![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
130 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
parasite |
an association between 2 different organisms of which one member is metabolically dependent on the other |
|
|
parasitasis |
the parasite is potentially pathogenic, animal dissent have clinical signs of disease |
|
|
parasitosis |
the parasite harms the individual in some way |
|
|
symbiosis |
describes any association, either temporary or permanent between at least 2 different organisms of different species |
|
|
parasitism |
when one organism becomes metabolically dependent on the other singing on or within |
|
|
predator prey |
short term, one organism benefits from another |
|
|
phoresis |
smaller organism being carried by a larger one |
|
|
mutualism |
both organisms benefit |
|
|
commensalism |
one organism benefits and the other is neutral |
|
|
aberrant parasite |
wanted from usual site of infection into a place it doesn't normally reside. reaches a dead end host where it can't continue its life cycle |
|
|
incidental parasite |
occurring in a host of which it doesn't usually reside |
|
|
facultative parasite |
free living, non parasitic that can become parasite to a host opportunist |
|
|
obligatory parasite |
must have parasitic existence in order to survive |
|
|
periodic parasite |
doesn't have to live on or within a host but can make frequent visits to gain energy to survive |
|
|
life cycles |
developmental stages that a parasite goes through infecting one or more different species of hosts living symbiotically or causing damage to that host |
|
|
host |
where the life cycle of a parasite develops |
|
|
definitive host |
mature stages of parasite |
|
|
intermediate hsot |
immature stages of parasite |
|
|
paratenic host |
encysted and dormant, waiting to be transported, does not undergo developmental stages |
|
|
reservoir host |
a source of infection for humans and domesticated animals the host isn't harmed |
|
|
dead end host |
type if IMH that the parasite can't complete its cycle, doesn't allow the parasite to go to its definitive host |
|
|
parasiticides |
generalized term of certain compounds to treat external and internal parasites |
|
|
infection |
inside hosts body |
|
|
infestation |
outside hosts body |
|
|
homoxenous |
will only infect one type of host |
|
|
stenoxenous |
a narrow host range dogs and cats |
|
|
euryxenous |
broad host range giardia |
|
|
linnaean classification system |
kingdom phylum class order family genus species |
|
|
nematodes |
free-living, plant, animal roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, heart worms cylindrical shape, unsegmented, simple linear digestive tract direct or indirect, produces eggs or larvae dioecious |
|
|
dioecious |
both sexes |
|
|
platyhelminths |
flatworms eucestodes-true tape worm trematodes-flukes |
|
|
eucestodes |
hermaphrodites need IMH no gut |
|
|
prepotent period |
the time it takes from the initial infection of a parasite to mature and then produce egg/larvae |
|
|
helminthology |
study of parasitic worms |
|
|
fecal flotation solution |
sodium nitrate SG 1.33, most efficient but forms crystals if wait too long |
|
|
fecal sedimentation |
detects more eggs, used to detect specimens the have too high a SG to float best for flukes |
|
|
diagnostics on protozoans |
direct smear with saline trophozoites-motile form find cysts using fecal flotation |
|
|
oocyst sporulation |
fecal culture process of development taken place in the oocyst |
|
|
baermann tecnhique |
receiving larvae of roundworms lungworms and threadworms |
|
|
modified knots test |
detect microfilariae and differentiate between D. immitis and A. recondium |
|
|
nematode anatomy |
