![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
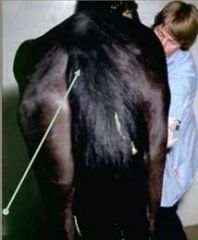
Side 1: describe what we are seeing?
Side 2: give a pathological explanation |
loss of muscle mass
|
gluteal atrophy
|
|
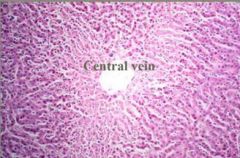
Side 1: describe what are we seeing?
Side 2: give a pathological description |
smaller and paler hepatocytes in the central region of the lobule
|
hepatocellular atrophy
|
|
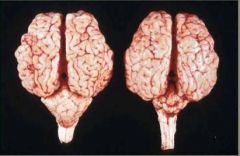
Side 1: what are we observing in the brain on the right?
Side 2: what are 2 common causes of this? |
hypoplasia cerebellum
|
late in utero infections: cat = panleukopenia, cattle = BVD virus
|
|
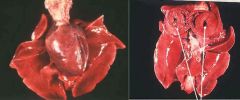
slide 1: what are 2 possible descriptions of the tissues?
slide 2: what does the slide on the right suggest is correct and why? |
enlarged heart or small lungs
|
cardia hypertrophy because we can see the thickened left ventricle
|
|

what are we seeing?
|
epidermal hyperplasia of the nose
|
|
|
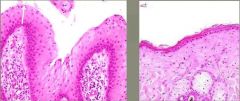
assuming the tissue on the right is normal, describe what we are seeing in the tissue on the left?
|
epidermal hyperplasia
|
|
|
how can we tell if this is an example of hypertrophy or hyperplasia?
|
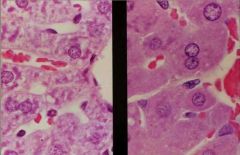
look on a cellular level, hint for what we are seeing
|
hypertrophy on the right side (compare to normal on left side)
|
|
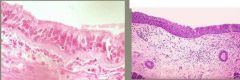
side 1: what type of tissue are we seeing on the left (organ, cell type)
side 2: what are we seeing in regards to the same tissue on the right? |
ciliated respiratory epithelium
|
squamous metaplasia of respiratory epithelium
|
|

what are we seeing in this tissue?
|
aortic aneurysm osseous metaplasia
|
|
|
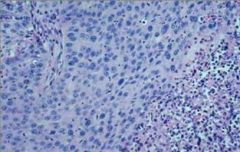
side 1: what is the cell change seen in this image?
side 2: what are exampled of causes of this type of change? |
dysplasia
|
ear tips of white cats with sun exposure, conjunctiva of white faced cattle
|
|
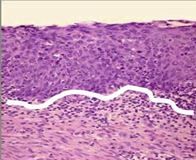
what is this cellular change called? (white line represents the basement membrane)
|
carcinoma-in-situ
|
|
|
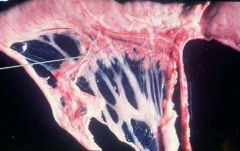
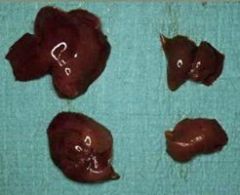
what are we seeing? organ and description
|
pancreatic hypoplasia
|
|
|
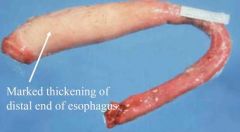
what are we seeing in this image?
|
smooth muscle hypertrophy
|
|
|
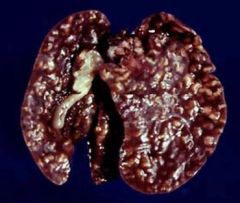
describe what we are seeing?
|
biliary epithelial hyperplasia - coccidosis
|
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of benign and malignant neoplasias?
|
|
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of benign and malignant neoplasias?
|
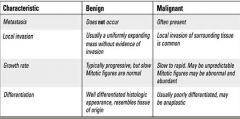
|
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of benign and malignant neoplasias?
|
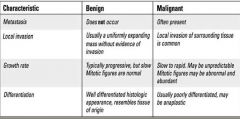
|
|
|
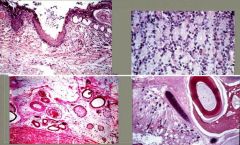
what is a one word term for the images shown?
|
teratoma
|
|
|
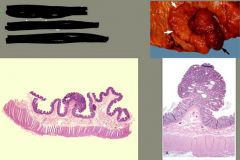
what are we seeing in these images?
|
polyp
|
|
|
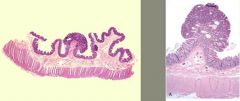
what is this? one word
|
papilla
|
|
|

what is this? one word
|
papilla
|
|
|
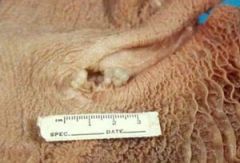
what are these images of? one word
|
polyps
|
|
|
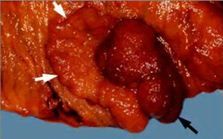
what is shown in this image?
|
polyp
|
|
|
|
what is the term for these lesions?
|
sessile
|
|
|
|
what is the term for these lesions?
|
sessile
|
|
|
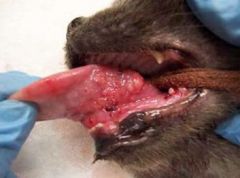
what is the term for these lesions?
|
sessile
|
|
|
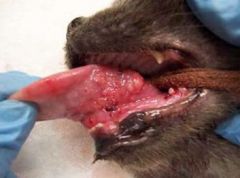
what is the term for this lesion?
|
sessile
|
|
|
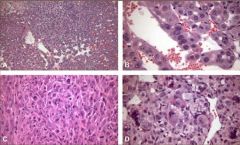
what are these slides an example of in malignant neoplasias?
|
pleomorphism
|
|
|
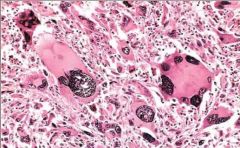
what feature of malignant neoplasias is displayed in this image?
|
anaplasia
|
|
|
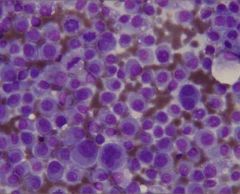
what are the histological features of this malignant neoplasia?
|
anisocytosis, anisokaryosis, hyperchromatic nuclei, abnormal nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio of 1:2, enlarged and multiple nucleoli, irregular clumping of chromatin, high mitotic index, abnormal mitosis, tumor giant cell
|
|
|
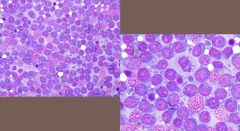
what is the name of this malignant neoplasia and what is the contradictory cytology featured?
|
lymphoma which has a more homogenous cytology as indicative of malignancy, because lymph nodes are typically heterogenous
|
|

