![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Used for sensory stimulation |
Short pulses and low-current amplitudes |
|
|
Use for motor stimulation |
Longer pulses and higher amplitudes |
|
|
T/F Further increasing the current amplitude or pulse duration does not make the action potential larger or longer |
True |
|
|
Action potential travel faster where? |
Large-diameter myelinated nerves than in small-diameter or unmyelinated nerves |
|
|
Contraindications for ES |
Demand cardiac pacemaker or unstable arrhythmias Placement of electrodes over carotid sinus Areas where venous or arterial thrombosis or thrombophlebitis is present Pregnancy |
|
|
Precautions for ES |
Cardiac disease pts with impaired mentation or with impaired sensation malignant tumors areas of skin irritation or open wounds |
|
|
T/F electrodes can be placed over bony prominences if patient says pain is over there |
False |
|
|
T/F when electrodes are father apart, the current is deeper |
true |
|
|
Application of an electrical current directly to muscle to produce a muscle contraction |
Electrical muscle stimulation (ES) |
|
|
Application of an electrical current to produce muscle contractions that are applied during a functional activity |
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) |
|
|
The total frequency-dependent opposition to current flow. |
Impedance |
|
|
the delivery of ions through the skin for therapeutic purposes using an electrical current |
Iontophoresis |
|
|
the place in a muscle where electrical stimulation will produce the greatest contraction with the least amount of electricity |
Motor point |
|
|
Motor point is usually found where? |
Middle of the muscle belly |
|
|
Application of an electrical current to motor nerve to produce contractions of the muscle they innervate |
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES) |
|
|
A continuous bidirectional flow of charged particles |
Alternating Current |
|
|
AC is most commonly delivered as what kind of wave? |
Sine Wave |
|
|
A series of pulses wherein the charged particles move in one direction and then in the opposite direction |
Biphasic pulse current |
|
|
continuous flow of charged particles without interruptions or breaks |
Continuous current |
|
|
waveform procduced by the interference of two medium frequency |
Interferential current |
|
|
series of pulses wherein the charges particles move in only one direction |
Monophasic pulse current |
|
|
Medium frequency AC with a frequency of 2500 Hz delivered in 50 bursts/seconds |
Russian Protocol |
|
|
A transient increase in threshold to nerve excitation |
Accommodation |
|
|
Physiological muscle contractions usually have a smooth onset, whereas electrically stimulated muscle contractions are? |
rapid, jerky, onset |
|
|
to increase strength, what kind of contractions should be used? |
higher-force contractions |
|
|
to increase endurance, what kind of contraction should be used? |
Prolonged stimulation, lower force contrations |
|
|
Used for denervated muscles |
EMS |
|
|
Used for innervated muscles? |
NMES |
|
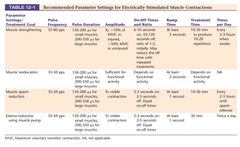
|
table for EMS |
|
|
when the pulse duration is shortened, what do we need to achieve the same strength of contraction produced by a longer pulse duration |
Higher amplitude |
|
|
a principle of strengthening muscles that states that the greater the load placed on a muscle, the higher the force contraction it produces |
Overload principle |

