![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the MOST COMMON NON-TRAUMATIC ULCERATION of oral tissues?
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS "Canker Sores"
|
|
|
What is the proper name for "Canker Sores"
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
|
CHRONIC RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS can be associated with which systemic conditions?
|
- Behcet Syndrome
- Crohn's disease - Celiac disease |
|
|
What is the MOST COMMON of the RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS?
|
MINOR APHTHOUS ULCERATIONS
|
|
|
What is the size range of MINOR APHTHOUS ULCERATIONS?
|
3-10 mm
|
|
|
What is the size range of MAJOR APHTHOUS ULCERATIONS?
|
1- 3 cm
|
|
|
WHat is the size range of HERPETIC APHTHOUS ULCERATIONS?
|
1-3 mm
|
|
|
Where does MINOR RAS commonly occur?
|
- exclusively on NON-KERATINIZED MUCOSA
|
|
|
Where does MAJOR RAS commonly occur?
|
- any site
- predilection for moveable oral mucosa (labial, soft palate, tonsilar) |
|
|
Where does HERPETIC RAS commonly occur?
|
- most commonly NON KERATINIZED MOVEABLE MUCOSA
|
|
|
What is the healing time of MINOR RAS?
|
- 7-14 days w/o scarring
|
|
|
What is the healing time of MAJOR RAS?
|
2-6 weeks
- may cause scarring |
|
|
What is the healing time of HERPETIC RAS?
|
7-10 days
|
|
|
When is the onset of MINOR, MAJOR, and HERPETIC RAS?
|
MINOR: childhood / adolescence
MAJOR: post-puberty HERPETIC: adults |
|
|
Which RAS has fewest recurrences and shortest duration?
|
MINOR
|
|
|
Which RAS has longest duration per episode?
|
MAJOR
|
|
|
Which has the GREATEST NUMBER of lesions and MOST FREQUENT RECURRENCE of RAS lesions?
|
HERPETIC
|
|
|
What is the treatment for patients with RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS?
|
- treatment is application of gel or cream based topical corticosteroids
- in severe and persistent cases systemic steroids |
|
|
What is one of the main features of BEHCET SYNDROME?
|
Vasculitis
|
|
|
BEHCET SYNDROME appears more commonly in which countries?
|
- Turkey
- Japan - East Mediterranean "silk route" |
|
|
Define BEHCET SYNDROME:
|
- uncommon multisystem disease with recurrent oral aphthae like ulcers
- may be immunodysfunction |
|
|
Why are the ORAL LESIONS significant in BEHCET's SYNDROME?
|
They are usually the first manifestations of the disease in 25-75% of cases
|
|
|
What are the features of the oral lesions of BEHCET'S SYNDROME?
|
Usually 6 or more ulcers, ragged borders, surrounded by a larger zone of diffuse erythema
|
|
|
What are the most common sites of oral lesions in BEHCET's SYNDROME?
|
- soft palate
- oropharynx (non-keratinized oral mucosa |
|
|
What are the overall clinical features of BEHCET's SYNDROME?
|
- GENITAL:
- EYE LESIONS: - SKIN: hyperreactivity - JOINTS - CNS |
|
|
Define "PATHERGY"
|
Skin hyperreactivity
|
|
|
What is the DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA for BEHCET's?
|
- recurrent oral ulcerations
- recurrent genital aphthae like uilcers - ocular lesions - cutaneous lesions - positive pathergy test |
|
|
Define SARCOIDOSIS:
|
- multisystem granulomatous disorder of unknown cause
- improper degradation of antigenic material with the formation of noncaseating granulomatous inflammation |
|
|
How is SARCOIDOSIS discovered on routine chest films?
|
BILATERAL HYLAR LYMPHADENOPATHY
|
|
|
Define HEERFORDT'S SYNDROME:
|
Uveoparotid fever: parotid enlargement, anterior uveitis of eye, facial paralysis, fever
|
|
|
How is diagnosis of SARCOIDOSIS confirmed?
|
- clinical
- biopsy - elevated serum angiotensin converting enzyme - chest xrays |
|
|
What is the treatment of SARCOIDOSIS?
|
Approx 60% resolve spontaneously in 2 years without tx. Immunosuppressive therapy if severe
|
|
|
Define OROFACIAL GRANULOMATOSUS:
|
Presence of granulomatous inflammation in the oral and facial regions
|
|
|
What is the most common area for OROFACIAL GRANULOMATOSUS?