cuticle-thin membrane wrapping body copulatory bursa-holds onto females with burial rays/spicules pseudocoelom- fluid filled body cavity surround internal organs |
|
|
nematode egg types |
ascarid-roundworm trichostrongyle/strongyle-hookworm spiruioid-esophageal worm trichuroid-whipworm |
|
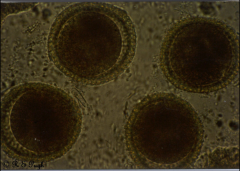
|
ascarid round worm toxocara |
|
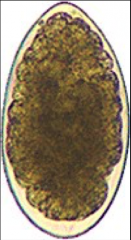
|
trichostronglye/strongyle hookworms in dogs and cats ruminants-cant tell apart |
|
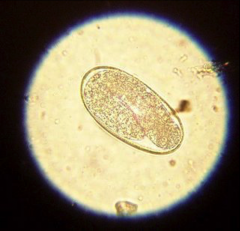
|
larvated strongylid |
|
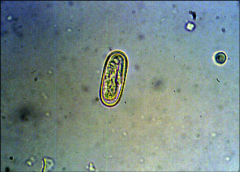
|
spiruroid egg contain larvae esophageal worm of dogs and heart worm |
|
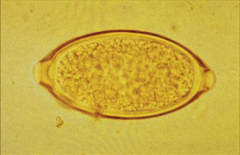
|
trichineloid/trichurioid whipworm |
|
|
oviparous |
single staged egg toxocara |
|
|
ovovivparous |
female producing egg containing a single L1 larvae spirocerca lupi |
|
|
larviparous |
retains eggs and incubates them to produce L1 stage larvae, live birth lungworms, D. immitis |
|
|
common life cycle of nematode |
direct or indirect 3rd stage larvae=infective stage molt-hatching of shedding cuticle to larval stage IMH-means of transmission to definitive host L5-adult lives inside definitive host |
|
|
seteria cervi |
abdominal cavity worm cattle IMH-female mosquito diagnose at necropsy damage organs |
|
|
seteria equine |
abdominal cavity worm horse IMH-female mosquito |
|
|
elaeophora schneideri
|
arterial worm of sheep
IMH-horse fly common carotid artery ppp-4-5 months sheep filarial dermatitis at poll, face, feet |
|
|
capillaria sssp. |
bladder worm |
|
|
pearsonema plica |
bladder worm of dog/cat IMH-eartworm urine sediment |
|
|
spirocerca lupi |
esophageal worm of dogs/cats IMH-dung beetle spirurid egg fecal-oral barium radiographs |
|
|
gongylonema pulchrum |
esophageal worm of sheep, cattle, goat, pigs IMH-dung beetle or cockroach fecal flotation mucosa of esophagus |
|
|
thelazia californiensis |
eye worm of cat and dog IMH-face fly surgical removal from eye |
|
|
thelazia rhodesii |
eye worm of cattle IMH-face fly |
|
|
thelazia lacrymalis |
eye worm of horse IMH-musca autumnalis blockage of lacrimal duct causing excessive tearing |
|
|
rhabditis strongyloids |
free living soil worm facultative parasite can invade skin and become parasitic DX_ larvae on superficial skin scarping |
|
|
dracunculus insignis |
guinea worm female dogs IMH- small aquatic crustaceans subcutaneous tissue female dogs surgical removal of adult female from ulcerative lesion by putting in water distinguish microfilariae between D. immitis and A. reconditum |
|
|
muellerius capiliaris |
hair lungworm of sheep and goats disease-obstruction of bronchioles dx-characteristic L1 lavage on fecal flotation kinked tail with dorsal spine |
|
|
dirofilaria immitis |
heart worm of dog/cat IMH-female mosquito PPP-6 months |
|
|
ancylostoma caninum |
dog hookworm transmammary transmission, ingestion anticoagulant in mouth causes former attachment sites to continue to bleed trichostrongyle egg direct, oviparous ppp-2-3 weeks larvae hatch from ova in warm environment |
|
|
ancylostoma tubaeform |
feline hookworm ingestion of L3 chronic disease paratenic host |
|
|
ancylostoma braziliense |
zoonotic hookworm skin penetration CLM in humans-cutaneous larval migrans dermatitis |
|
|
uncrinaria stenocephala |
northern US/canada hookworm direct cutting plate instead of buccal mouth L3 ingestion ivermectin |
|
|
equine strongylid |
intestinal worm of horses |
|
|
dioctophyma renale |
giant kidney worm in dogs IMH- aquatic/terrestrial worm right kidney eggs passed in urine centrifugation of urine zoonotic surgical removal |
|
|
stephanurus dentatus |
kidney worm in pigs IMH- earthworm or through the skin found outside of kidney or ureters |
|
|
filarioides osleri |
canine lungworm L1 immediately infected ppp-10 weeks no development outside host mom-pup saliva baermann technique |
