![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
398 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Early City Structures centered |
On features like the church, the monarchy, industry. |
|
|
|
Grid system cities utilized |
Uniformity, grids, building setbacks, and garden spaces |
|
|
|
Satellite Towns are |
The beginnings of the megalopolis
Small towns that are near each other and support each other |
|
|
|
Ward |
A plot of land nearly 600 feet x 600 feet square
4 residential blocks with 40 lots each and 4 Civic blocks
Arranged in a regular grid |
|
|
|
Urban Development affects city planning historically by |
- Proximity to vital services like food and water - Location of Centers of activity like the church, temple, or ruling authority - Military forifications like moats and city walls - later aesthetic needs |
|
|
|
City Planning and Aesthetics prompted... |
City arrangements that used linearity, regularity Traffic control measures Green space Setbacks |
|
|
|
The industrial Revolution curtailed City planning by |
Shifting focus from aesthetics to industry. |
|
|
|
Negative affects to Urban residents as a result of the Industrial Revolution include |
Plague Filth Lack of Open Space Limited to No recreation space Decrease in emphasis on social issues |
|
|
|
The cite industrielle responded to the Industrial Revolution by |
Zoning concepts like separate residential, industrial, public, and agricultural land use
Individual buildings with setbacks and building separation |
|
|
|
The gridiron street system planned for |
Public open spaces Uniform lots Setbacks |
|
|
|
The West was settled into a ____ arrangement featuring ______. |
Grid/townships |
|
|
|
Townships |
Subdivision of a 24x24 square miles and mass further divided into 16 townships (6 miles square) |
|
|
|
Sections of a township |
1 mile square subdivisions of township |
|
|
|
Urban Sprawl |
A post WWII movement featuring mass exodus of families from Urban centers to suburban developments Individuals left seeking respite from crime, and overcrowding. |
|
|
|
New Urbanism seeks to |
Connect suburbs to regional transportation Allow for pedestrian, bike transportation Utilize mixed use development Promote safer streets |
|
|
|
City Development Patterns |
Expanding Grid Star Satellite Field Megalopolis |
|
|
|
Expanding Grid City Development Pattern |
A grid is established at the intersection of two major roads and is extended out on that same grid until stopped by a natural land feature |
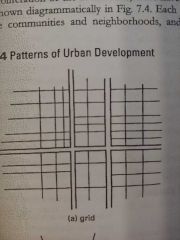
|
|
|
Star Pattern City Development Pattern |
City starts at a dense urban core then grows outward in spokes Similar to Baltimore |
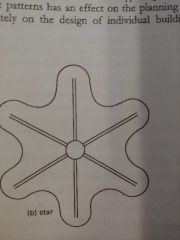
|
|
|
Satellite City Development Pattern |
When a dense Urban cores occurs near other major urban areas
Utilizes a beltway road system
Leads to the megalopolis |
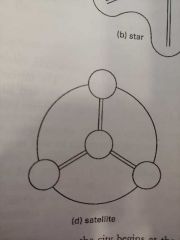
|
|
|
Field City Development Pattern |
Amorphous, non centralized conglomeration of development incorporating highways and natural features |
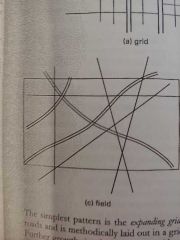
|
|
|
Megalopolis City Development Pattern |
Very close district urban centers located near each other. Like DC/MD/VA |
|
|
|
The Golden Gate Bridge or the St. Louis Arch give an area... |
Imageability |
|
|
|
5 Basic Elements of an Urban Image per Lynch's The Image of The City |
Paths Edges Districts Nodes Landmarks |
|
|
|
Paths are... |
Circulation ie roads, rails, rivers, and walkways, etc |
|
|
|
Edges are... |
Boundaries that break continuity |
|
|
|
Districts are |
Parts of an area that share a character distinct from it's surroundings |
|
|
|
Nodes are |
Focal points indicating an entrance to a district |
|
|
|
Landmarks are |
Focal points that can be viewed from outside of the district but cannot be entered |
|
|
|
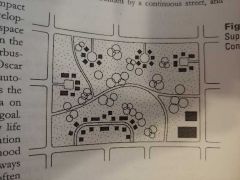
The Superblock seeks to |
Enhance park spaces while minimizing the automobile as the focal point for housing |
|
|
|
Planned Unit Development |
Parcels of land have different uses FAR limits Open Space Requirements Parking Requirements Max Building Heights Setbacks Building separation Diversity of housing types |
|
|
|
Transit Oriented Development |
Interconnection of urban sprawl to downtown's with mass transit |
|
|
|
Population Density, as affected by cultural influences and socioeconomic status, can |