|
Lips
- non-tender persistent swelling of one or both lips |
|
|
Define CHEILITIS GRANULOMATOSA:
|
OROFACIAL GRANULOMATOSUS involving only the lips.
|
|
|
What is MELKERSON ROSENTHAL SYNDROME?
|
- Orofacial swelling, and facial paralysis, and fissured tongue
|
|
|
What is the treatment of OROFACIAL GRANULOMATOSUS?
|
- remove sources of inflammation
- intralesional corticosteroids |
|
|
What is WEGENER'S GRANULOMATOSUS?
|
necrotizing granulomatous process with vasculitis
|
|
|
What are the different spectrums of WEGENERS?
|
CLASSIC: upper airway, lungs, kidney
LIMITED: respiratory SUPERFICIAL: skin and mucosa |
|
|
How is diagnosis of WEGENERS GRANULOMATOSUS made?
|
- clinical
- biopsy - chest and sinus radiographs |
|
|
Define STOMATITIS MEDICAMENTOSA:
|
Allergic reaction of the oral mucosa to the systemic administration of a medication
|
|
|
What are the most common drugs to cause ALLERGIC MUCOSAL REACTION?
|
- antibiotics (penicillins)
- sulfa drugs |
|
|
How does MUCOSAL FIXED DRUG REACTION look like?
|
- localized areas of erythema and edema
- develop into vesiculoeruptive lesions - frequently on labial mucosa |
|
|
How is a diagnosis of STOMATITIS MEDICAMENTOSA made?
|
- detailed medical history: recent use of drugs
- temporal relationship between drug use and mucosal alteration |
|
|
What is the treatment of STOMATITIS MEDICAMENTOSA?
|
- LOCALIZED: topical corticosteroids
- CHRONIC: resolve on cessation of offending drug, topical cortico may be required to assist - SYSTEMIC: need systemic cortico |
|
|
Define ALLERGIC CONTACT STOMATITIS:
|
- can be acute and chronic
- similar to those cases of chronic irritation - chronic dryness, scaling, fissuring, cracking |
|
|
What does ACUTE CONTACT STOMATITIS present with usually?
|
- burning most frequent symtpoms
- redness with or without edema - superficial aphthous like ulcerations may be seen |
|
|
What does CHRONIC CONTACT STOMATITIS present with usually?
|
- may be erythematous or white and hyperkeratotic
- periodic erosion may develop - some allergens, such as toothpaste, can cause widespread erythema, desquamation of superficial layers of epithelium |
|
|
What is hte difference of CONTACT STOMATITIS between TOOTHPASTE and CHEWING CANDY?
|
Toothpaste: more diffuse pattern
Chewing gum: localized |
|
|
How long do symptoms of CONTACT STOMATITIS take to disappear?
|
1 week after discontinuation of cinnamon product
|
|
|
How is diagnosis of CHRONIC ORAL MUCOSAL CONTACT REACTIONS TO DENTAL AMALGAM made?
|
- clinical appearance: similar to lichen planus
- lack of migration - correlation to adjacent amalgam |
|
|
Define ANGIOEDEMA:
|
Common clinical presentation of allergic conditions with different etiologic pathways.
|
|
|
How does ANGIOEDEMA develop?
|
- rather quickly as regional, painless, swelling of lips, anterior cheeks, and tongue
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of ANGIOEDEMA?
