![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the five functions of the body?
|
Movement - at joint
Support - for muscles Shape - for maintaining our body shapes Protection - such s skull protecting our brains Blood-cell Production - in the bone marrow |
|
|
What are the four different types of bones?
|
Long bones - femur, humerus
Short bones - Phalanges Flat - cranium, Sternum Irregular - vertebrate, patella |
|
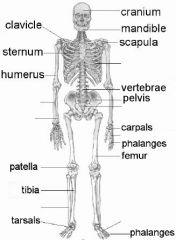
Label the Skeleton
|
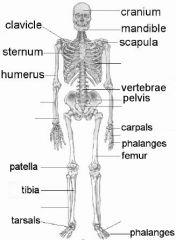
|
|
|
What is a Synovial Joint? and Give the definition of Articulating
|
A joint that allows movement is called a 'Synovial joint' e.g. knee
A joint is where two bones meet. if a movement is possible the bones are said to be 'articulating'. |
|
|
Give the two types of joints and an example
|
Hinge - a synovial joint - knee and elbow
Ball and Socket - a synovial joint - shoulder and hip |
|
Label the muscles
|
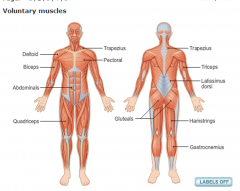
|
|
|
What types of muscles are there?
|
Skeletal - Make the skeleton move - these are voluntary muscles are you choose to move them.
Cardio Muscles - these are found in the walls of your heart and are involuntary Involuntary Muscles - muscles within the body that allows the body to keep functioning |
|
|
What are the three connective tissues?
|
Tendons - strong elastic tissue that connects muscle to bone
Ligaments - Stabilise a joint and connect bone to bone Cartilage - Found around the end of bones, acts as a butter |
|
|
Give definitions of Origin and Insertion and an example.
|
The end of the muscle attached to the stationary bone is called the origin.
The end of the muscle attached to the moving bone is called the insertion e.g. The biceps origin is the shoulder and the insertion is at the elbow |
|
|
Why do muscles work in pairs?
|
Muscles cannot push bones, they can only pull them, this means that they need to work in pairs.
|
|
|
Give the definition of Antagonistic
The Prime Mover Antagonist |
These pairs are called antagonistic pairs
The contracted muscle is called the prime mover The muscle relaxing is the antagonist |
|
|
Give the definition of muscle tone and posture
|
Muscle tone is the muscles state of slight tension and readiness to work. muscle tone helps with posture
Posture related to the way the body is supported by the muscles when standing or moving |
|
|
Give the definition of Flexion
Extension Adduction Abduction |
Pictures :
|
|
|
What are isotonic contractions and isometric contractions?
|
Muscles contract when they work. If a muscle contracts to create movement, it is called an isotonic contraction
When a muscle contracts with no resulting movement, it is an isometric contraction. e.g. plank, tug of war, wall sits |
|
|
Give definitions of concentric and eccentric in isotonic
|
Concentric - muscle shortens (bulges)
e.g. your biceps when you flex Eccentric - Muscle lengthens e.g. your triceps when you to tricep dips |

