![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Marfan's syndrome? |
• Autosomal dominant • Connective tissue disorder |
|
|
Pathogenesis of Marfan's syndrome |
• Inherited defect in fibrillin-1 • Fibrillin-1: Glycoprotein, major component of microfibrils in the ECM |
|
|
Skeletal abnormalities of Marfan |
• Unusually tall, long extremities, long tapering fingers and toes • Lax joint ligaments of hand and feet; thumb hyperextends upto wrist • Dolichocephalic, frontal bossing, supraorbital ridges prominent • Spinal deformities: kyphosis/scoliosis/slipping or rotation of lumbar vertebrae • Chest deformities: pectus excavatum or carinatum
|
|
|
Ocular change in Marfan |
• Bilateral dislocation of the lens - Ectopia Lentis |
|
|
Cardiovascular lesions in Marfan |
• Mitral valve prolapse
• Dilated ascending aorta due to cystic medionecrosis
• Severe aortic incompetence |
|
|
What is Down Syndrome? |
• Chromosomal disorder • Extra copy of genes on Chromosome 21 |
|
|
Down syndrome karyotypes |
1. Trisomy 21- 95% cases: 47, XY or XX,+21 2. Translocation - 4% cases: Fill later 3. Mosaic - 1% cases: 46,XX/47,XX,+21 |
|
|
Features of Down Syndrome |
- Flat facial profile, oblique palpebral fissures, epicanthic folds - Single palmer crease (Simian) - Severe mental retardation (IQ 25-50) - 10-20x risk of acute leukaemia (ALL, AML) - Neurodegeneration after 40y (Alzheimer's) - ↑Risk of umbilical hernia - Muscular hypotonia - ↑Gap b/w toe1 and toe2 - ↓Immunity |
|
|
What is Klinefelter syndrome? |
- Male hypogonadism - X≥2, Y≥1 - 1/600 |
|
|
Autosomal dominant disorders |
Skeletal: • Marfan • Osteogenesis imperfecta • Achondroplasia
Nervous: • Huntington • Neurofibromatosis
Haematological: • Hereditary spherocytosis • von Willebrand
Urinary: • Polycystic kidney
GIT: • Familial polyposis coli
Metabolic: • Familial hypercholesterolaemia • Acute intermittent porphyria |
|
|
Sickle cell mutation |
GAG → GUG
Glutamic acid → Valine |
|
|
Thalassemia mutation |
CAG → UAG
Glutamine → STOP |
|
|
Genetic disorders types |
- disorders of mutant genes with large effect
- diseases with multifactorial/multigenic inheritance
- chromosomal disorder
- single gene disorders with nonclassical patterns of inheritance |
|
|
Types of frame shift |
- deletion - insertion - gene amplification |
|
|
Types of gene mutation |
- Point - Frame shift - Tri nucleotide repeat |
|
|
Diagnosing genetic disorders |

Molecular : PCR FISH Southern, Northern, Western blotting DNA profiling * Amniocentesis: a process in which amniotic fluid is sampled using a hollow needle inserted into the uterus, to screen for abnormalities in the developing fetus |
|
|
Autosomal recessive disorders |
Metabolic: • Cystic fibrosis • Homocysteinuria • Lysosomal storage disease • Glycogen storage disease • Wilson's disease • Haemochromatosis • α1 antitrypsin deficiency
Haemopoietic: • β-thalassemia • Sickle cell anaemia
Endocrine: • Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Skeletal: • EDS – Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome • Alkaptonuria
Nervous: • Neurogenic muscular atrophy • Spinal muscular atrophy • Friedreich ataxia
|
|
|
X-linked recessive disorders |
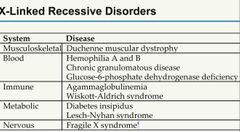
• DMD • Haemophilia • Diabetes insipidus • G6PD deficiency • Fragile X syndrome • Agammaglobulinaemia
|
|
|
Types of mutation |
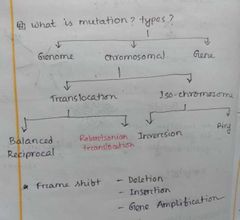
|

