![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
MCC of tertiary hyperparathyroidism (least common type) |
Post renal transplant (PTH raised long after calcium levels corrected) |
|
|
|
White pulp of spleen undergoes necrosis due to |
Beta hemolytic streptococcus |
|
|
|
Pipe Stem hepatic fibrosis |
Schistosomiasis |
This leads to congestive splenomegaly |
|
|
Splenic infarcts |
White and bland |
|
|
|
Hassall corpuscles |
Thymic medullary epithelial cells |
|
|
|
Thymic hyperplasia due to |
Proliferation of B CELLS |
|
|
|
MCC of thymic follicular hyperplasia |
Myasthenia gravis |
|
|
|
Thymomas |
Tumors of thymic epithelial cells |
|
|
|
Non invasive thymomas |
Medullary type epithelial cells Less thymocytes |
|
|
|
Invasive thymomas |
Cortical type epithelial cells More thymocytes |
|
|
|
MC type of thymic carcinoma |
SCC |
Second MC-lymphoepithelioma type (EBV causal) |
|
|
MC variety of thymomas associated with Autoimmune dz |
Cortical type |
|
|
|
PARATHYROID GLANDS |
pathology of parathyroid glands |
|
|
|
PTH released by |
Chief cells of PTH gland |
|
|
|
Function of PTH |
Increases ionized calcium in serum |
-increases bone osteoclast action -increases small bowel calcium and phosphate absorption (via Vit D ) -increases renal calcium reabsorption ( distal tubule ) -deceased renal phophate reabsorption ( proximal tubule) |
|
|
MCC of primary hyperparathyroidism |
Solitary Parathyroid adenomas |
|
|
|
MCC of secondary hyperparathyroidism (compensatory raised PTH secretion) |
Chronic renal failure |
|
|
|
MCC of tertiary hyperparathyroidism (least common type) |
Post renal transplant (PTH raised long after calcium levels corrected) |
|
|
|
Causes of Hypercalcemia with raised PTH |
1° hyperparathyroidism 2° hyperparathyroidism 3° hyperparathyroidism Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia |
|
|
|
Causes of Hypercalcemia with decreased PTH |
Malignancy Sarcoidosis Vit D intoxication Thiazides Immobilization |
|
|
|
Clinical feature of hypercalcemia |

|
|
|
|
MCC of hypercalcemic crisis (Ca>15mg/dl) |
CA breast |
|
|
|
Excess calcium ingestion causes |
Milk alkali syndrome (as antacids of calcium carbonate/milk) Hypercalcemia Alkalosis Renal failure |
Chronic form of DZ-BURNETT SYNDROME |
|
|
Pancreatitis leads to |
Hypo calcemia |
Calcium levels? |
|
|
Case of 1° hyperparathyroidism |

|
|
|
|
Lab findings in primary hyperparathyroidism |
Increased PTH Increased Ca2+ Decreased PO43- Increased urinary cAMP Increased serum alkaline phosphatase
|
Lab findings in 2° hyperparathyroidism-
Decreased PO4 excretion Increased serum PO4 Decreased serum Ca Increased PTH (renal osteodystrophy) Increased SALP |
|
|
Radiological features of 1° hyperparathyroidism |

|
|
|
|
Clinical features of primary hyperparathyroidism |
-Bones (osteoporosis) -Renal Stones (calcium oxalate) -Abdominal Groans (constipation, acute pancreatitis, pud) -Psychiatric Moans (depression, seizures) -polyuria -brown tumors (osteitis fibrosa cystica)-hallmark of severe hyperparathyroidism-von recklinghausen dz of bone -proximal myopathy -gout/pseudo gout -nephrocalcinosis |
T/T of 1° hyperparathyroidism-sx removal of affected gland |
|
|
Vitamin intoxication leading to hypercalcemia |
Vit A>D |
|
|
|
Initial management of Hypercalcemia |

|
|
|
|
MC presentation of 1° hyperparathyroidism in developing countries |
Bones Stones Groans Moans |
|
|
|
MC presentation of 1° hyperparathyroidism in developed countries |
Asymptomatic hypercalcemia |
|
|
|
Are steroids useful in 1° hyperparathyroidism induced Hypercalcemia? |

NO
|
|
|
|
Rugger jersey spine |
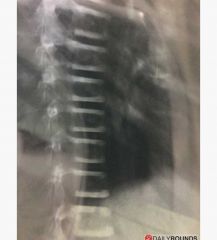
|
|
|
|
Normal calcium levels |
9-11 gm% |
|
|
|
Signs in hypocalcemia |

Trousseau sign (carpopedal spasm) Chvostek sign (tapping facial nerve) Circumoral tingling, numbness Latent tetany Prolonged QT interval |
|
|
|
Hypocalcemia with hypophosphatemia |
Vit D dependent rickets type 1 |
|
|
|
Hypocalcemia with hyperphophatemia |

