![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define "FORDYCE GRANULES"
|
- ectopic sebaceous glands in the oral mucosa
|
|
|
Define "ECTOPIC"
|
- normal tissue in an abnormal location
|
|
|
What is the etiology of FORDYCE GRANULES?
|
developmental
|
|
|
FORDYCE GRANULES are most commonly found where?
|
- buccal mucosa
- lateral portions of the vermillion of the upper lip |
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of FORDYCE GRANULES?
|
- asymptomatic
- multiple white yellow papular lesions |
|
|
How is a diagnosis of FORDYCE GRANULES made?
|
usually based on clinical criteria
|
|
|
What complications may arise with FORDYCE GRANULES?
|
- rarely solitary sebacious gland may undergo adenomatous hyperplasia
- keratin-filled pseudocyst |
|
|
Define "LEUKOEDEMA"
|
- common alteration of oral epithelium characterized by accumulation of fluid (edema) in the spinous layer
|
|
|
LEUKOEDEMA is more pronounced in which demographic:?
|
smokers
|
|
|
What is the most common localization of LEUKOEDEMA?
|
- blateral buccal mucosa
|
|
|
How is a diagnosis of LEUKOEDEMA confirmed?
|
- affected mucosa should be stretched during clinical examination - the white appearance greatly diminishes or disappears when the cheek is everted and stretched
|
|
|
What is the treatment of LEUKOEDEMA?
|
- no treatment
- smoking cessation results in good prognosis |
|
|
Define "AGLOSSIA"
|
no tongue
|
|
|
Define MICROGLOSSIA:
|
- uncommon condition characterized by abnormal small tongue
|
|
|
MICROGLOSSIA is MOSTLY associated with _____ and frequently associated with _______.
|
a) syndromes
b) hypoplasia of the mandible and lower incisors may be missing |
|
|
Define SYNDROME:
|
combination of signs and symptoms occurring commonly enough to constitute a distinct clinical entity
|
|
|
What are the two most frequent causes of MACROGLOSSIA?
|
- vascular malformation
- muscular hypertrophy |
|
|
What are the first signs of manifestation of MACROGLOSSIA in infants?
|
- noisy breathing
- drooling - difficulty eating |
|
|
MACROGLOSSIA may produce what clinical features?
|
- open bite
- mandibular prognathism - eating problems - lisping speech - crenations of lateral border of the tongue - tongue may ulcerate and become secondarily infected - if SEVERE may produce airway obstruction |
|
|
MACROGLOSSIA is a characteristic feature of what syndrome?
|
Beckwith-Wideman syndrome
|
|
|
What treatment is done in symptomatic patients with MACROGLOSSIA?
|
- reduction glossectomy
- may benefit from speech therapy in mild cases |
|
|
Define ANKYLOGLOSSIA:
|
abnormal attachment of the lingual frenum, limiting tongue mobility
|
|
|
What is the etiology of ANKYLOGLOSSIA?
|
developmental
|
|
|
What are some complications of ANKYLOGLOSSIA?
|
- speech problems
- clefting of tongue tip - periodontal problems due to high mucogingival attachment of the lingual frenum |
|
|
Define LINGUAL THROID:
|
ectopic thyroid tissue located on posterior dorsal tongue
|
|
|
Most (90%) of ectopic thyroids are found in what region?
|
FORAMEN CAECUM AND EPIGLOTTIS
|
|
|
What are the most common symptoms of LINGUAL THYROID?
|
- dysphagia (difficulty eating)
- dysphonia (difficulty speaking) - dyspnea (difficulty breathing) |
|
|
Which systemic condition has been reported in up to 1/3 of LINGUAL THYROID patients?
|
HYPOthyroidism
|
|
|
Why is a biopsy often avoided in LINGUAL THYROID cases?
|
Because in 70% of cases this ectopic gland is the patients only functioning thyroid tissue
- risk of hemorrhage is large |
|
|
How is a diagnosis made of LINGUAL THYROID?
