![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are parasites? |
Parasite lives on or in other host organism.
Damage is a variable
Parasite that causes disease are called pathogens |
|
|
|
Parasite that cause disease are called? |
Pathogens |
|
|
|
What is the study of parasite? |
Parasitology |
|
|
|
Parasitology is the study of _______? |
Parasite |
|
|
|
Ectoparasites |
Live on the surface of the organisms Ex. Ticks , lice |
|
|
|
Endoparasite |
Live within the bodies of other organism Ex. Protozoa, worms |
|
|
|
True or false: most parasites are obligate parasite: must spend at least some of their life cycle in or on a host. |
True |
|
|
|
The protozoa that causes malaria invades what cells? |
Red blood cells |
|
|
|
What is the vector for malaria? |
Female Anopheles mosquito |
|
|
|
What are the life cycle of Malaria parasite? |
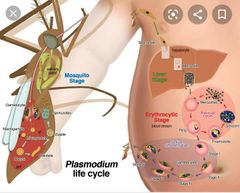
1 stage: the mosquito injects the sporozoites when it bites the human; the sporozoites travel to the liver via bloodstream does invade hepatocytes
2 stage: sporozoites multiply and become merozoites, which shed in blood stream due to rupurting in the liver cell
3rd stage: merozoites invade RBCs and multiply again, causing the RBCs to rupture, releasing more merozoites. * (when merozoites rupture RBC it causes chills, high fever, and sweating; infect other RBCs)
4th stage: after several asexual cycles gametocytes are produced
5th stage: mosquitoes ingest male and females gametoyctes when it vites an infected human . These will mature in the gut to form gametes.
6th stage: form zygote giving arise to the sporozoites in the salivary glands |

|
|
|
P. Falciparum |
Most severe Can be fatal within 24hrs of onset Chloroquine resistance Infrcts RBCs of all ages |
|
|
|
P. Virvax |
Less severe Infects young RBCs Found in subtopics and more temp regions |
|
|
|
P.ovale |
Infects young RBCs |
|
|
|
P.malariae |
Present subclinically May presist for life Infect old RBCs |
|
|
|
Hyphae |
A collection of tubular structures |
Fungi |
|
|
What are the two types of hyphae? |
Septate: division btw each cell in the filment Appears as a string of individual cells
Aseptate: no division Appears as a long continuous chain with many nuclei |
Fungi |
|
|
Asexual spores |
Arise from mitosis (no genetic variations) *Includes conidiospores and sporangiospores |
|
|
|
Sexual spores |
Arise from meiosis ( genetic variation) *Includes zygospores, ascospores, basidiospores |
|
|
|
What is mycoses? |
Diseases caused by fungi |
|
|
|
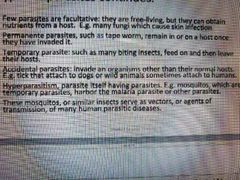
Type of parasites continues |
|
|
|
|
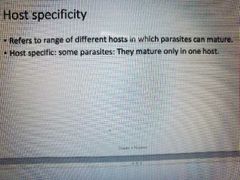
Host specificity |
|
|
|
|
Protists |

|
|
|
|
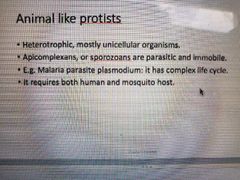
Animal like protists |
|
|
|
|
Parasitic helminths |

|
|
|
|
Flukes |

|
|
|
|
Fungi |

|
|

