvin cycle |
The calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to fix atmospheric CO2 into organic molecules |
|
|
what is Rubisco |
Rubisco is found in the Calvin Cycle, It is inhibited by 02, is a very slow enzyme and is a protein |
|
|
How many DNA molecules are in each sister chromatid of a chromosome at metaphase of mitosis |
1 |
|
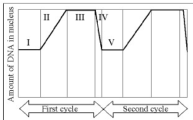
The figure illustrates DNA content in a cell progressing through two rounds of the cell cycle. Which phase or phases show a cell in G2? |
III |
|
|
Communication between cells is analogous to communication between people. Which form of intercellular communication is most like conversation at a party? |
paracrine signaling |
|
|
Ligand-receptor binding is most like |
The interaction of enzyme and substrate |
|
|
Only when the receptor is bound to its ligand can it interact with the first protein in a signal transduction cascade. This is because |
the receptor bound to its ligand has the proper shape |
|
|
Image the following: you examine proteins in a cell and find one protein that is phosphoylated to unusually high levels. A plausible explantion is that |
a protein phosphatase is inactive or a protein kinase is overly active. |
|
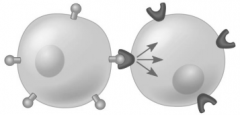
Which is a ligand |
The ball shaped thingies on the signal cell |
|
|
True or False, a signal binding to the same type of receptor will always lead to the same cellular response |
False |
|
|
Apoptosis occurs ___________ in cancer cells |
inefficiently |
|
|
Which is the shortest cell cycle phase |
M phase |
|
|
Human nuclei contain 46 chromosomes. Therefore, just before mitosis, each nucleus contains ____________ molecules of DNA |
92 |
|
|
A human nucleus entering prophase contains 46 chromosomes. At the end of telophase, each human nucleus contains ________ chromosomes and ________ DNA molecules |
46:46 |
|
|
A particular cyclin called cyclin E forms a complex with a cyclin dependent kinase called CDK 2. This complex is important for the progression from G1 into the S phase of the cell cycle. At what point in the amount of cyclin highest |
Late in G1 and early S phase |
|
|
What fluctuates throughout the cell cycle? |
The amount of cyclin and the activity of CdK protein |
|
|
True or false, Mitosis and meiosis occur only in diploid cells |
False |
|
|
The immediate energy source that drives ATP Synthesis by ATP synthase during oxidative pshosphorylation is the |
H+ concentration across the membrane holding ATP synthase |
|
|
Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration of a glucose molecule? |
glycolysis
|
|
|
The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in aerobic oxidative phosphorylation is |
Oxygen
|
|
|
in mitochondria, exergonic redox reactions: |
Provide the energy that establishes the proton gradient
|
|
|
What is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? Pyruvate + NADH + H+ S Lactate + NAD+ |
Pyruvate
|
|
|
When electrons flow along the electron transport chains of mitochondria, what occurs? |
The pH of the matrix increases
|
|
|
most Co2 from catabolism is released during |
the citric acid cycle |
|
|
The light reactions of photosynthesis supply the calvin cycle with |
ATP and NADPH |
|
|
What is the correct flow of electrons during photosynthesis |
H2O → NADPH → Calvin cycle |
|
|
How is photosynthesis similar in C4 plants and CAM plants |
In both cases, rubisco is not used to fix carbon initially |
|
|
What is the correct distinction between autotrophs and heterotrophs |
autotrophs, but not heterotrophs, can nourish themselves beginning with CO2 and other nutrients that are inorganic
|
|
|
What are some things that occur during the calvin cycle? |
consumption of ATP, regeneration of the CO2 acceptor ,carbon fixation , oxidation of NADPH, |
|
|
In mechanism, photophosphorylation is mostly similar to |
oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration |
|
|
Which process is most directly driven by light energy? |
Removal of electrons from chlorophyll molecules |
|
|
Binding of a signaling molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the ions on opposite sides of the membrane? |
Ligand-gated ion channel |
|
|
The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases is characterized by: |
dimerization and phosphorylation |
|
|
Lipid soluble signaling molecules, such as aldosterone, cross the membranes of all cells but target cells because |
Intracellular receptors are present only in target cells
|
|
|
Consider this pathway: epinephrine → G protein-coupled receptor → G protein → adenylyl cyclase → cAMP. Identify the second messenger |