|
thyroid scan using iodine isotopes or technetium 99m
|
|
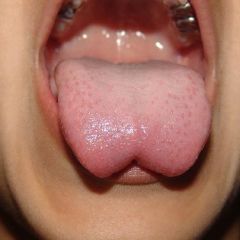
Identify the developmental defect:
|
ANKYLOGLOSSIA
|
|
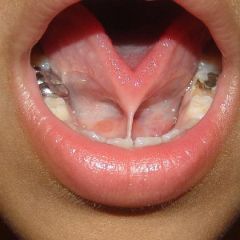
Identify the developmental defect:
|
ANKYLOGLOSSIA
|
|
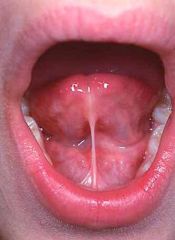
Identify the developmental defect:
|
ANKYLOGLOSSIA
|
|
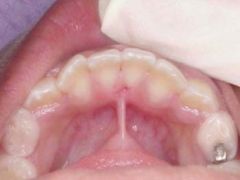
Identify the developmental defect:
|
ANKYLOGLOSSIA
|
|
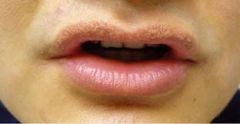
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FORDYCE GRANULES
|
|
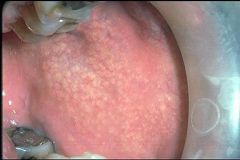
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FORDYCE GRANULES
|
|
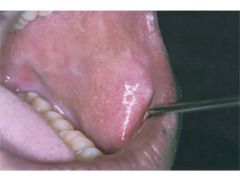
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FORDYCE GRANULES
|
|
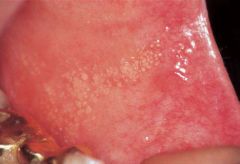
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FORDYCE GRANULES
|
|
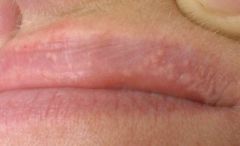
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FORDYCE GRANULES
|
|
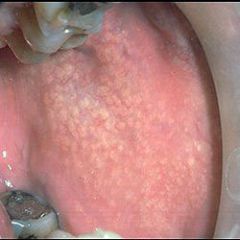
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FORDYCE GRANULES
|
|
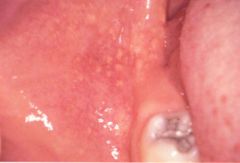
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FORDYCE GRANULES
|
|
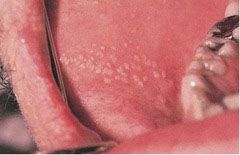
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FORDYCE GRANULES
|
|
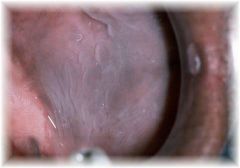
Identify the developmental defect:
|
LEUKOEDEMA
|
|
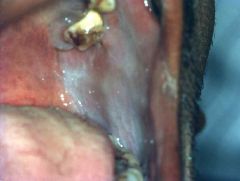
Identify the developmental defect:
|
LEUKOEDEMA
|
|
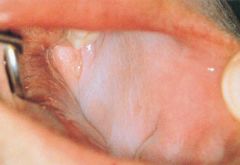
Identify the developmental defect:
|
LEUKOEDEMA
|
|
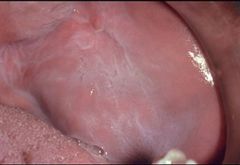
Identify the developmental defect:
|
LEUKOEDEMA
|
|
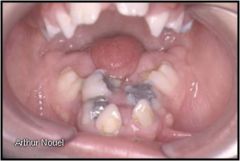
Identify the developmental defect:
|
MICROGLOSSIA
|
|
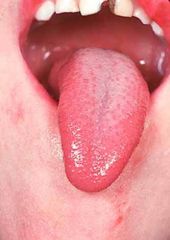
Identify the developmental defect:
|
MICROGLOSSIA
|
|
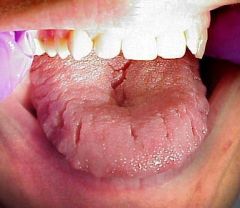
Identify the developmental defect:
|
MACROGLOSSIA
|
|
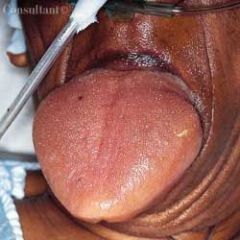
Identify the developmental defect:
|
MACROGLOSSIA
|
|
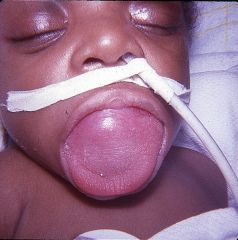
Identify the developmental defect:
|
MACROGLOSSIA
|
|
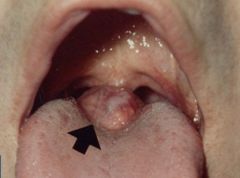
Identify the developmental defect:
|
LINGUAL THYROID
|
|
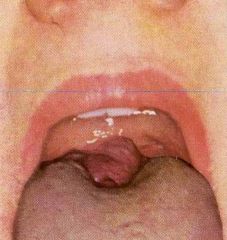