|
|
aeulurostrongylus abstrusus |
cat lungworm IMH- snails and slugs ppp-30 days only ID from L1 larvae baermann technique ovoviviparous |
|
|
dioctycaulus viviparous |
cattle lungworm spread through lymph nodes to heart ppp-28 days baermann coughing |
|
|
dictyocaulus filarial |
goat lungworm spread through lymph nodes to heart baermann coughing |
|
|
dictyocaulus arnfieldi |
equine lungworm ppp-42-56 days bronchi and bronchioles obstruction larvae hatch from ova within hours of passing in feces |
|
|
metastrongylus elongatus |
swine lungworm IMH-earthworm fecal sedimentation |
|
|
angiostrongylus vasorum |
dogs and foxes lungworm IMH-snails and slugs |
|
|
eucoleus aerophilus |
lungworm dogs and cats capillaries nematode ppp-40 days inflammatory response to host |
|
|
trichinella spiralis |
pig muscle worm IMH and direct host-pig adults in small intestine larvae in muscle cause trichinosis in people-raw pork |
|
|
trichinosis navita |
muscle worm of wild animals |
|
|
oseophagostomum columbianum/venulosum |
nodular worm of sheep and goats colon |
|
|
oseophagostomum radiatum |
cattle nodular worm pimply gut colon feeds on host blood serious pathogen |
|
|
oseophagostomum dentatum |
nodular worm of pigs direct, LI |
|
|
enterobius vermicularis |
human pinworm carnivores are never the host parasite of herbivores and omnivores |
|
|
oxyuris equi |
horse pinworm cecum, colon, rectum cellophane tape impression eggs infective 3-5 days ppp-3-5 months |
|
|
toxocara canis |
dog roundworm, ascarid direct but can have paratenic host, pass through placental barrier, tracheal migration, transmammary route zoonotic-VLM, OLM PPP-3-6 weeks dormancy of L2 until hormones of pregnancy creat activity |
|
|
toxocara cati |
cat roundworm direct, ingestion of infected larvated eggs, ingestion of paratenic host, transmammary larvae don't cross placenta ppp-5-8 weeks |
|
|
toxocaris leonina |
cat/dog/wild carnivore roundworm direct ppp-74 days more elliptical than toxocara |
|
|
baylisascaris procyonis |
raccoon roundworm Zoonotic- VLM, OLM, NLM eggs in environment take 2-4 weeks to become infective |
|
|
parascaris equorum |
horse roundworm direct, largest equine nematode ppp-75-80 days ascarid fecal flotation migration through liver portal system and veins to lungs and coughed up and swallowed in SI |
|
|
cooperia spp. |
roundworm of ruminants |
|
|
bovine trichostrongylus |
roundworm of ruminant ingestion of infective ova adults in abomasum or SI/LI feeding on blood ivermectin, fenbendazole |
|
|
chabertia ovina |
roundworm of sheep plug feeders poor wool growth, diarrhea with blood, anemia firmly attached to mucosa of colon on necropsy |
|
|
ascaris suum |
largest roundworm of pigs direct fecal flotation migrate through liver, lungs, cough, swallowed, SI necropsy finding-milk spots abdominal breathing, coughing/thumps |
|
|
stefhanofilaria stilesi |
skin worm of ruminants IMH- horse fly disease-ventral midline skin dermatitis skin scape under thick moist crust |
|
|
haemonchus contortus |
stomach worm of sheep and goats direct, most important pathogen trichostrongyle egg barber pole abomasal worm anthelmintic resistance treat based on severely affected anemia/ocular conjunctiva spring rise |
|
|
ostertagia spp. |
ruminant stomach worm abomasum, SI, LI direct life cycle |
|
|
ollulanus tricuspis |
stomach worm of cat strongyle egg ingestion of L3 larvae baermann test |
|
|
draschia megatoma |
horse stomach worm summer sores ppp-60 days fecal flotation larvae parasitize skin |
|
|
habronema microstoma |
horse stomach worm IMH-house fly/muscid fly summer sores PPP-60 days fecal flotation larvae parasitize skin |
|
|
physaloptera canis |
dog stomach worm IMH- cockroach, beetle, cricket spiruid egg fecal sedimentation feed off blood and tissue |