Hypoparathyroidism causes- Autoimmune (MC) Sx excision DiGeorge syndrome |
|
|
|
Pseudo pseudo hypoparathyroidism |
Normal calcium Normal phosphate |
Pseudo hypoparathyroidism- -end organ PTH resistance (PTH raised with decreased Ca) -Autosomal dominant form (short ht+short IV, V digits) |
|
|
Management of hypocalcemia in hypoparathyroidism |
1. Calcitriol supplements 2. Oral calcium intake 3. Thiazides (to increase reabsorption) |
|
|
|
Case of 2° hyperparathyroidism |

|
|
|
|
Ca, PO4, serum ALP, PTH in OSTEOPOROSIS |
All normal |
|
|
|
Ca, PO4, serum ALP, PTH in PAGETS DZ |
Ca, PO4, PTH-normal SALP-highly increased |
|
|
|
Ca, PO4, serum ALP, PTH in CRF |
Ca-decreased Rest all-increased |
|
|
|
Ca, PO4, serum ALP, PTH in RICKETS |
Ca-decreased PO4-decreased SALP-increased PTH-increased |
|
|
|
Ca, PO4, serum ALP, PTH in HYPERPARATHYROIDISM |
Ca-increased PO4-decreased SALP-increased PTH-increased |
|
|
|
Case of hypercalcemic crisis |

|
|
|
|
Stepwise management of Hypercalcemic crisis |
1. IV FLUIDS (200-500ml/h NS for a UO of >100ml/h) 2. LOOP DIURETICS (furosemide to increase excretion) 3. Bisphophonates (to decrease calcium release from bones) |
|
|
|
Calcium levels directly related to |
Magnesium levels |
Another ion) |
|
|
MCC of asymptomatic Hypercalcemia in adults |
1° hyperparathyroidism |
|
|
|
MCC of symptomatic Hypercalcemia in adults |
Malignancy |
|
|
|
MC mech by which osteolytic tumors cause Hypercalcemia |
PTHrP |
|
|
|
ADRENAL MEDULLA |
Pathology of adrenal medulla |
|
|
|
Cells in adrenal medulla |
Neural crest derived chromaffin cells |
|
|
|
TX of chromaffin cells |
Phaeochromocytoma |
Also called as the great masquerader due to variable presentation |
|
|
Triad of phaeochromocytoma (MC symptoms of phaeochromocytoma) |
Headache-MC symptom Profuse sweating Palpitations/tachycardia |
|
|
|
MC sign of phaeochromocytoma |
Episodic hypertension (or sustained) |
|
|
|
Other clinical features of phaeochromocytoma |
Anxiety Panic attacks Wt loss Polyuria Polydipsia Orthostatic hypotension Erythrocytosis Hyperglycemia Hypercalcemia (due to PTHrP) DCMP Constipation |
|
|
|
MC catecholamine from phaeochromocytoma |
Norepinephrine |
|
|
|
MC catecholamine from extra adrenal phaeochromocytoma |
Norepinephrine |
|
|
|
MC catecholamine from adrenal phaeochromocytoma |
<3cm-epinephrine >3cm-norepinephrine (mc size-5cm) |
|
|
|
MC catecholamine from malignant phaeochromocytoma |
Norepinephrine |
|
|
|
MC catecholamine from phaeochromocytoma in MEN syndromes |
Epinephrine |
|
|
|
Cellular pattern characteristic of phaeochromocytoma |
Zelballen pattern Salt and pepper chromatin
(also of paragangliomas) |
|
|
|
Rule of tens |

10% Familial 10% NOT associated with episodic HTN |
|
|
|
Phaeochromocytoma with distant metastasis is called |
Malignant phaeochromocytoma (cellular atypia, mitotic figures, invasion of vessels and adjacent structures) |
|
|
|
To distinguish malignant from benign phaeochromocytoma, best parameter? |
Presence of metastasis |
|
|
|
Associated syndromes with phaeochromocytoma |
NF 1 (Cafe au lait spots, option nerve glioma) MEN 2A (Medullary carcinoma of thyroid, PTH hyperplasia) MEN 2B (Marfanoid habitus, medullary carcinoma of thyroid, ganglioneuromas) VHL syndrome (RCC, pancreatic endocrine neoplasms) Paraganglioma syndrome |
|
|
|
NEVER do this diagnostic test in phaeochromocytoma |
FNAC |
It is vascular |
|
|
Best investigation for phaeochromocytoma |
24-h urinary fractionated metanephrines
Other investigations- Increased serum metanephrines Increased 24h urinary VMA |
|
|
|
Gold standard for locating tumors in phaeochromocytoma |
Fluorodopa-PET |
|
|
|
DOC for HTN in phaeochromocytoma |
Phenoxybenzamine (irreversible alpha blocker) (may be followed by beta blockers-propanolol) (prazosin/phentolamine for parpxysms)
Other drugs- Nitroprusside Metyrosine |
|
|
|
Drug NEVER GIVEN ALONE in phaeochromocytoma |
Beta blockers |
|
|
|
Chemotherapy protocol for phaeochromocytoma |

|
|
|
|
TOC for residual phaeochromocytoma/malignant phaeochromocytoma/metastatic phaeochromocytoma |
MIBG (nuclear med therapy) |
|
|
|
MC site for extra adrenal phaeochromocytoma |
Abdomen (organ of Zuckerkandl) (More risk of malignancy in extra adrenal phaeochromocytomas) |
|
|
|
Treatment of phaeochromocytoma |
Surgical excision preceded by phenoxybenzamine pre op (to prevent hypertensive crisis) |
|
|
|
MC mutations in Familial Paraganglioma |
SDH (succinate dehydrogenase mutations) |
|
|
|
Why the name 'chromaffin' for phaeochromocytoma? |
Turns brown on incubation with potassium dichromate solution (d/T oxidation of stored catecholamines) |
|
|
|
IHC Markers of phaeochromocytoma |
Chromogranin Synaptophysin |
|
|
|
Special name for phaeochromocytomas in extra adrenal sites |
Paragangliomas |
|