Identify the developmental defect:
|
LINGUAL THYROID
|
|
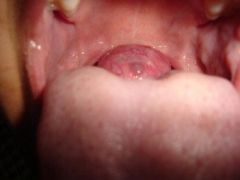
Identify the developmental defect:
|
LINGUAL THYROID
|
|
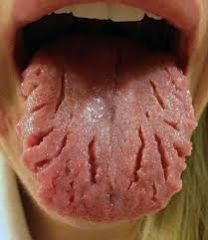
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FISSURED TONGUE
|
|
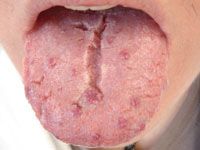
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FISSURED TONGUE
|
|
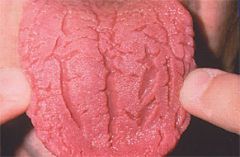
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FISSURED TONGUE
|
|
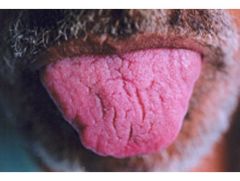
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FISSURED TONGUE
|
|
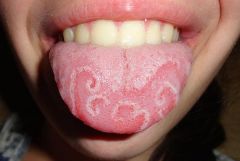
Identify the developmental defect:
|
GEOGRAPHIC TONGUE
|
|
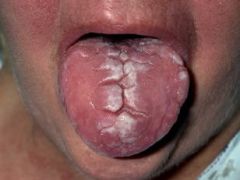
Identify the developmental defect:
|
FISSURED TONGUE
|
|
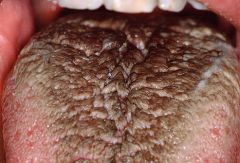
Identify the developmental defect:
|
HAIRY TONGUE
|
|
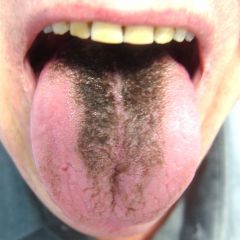
Identify the developmental defect:
|
HAIRY TONGUE
|
|
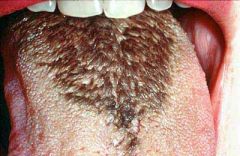
Identify the developmental defect:
|
HAIRY TONGUE
|
|
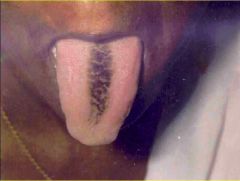
Identify the developmental defect:
|
HAIRY TONGUE
|
|
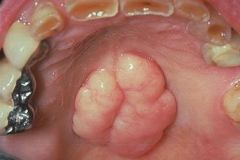
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS PALATINUS
|
|
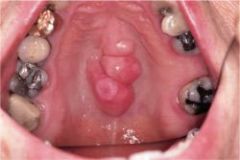
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS PALATINUS
|
|
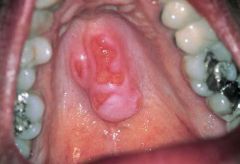
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS PALATINUS
|
|
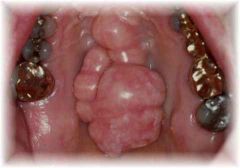
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS PALATINUS
|
|
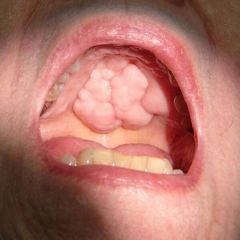
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS PALATINUS
|
|
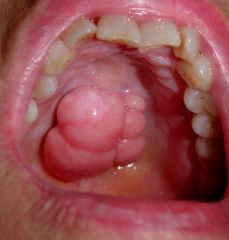
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS PALATINUS
|
|
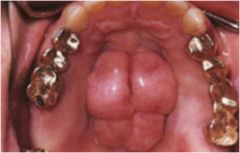
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS PALATINUS
|
|
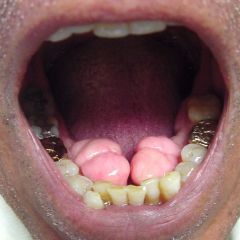
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS MANDIBULARIS
|
|
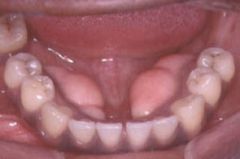
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS MANDIBULARIS
|
|
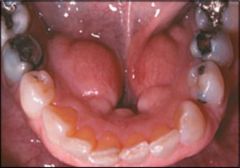
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS MANDIBULARIS
|
|
