![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the normal anatomy of a tooth
|
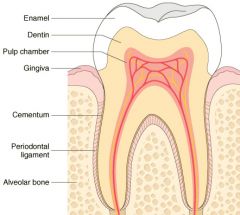
Schematic representation of the normal dental anatomy and surrounding supporting tissues.
|
|
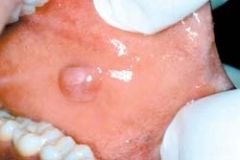
What is demonstrated here
|
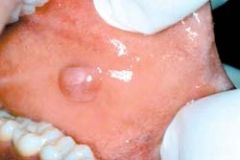
Fibroma. Smooth, pink, exophytic nodule on the buccal mucosa
|
|
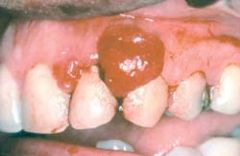
What is shown here
|
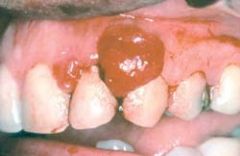
Pyogenic granuloma. Erythematous, hemorrhagic, and exophytic mass arising from the gingival mucosa
|
|
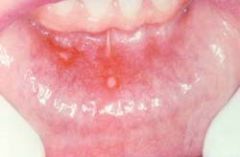
What is shown here
|
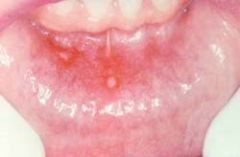
Aphthous ulcer (Canker). Single ulceration with an erythematous halo surrounding a yellowish fibrinopurulent membrane
|
|
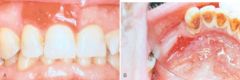
What is shown here
|
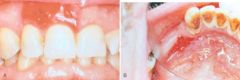
Erythroplakia. A, Lesion of the maxillary gingiva. B, Red lesion of the mandibular alveolar ridge. Biopsy of both lesions revealed carcinoma in situ
|
|
What is shown here
|
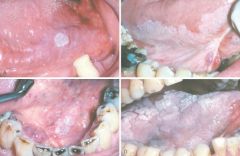
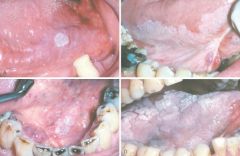
Leukoplakia. Clinical appearance of leukoplakias is highly variable and can range from A, smooth and thin with well-demarcated borders. B, diffuse and thick. C, irregular with a granular surface. D, diffuse and corrugated
|
|
|
What is the clinical, histologic, and molecular progression of oral cancer
|
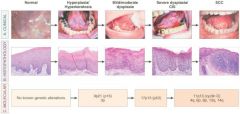
Clinical, histologic, and molecular progression of oral cancer. A, The typical clinical progression of oral cancer. B, The histologic progression of squamous epithelium from normal, to hyperkeratosis, to mild/moderate dysplasia, to severe dysplasia, to cancer. C, The sites of the most common genetic alterations identified as important for cancer development
|
|
|
Where does squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity arise
|
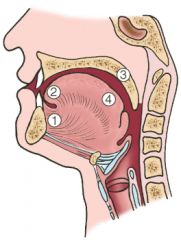
Schematic representation of the sites of origin of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, in numerical order of frequency
|
|
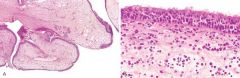
What is shown here
|
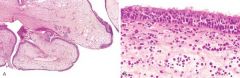
A, Nasal polyps. Low-power magnification showing edematous masses lined by epithelium. B, High-power view showing edema and eosinophil-rich inflammatory infiltrate.