|
- mast cell degranulation which leads to histamine release
|
|
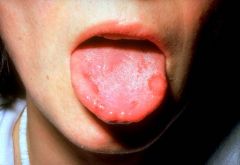
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
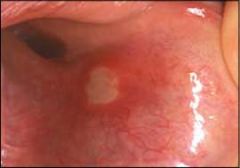
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
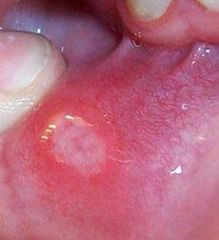
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
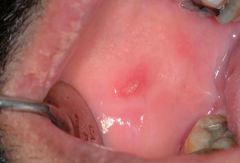
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
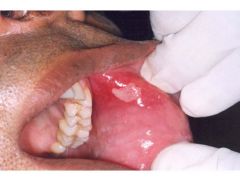
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
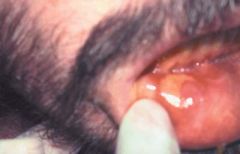
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
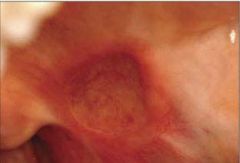
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
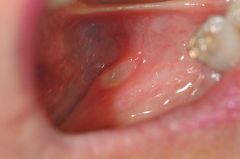
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
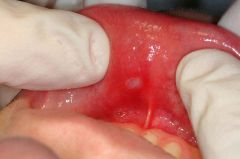
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
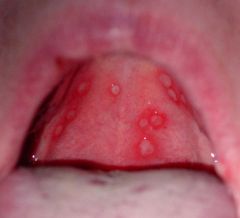
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
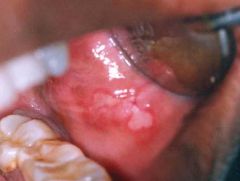
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
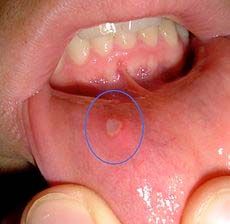
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
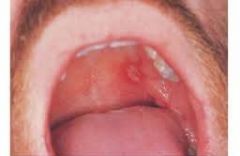
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
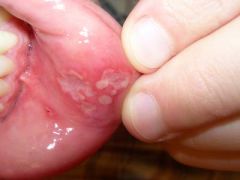
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
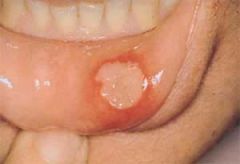
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
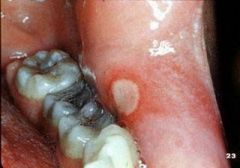
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
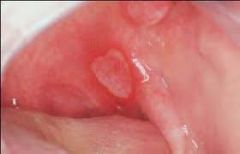
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
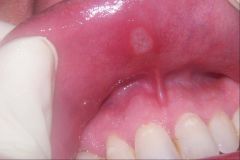
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
RECURRENT APHTHOUS STOMATITIS
|
|
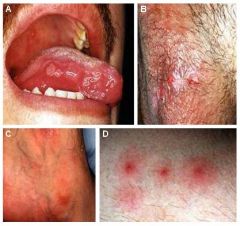
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
BEHCET'S SYNDROME
|
|
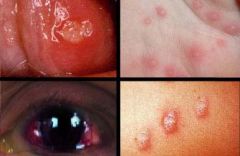
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
BEHCET SYNDROME
|
|
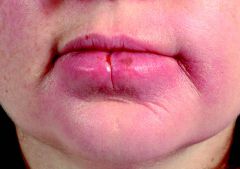
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
OROFACIAL GRANULOMATOSA
|
|
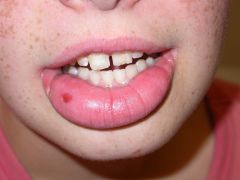
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
OROFACIAL GRANULOMATOSA
|
|
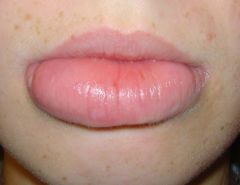
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
OROFACIAL GRANULOMATOSA
|
|
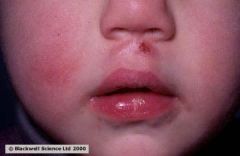
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
OROFACIAL GRANULOMATOSA
|
|
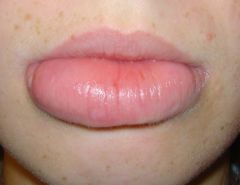
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
OROFACIAL GRANULOMATOSA
|
|
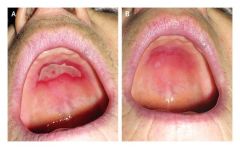
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
CONTACT STOMATITIS
|
|
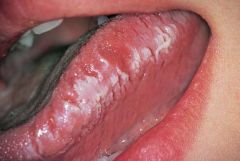
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
CONTACT STOMATITIS
|
|
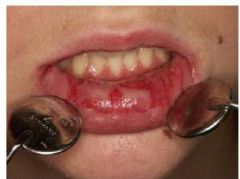
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
CONTACT STOMATITIS
|
|
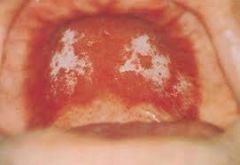
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
CONTACT STOMATITIS
|
|
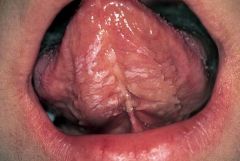
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
CONTACT STOMATITIS
|
|
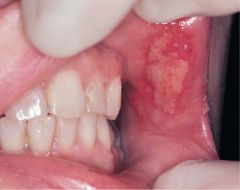
Identify the following allergic condition:
|
CONTACT STOMATITIS
|