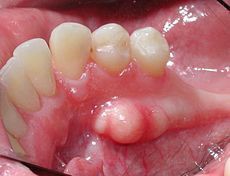
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS MANDIBULARIS
|
|
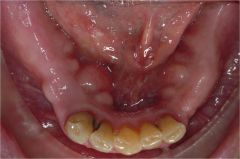
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS MANDIBULARIS
|
|
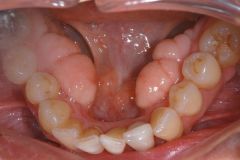
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS MANDIBULARIS
|
|
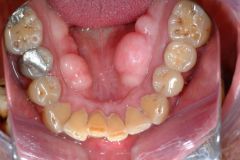
Identify the developmental defect:
|
TORUS MANDIBULARIS
|
|
|
Define "VARICOSITY"
|
a varicosity , or venous varix, is a type of acquired vascular malformation that represents focal dilation of a single vein
|
|
|
What is the most common location of VARICOSITIES?
|
sublingual varices on ventral surface of the tongue and lateral border of the tongue
|
|
|
SOLITARY VARICES of the lips and buccal mucosa may need surgical removal why?
|
- TO CONFIRM DIAGNOSIS:
- phlebolith, thrombus formation, or esthetic purposes |
|
|
Define EXOSTOSES:
|
localized bony protruberances that arise from the cortical plate
|
|
|
What are the two most common EXOSTOSES?
|
- torus mandibularis
- torus palatinus |
|
|
EXOSTOSES are usually removed for which reasons?
|
- if frequent trauma occurs
- for prosthetic reasons and to allow proper flap adaptation during periodontal surgery |
|
|
Define STAFNE BONE DEFECT:
|
focal concavity of the cortical bone on the lingual surface of the mandible
|
|
|
What is the radiographic presentation of a STAFNE BONE DEFECT?
|
- well circumscribed radiolucency with sclerotic borders, BELOW THE MANDIBULAR CANAL
|
|
|
What is the treatment for a STAFNE BONE DEFECT?
|
no treatment necessary
|
|
|
HEMIFACIAL HYPERPLASIA occurs more often on whcih side of the body?
|
RIGHT SIDE
|
|
|
HEMIFACIAL HYPERPLASIA occurs more commonly in which gender?
|
Females (2:1)
|
|
|
What are the FOUR types of HYPERPLASIA?
|
1. Complex hyperplasia (one whole side of the body)
2. Simple hyperplasia (single digit) 3. Segmental hyperplasia (a limb) 4. Hemifacial hyperplasia (one side of face) |
|
|
Patients with HEMIFACIAL HYPERPLASIA have increased incidence of what?
|
abdominal tumours
20% have mental retardation |
|
|
What are the ORAL FEATURES of HEMIFACIAL HYPERPLASIA?
|
- unilateral macroglossia
- mandibular canal and teeth can be larger - malocclusion with open bite - premature developemnt of the affected teeth along with precocious eruption |