cAMP
|
|
|
Apoptosis involves all but which of the following? |
lysis of the cell
|
|
|
which observation suggested to Sutherland the involvement of a second messenger in epinephrine's effect on liver cells? |
clycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine was administered to intact cells
|
|
|
Protein phosphorylation is commonly involved with what? |
enzyme activation. activation of protein kinase molecules. activation of receptor tyrosine kinases. regulation of transcription by extracellular signaling molecules. |
|
|
Through a microscope, you can see a cell plate beginning to develop across the middle of a cell and nuclei forming on either side of the cell plate. This cell is most likely: |
A plant cell in the process of cytokinesis |
|
|
Vinblastine is a standard chemotherapeutic drug used to treat cancer. Because it interferes with the assembly of micro-tubules, its effectiveness must be related to |
disruption of mitotic spindle formation
|
|
|
One difference between cancer cells and normal cells is that cancer cells |
continue to divide even when they are tightly packed together
|
|
|
The decline of MPF activity at the end of mitosis is due to |
The degradation of cyclin
|
|
|
In the cells of some organisms, mitosis occurs wihtout cytokinesis. This will result in |
cells with more than one nucleus
|
|
|
A particular cell has half as much DNA as some other cells in a mitotically active tissue. The cell in question is most likely in |
G1
|
|
|
The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. Which aspect of the cell cycle would be most disrupted by cytochalasin B? |
Cleavage furrow formation and cytokinesis |
|
|
Catabolic pathway |
a metabolic pathway that releases energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler molecules |
|
|
Reduction |
The complete or partial addition of electrons to a substance involved in a redox reaction |
|
|
A cell containing two sets of chromosomes (2n), one set inherited from each parent |
diploid cell |
|
|
Mitosis |
A process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells conventionally divided into five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Mitosis conserves chromosome number by allocating replicated chromosomes equally to each of teh daughter nuclei |
|
|
Induced fit |
caused by entry of the substrate, athe change in shape of the active site of an enzyme so that it binds more snugly to the substrate |
|
|
G2 phase |
the second gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs |
|
|
feedback inhibition |
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway |
|
|
Somatic cell |
Any cell in a multicellular organism except a sperm or egg or their precursors |
|
|
Cyclin dependent kinase |
A protein kinase that is only active when attached to a particular cyclin |
|
|
cooperativity |
A kind of allosteric regulation whereby a shape change in one subunit of a protein caused y substrate binding is transmitted to all the other subunits, facilitating binding of additional substrate molecules to those subunits |
|
|
noncompetitive inhibitor |
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing the enzyme's shape so that the active site no longer effectively catalyzes the conversion of substrate to product |
|
|
autosome |
A chromosome that is not directly involved in detemining sex; not a sex chromosome |
|
|
adenylyl cyclase |
an enzyme that converts ATP to cyclic AMP in response to an extracellular signal |
|
|
metaphase |
The third stage of mitosis, in which the spindle is complete and the chromosomes, attached to microtubules at their kinetochores, are all aligned at the metaphase plate |
|
|
photorespiration |
A metabolic pathway that consumes oygen and ATP, releases carbon dioxide, and decreases photosynthetic output. Photorespiration generally occurs on hot, dry, bright days, when stomata close and the o2/CO2 ratio in the leaf increases, favoring the binding of o2 rather than CO2 by rubisco. |
|
|
bar graph |
a graph in which the independent variable represents groups or nonnumerical categories and the values of the dependent variables are shown by bars |
|
|
lactic acid fermentation |
Glycolysis followed by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate, regenerating NAD+ with no release of carbon dioxide |
|
|
crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) |
An adaptation for photosynthesis in arid conditions, first icovere in the family crassulaceae. In this process, a plant takes up CO2 and incorporates it into a variety of organic acids at night; during theday, Co2 is released from organic acids for use in the Calvin cycle. |