|
|
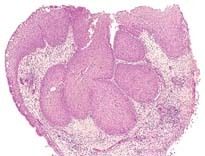
What is shown here
|
Inverted papilloma, the most important of the Sinonasal Papillomas. The masses of squamous epithelium are growing inward; hence, the term inverted
|
|
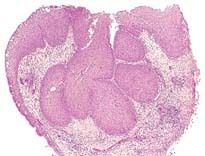
This specimen came from the upper airway. What does it demonstrate
|
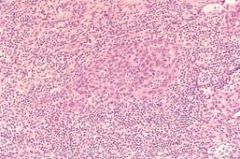
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma, lymphoepithelioma type. The syncytium-like nests of epithelium are surrounded by lymphocytes
|
|
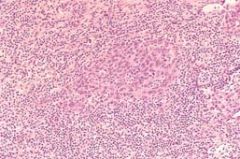
What is shown here
|
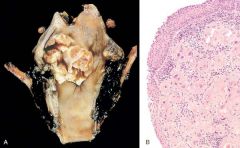
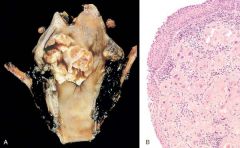
A, Laryngeal carcinoma. Note the large, ulcerated, fungating lesion involving the vocal cord and piriform sinus. B, Histologic appearance of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Note the atypical lining epithelium and invasive keratinizing cancer cells in the submucosa
|
|
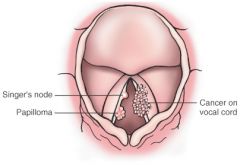
What does this picture demonstrate
|
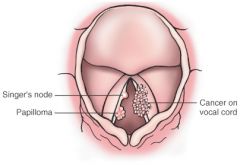
Diagrammatic comparison of a benign papilloma and an exophytic carcinoma of the larynx to highlight their quite different appearances
|
|
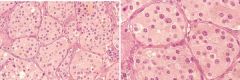
What is shown here
|
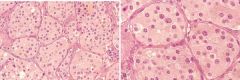
Carotid body tumor (Paraganglioma of the neck). A, Low-power view showing tumor clusters separated by septa (zellballen). B, High-power view of large, eosinophilic, slightly vacuolated tumor cells with elongated sustentacular cells in the septa
|
|
What do these pictures demonstrate
|
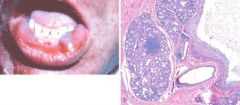
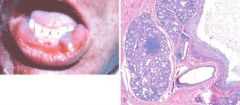
Mucocele, the most common lesion of the salivary glands. A, Fluctuant fluid-filled lesion on the lower lip subsequent to trauma. B, Cystlike cavity filled with mucinous material and lined by organizing granulation tissue.
|
|
What do these pictures demonstrate
|
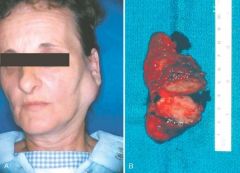
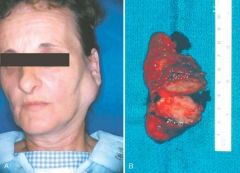
Pleomorphic adenoma, or mixed tumor. A, Slowly enlarging neoplasm in the parotid gland of many years duration. B, The bisected, sharply circumscribed, yellow-white tumor can be seen surrounded by normal salivary gland tissue
|
|
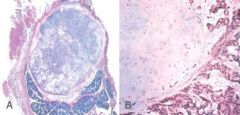
What do these pictures represent
|
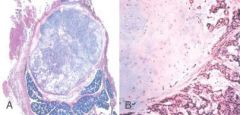
Pleomorphic adenoma. A, Low-power view showing a well-demarcated tumor with adjacent normal salivary gland parenchyma. B, High-power view showing epithelial cells as well as myoepithelial cells found within a chondroid matrix material
|
|
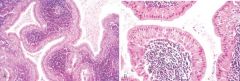
What do these pictures demonstrate
|
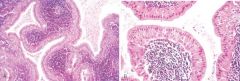
Warthin tumor. A, Low-power view showing epithelial and lymphoid elements. Note the follicular germinal center beneath the epithelium. B, Cystic spaces separate lobules of neoplastic epithelium consisting of a double layer of eosinophilic epithelial cells based on a reactive lymphoid stroma
|
|
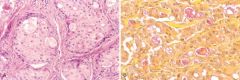
What do these pictures demonstrate
|
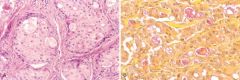
A, Mucoepidermoid carcinoma showing islands having squamous cells as well as clear cells containing mucin. B, Mucicarmine stains the mucin reddish-pink
|
|
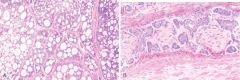
This sample was taken from the salivary glands. What does it represent
|
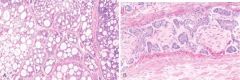
Adenoid cystic carcinoma in a salivary gland. A, Low-power view. The tumor cells have created a cribriform pattern enclosing secretions. B, Perineural invasion by tumor cells.
|