|
|
ascarops strongylina
|
stomach worm of pigs
IMH-dung beetle PPP-42 days fecal flotation |
|
|
physocephauls sexaltus |
pig thick stomach worm IMH-dung beetle |
|
|
hyostrongy rubidus |
red pig stomach worm trichostrongyle egg ppp-20 days gastric enteritis |
|
|
trichostrongylus axei |
stomach worm of horse, cattle, pigs and sheep cross animals blood sucking |
|
|
cyanthosotome/trichonema |
small strongyle horse burrow in mucosa of LI to mature to adults arrested development of 2.5 years |
|
|
strongyoides vulgaris |
horse large strongyle most pathogenic due to migration anterior mesenteric arteries and liver causes thrombi and colic cecum colon fecal egg count, selective treatment due to resistance of benzimidazoles treat >250 eggs/gram of feces |
|
|
acanthocheilonema reconditum |
thorny lipped worm dogs IMH-infected flea peripheral blood sample with modified knots test distinguish from D. immitus |
|
|
strongyloides papillosus |
threadworm of cattle ppp-5-7 days intestinal worm female worms only parasitic host produce eggs into feces infective stage female larvae by penetration via skin, ingestion of infective larvae, transmammary through colostrum free living adults in environment |
|
|
strongyloides sterocalis |
threadworm of dogs PPP-8-14 days strongyloides egg zoonotic-strongyloidasis in humans ovoviviparous L1-L3 are free living in environment female can produce eggs without male transmammary transmission |
|
|
strongyloides westeri |
horse threadworm transmammary, larval penetration only female pathogenic to host fecal flotation PPP 5-7 days blood sucking ivermectin |
|
|
onchhocerra cervicallis |
filarial worm horse causes dermatitis on nuchal ligament patchy alopecia, ventral midline, itchy IMH- biting midge |
|
|
nematodirus |
large trichostrongyle ruminants |
|
|
trichuris vulpis |
canine whipworm fecal oral only transmission cecum colon attachment trichuroid egg NO IMH ppp-70-90 days eggs passed into feces every 3 days centrifugal flotation |
|
|
trichuris serrate |
feline whipworm direct trichuroid egg cecum colon fecal oral only route |
|
|
trrichuris ovis |
sheep whipworm direct cecum colon fecal flotation |
|
|
trichuris suis |
pig whipworm direct cecum colon ppp-42-49 days |
|
|
treatment of roundworms |
vermifuge or vermicide |
|
|
vermifuge |
antithelminthic that paralyzes the parasites so that it passes out into feces pyrantal pamoate, strongid, drontal |
|
|
vermicide |
kills the parasite and allows body to break it up thiabendazole or panacur/fenbendazole |
|
|
eucoleous spp. |
capllarid/respiratory nematodes ppp- 40 days inflammatory response to host ivermectin, panacur |
|
|
hypobiosis |
arrested stage of development of larvae larvae hide and then resume development |
|
|
ventral midline dermatitis causes |
stephanofilaria stilesi oncchhocera cervicalis rhabditis strongyloides |
|
|
heartworm disease |
nematode of circulatory system dog, cat, ferret IMH-female mosquito/culex adults found in right ventricle and pulmonary artery offspring-microfilariae skin, anterior chamber of eye, brain PPP-6 months |
|
|
clinical signs of heartworm |
pulmonary hypertension lethargy, exercise intolerance, right sided heart enlargement, ascites, right sided heart failure, cor pulmonate-RCHF secondary to pulmonary hypertension 3-5 years |
|
|
right sided congestive heart failure |
adult D. immitis in RT ventricle of heart causing excessive work load ascites/fluid in abdomen, hepatomegaly, cachexia/wasting away thromboembolism |
|
|
diagnose of heartworm |
ELISA antigen test adult female antigen modified knotts for microfilarae radiograph- right side D shaped heart |
|
|
feline heartworm |
rarely a source of transmission respiratory disease and lung parenchyma damage asthma like symptoms, thromboembolism |

