![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the difference btw Prokaryotic and Eukatyotic Cells |
Prokaryotic : 1.Lacks nucleus and other membrane encolsed structures 2.Single-celled 3.DNA is a nuclear region not surrounded by a membrane Eukaryotic Cells: 1. They have nucleus and membrane enclosed structure called organelles. 2. Multicellular organisms 3.DNA is in nucleus surrounded by a membranous nuclear envelope |
|
|
|
What are the similarities btw Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells? |
Surrounded by cell membrane or plasma membrane Encode genetic information in DNA molecules |
|
|
|
There are three domains: two for Prokaryotic and one for eukaryotic. What are the Prokaryotic domains? |
Archaea Bacteria |
*Whenever your writing a domain always write the letter in capital letter |
|
|
True or false: Prokaryotes are among the smallest of all organisms |
True |
|
|
|
Prokaryotes are among the smallest of all organisms. They range from? |
Most range from 0.5 to 2.0 um in diameter A human red blood cell is about 7.5 um in diameter Not all are round shape some are spiral and therefore can have larger diameter |
|
|
|
What shape is the coccus ? |

Spherical |
|
|
|
What shape is Bacillus? |

Rod like |
|
|
|
What shape is coccobacilli? |

Short rods intermediate between rods and spherical |
|
|
|
What shape is Vibrio? |

Curved rods, or common shape |
|
|
|
What is the shape of Spirillum? |

Wavy-shaped |
|
|
|
What is the shape of Spirochete? |

Corkscrew-shaped |
|
|
|
What other shapes? |
Spindle or irregular shaped, loved shapes , square shaped |
|
|
|
What are the Bacterial arrangements? |
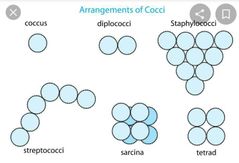
Diplo: two Tetrads: four cells in cube Sarcine: 8 cells in cube Staphylo: grapelike cluster Strepto: chains ( streptococcus; streptobacilli) Rosette Star shaped Square shaped |
|
|
|
What is the definition of Pleomorphism? |
Bacteria of same kind may vary in shapes and sizes, depending on nutrients available in their environment. (Cells of same species to vary in shape/ size; due to differences in structure by nutritional/ genetic differences. ) * own word Most noticeable in aging culture where organisms have used up most of the nutrients and have deposited wastes. |
|
|
|
What is outside the cell membrane and composed of polymer peptidoglycan? |
Cell wall |
|
|
|
________ form supporting net around a bacterium that resembles multiple layers of chain-like fence. |
Peptidoglycan |
|
|
|
Cell wall is consist of thick, dense layer of peptidoglycan. They have as many as 40 layers of peptidoglycan, 60 to 90% of the cell wall. |
Gram positive |
|
|
|
Teichoic Acid |
Found in gram positive Consist of glycerol, phosphates, and sugar alcohol ribitol |
|
|
|
*What blocks the final stage synthesis of peptidoglycan? And why? |
Pencillin. They divide the bacteria making it difficult to form and complete cell wall causing them to die. |
|
|
|
*_________ can damage the cell wall by digesting the peptidoglycan |
Lysozyme |
|
|
|
Most garm positive cell walls, except streptococci , contain very ______ protein |
Little |
|
|
|
What is protoplasts? |
When a gram positive cell is completely stripped of all peptidoglycan ( cell wall)
|
Cells with a cell membrane but no cell walls |
|
|
True or false: Protoplasts can burst unless they are kept in isotonic solution. |
True |
|
|
|
The thinkess of the gram positive cell wall can retain stains as ? |
Crystal violet iodine dye |
|
|
|
Physiological damage or aging can make Gram positive cell wall _______ |
Leaky |
|
|
|
A Gram- positive cell wall leaky gives ? |
A gram variable or even a gram negative results |
|
|
|
Gram staining must be performed on cultures less than _____? |
24 hrs old |
|
|
|
True or False: Gram negative bacteria has a thick layer of peptidoglycan |
False
It has a thin layer of peptidoglycan , only 20 to 20% Cell walls consist of various polysaccharides proteins and lipids |
|
|
|
What is sheroplasts? |
Associated with Gram negative cells, always some residual cell wall, will never be completely stripped of cell wall Have both a cell membrane and most of the outer membrane |
|
|
|
Acid fast bacteria |
Thick cell walls Approx 60% lipid Less peptidoglycan Carbolfuchsin is used to stain acid fast bacteria Carbolfuchsin binds to the cytoplasm and resists removal by an acid alcohol mixture |
|
|
|
Hydrophobic |
Water fearing |
|
|
|
Hydrophilic |
Water loving |
|
|
|
Difference btw eukaryotes ribosomes vs prokaryotes ribosomes |

Eukaryotes ribosomes have sediment rate of 80s, subunits are 60s and 40s
Prokaryotes ribosomes have sediment rate of 70s and their subunits are 30s and 50s |
Know the numbers for the exam |
|
|
Inclusion bodies are |

Granules Vesicles |
|
|
|
Monotrichous definition: |
Single polar flagellum, located at one end or pole |
|
|
|
Amphitrichous definition: |
Two polar flagella, one at each end |
|
|
|
Lophotrichous definition |
Two or more flagella, at one or both ends |
|
|
|
Peritrichous definition |
Flagella all over |
|
|
|
Atrocious definition: |
Without flagella |
|
|
|
Chemotaxis |
Some bacteria exhibit this. It is movement towards attractants ( positive chemotaxis) and away from repellents (negative chemotaxis) Aka controlling the frequency of runs and tumbles to move towards attractants or away from repellents. movement of cell towards or away from chemical signal (att or repell) run. |
|
|
|
Phototaxis |
Bacteria that moves toward light ( positive phototaxis) or away from light (negative phototaxis) Some move with the help of flagella |
|
|
|
Bacterstatic |
It just stops the bacteria from growing |
|
|
|
What are Pili? |
Some bacteria has pili They are tiny , hollow projections They are used to attach bacterial surfaces and are not involved in movement Pilus is composed of subunits of the proteins pilin There are two kind , conjugation and attachment |
|
|
|
Conjugation pili |
Some bacteria conjugation pili, or F pili (aka sex pili) attaches two cells and allow exchange of DNA Transfer of DNA furnishes genetic variety for bacteria Can cause problem for humans because antibotic resistance can be passed on with the DNA transfer |
|
|
|
Attachment pili |
(Fimbriae) help bacteria adhere to surface |
|
|
|
Glycocalyx |

|
|
|
|
Simple diffusion |

|
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |

|
|
|
|
Osmosis |

|
|
|
|
Active transport |

|
|
|
|
Endocytosis and Exocytosis |

|
|
|
|
The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane |
Osmosis |
|
|
|
Cells lose water by osmosis and shrink in a ______________( contains a higher concentration of solutes than are present inside the cells) |
Hypertonic solutions |
|
|
|
Less solute in solution than molecule and when water enters cell, cell swells |
Hypotonic solution |
|
|
|
Shapes (for quick view) |
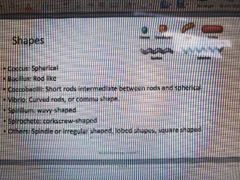
|
|
|
|
Gram negative bactetia |

|
|
|
|
Endotoxins vs exotoxins |

|
|
|
|
Cell mebrane or plasma membrane |

|
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |

|
|
|
|
Chromatophores |

|
|
|
|
Endospores |

|
|