define comfort in high and low density areas. All cultures have density limits that beyond which result in declines in wellness |
|
|
|
Human territoriality leads to |
Definition of personal space on - a minimal scale ie decorating ones office - a macro scale is property lines and rows of trees |
|
|
|
Personal Space, comfort, and distance are governed by... |
Intimate distance - within 18" defense zone Personal distance - 18" to 30" comfort zone Social distance - 4' - 12' strangers Public distance - 12'+ very formal |
|
|
|
Design the Crime Away |
By creating private spaces, locating entrances off of private spaces, creating areas of surveillance |
|
|
|
Catchment Areas |
Population demographics within a certain zone used to determine feasibility of design projects and civic needs like school populations |
|
|
|
Catchment Area Boundaries |
Determined by geographical features, transportation availability, politcal boundaries, divisions between ethnic neighborhoods, proximity to customers requiring a service (ie a corner store) |
|
|
|
What are Catchment areas used for? |
To determine if an area can support certain development (ie an area with a low median income may not be able to support development of a high-end shopping mall) |
|
|
|
Do your transportation accessibility enable you to develop this site? |
___ Roads support transpo to site? ___ Enough drive-by exposure? ___ Will development overload the existing roads? ___ Can trucks get in? ___ Will the road noise affect the development? ___ If pedestrian access is needed, does it safely exist? ___ Will public transpo support your site? Is there access? ___ Are shipping lines available for your industrial development? |
|
|
|
Development shall respect the fabric of a neighborhood by respecting... |
- pedestrian access - building size and scale - architectural character - views |
|
|
|
Development shall respect the amenities of an area by... |
creating/providing/improving access to schools, churches, fire stations, police stations, post offices, etc - preserving/enhancing connections between the existing public facilities |
|
|
|
During Programming, respecting user's and owner's psychological needs requires examination of... |
- Proxemics - Behavior Settings - Territoriality - Personalization - Group Interaction - Status |
|
|
|
Proxemics psychologically affects development by... |
culture determining the spacing of people |
|
|
|
Behavior Settings psychologically affects development by... |
arranging items and people in a space to support a specific task (ie a board room supports board meetings with room shape, furniture placement, lighting etc) |
|
|
|
Territoriality psychologically affects development by... |
creating spaces where individuals express self-identity, group-identity, and comfort from those outside of their territory |
|
|
|
Personalization psychologically affects development by... |
providing amenities for individual to move, adapt, and augment for comfort and establishing territory |
|
|
|
Group Interactionpsychologically affects development by... |
Guiding design that promotes or discourages human connections (ie the grouping of desks, seating areas, etc) |
|
|
|
Statuspsychologically affects development by... |
creating hierarchical divides with placement of walls, rooms, buildings, and amenities within districts |
|
|
|
USGS |
United State Geological Survey - Determines 100 Year flood plain |
|
|
|
Types of Roadways |
- Local Streets (Dalton Dr) - Collector Streets (Patterson Ave) - Arterial Streets (Reisterstown Rd) - Expressways (I-695) |
|
|
|
Road access to a site standards |
- Leave ~ 150' to the site entrance - intersections at no less than 80 degrees - No diverging roads - Ample turning radius - Smooth grade transitions |
|
|
|
When developing a site, transportation factors like ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, and _____ need to be taken into account. |
- Road location - Public Transit - Service Access (Loading) - Utilities (Water retention, telecom, etc) - Municipal Services (Waste disposal) |
|
|
|
Ways utilities affect development |
- If Access to power, water, and sewer have to connected from far away, substantial costs apply |
|
|
|
Easements |
private land that public entities are permitted to use for installation and maintenance of utilities |
|
|
|
Under the road utilities |
Typ. sanitary sewers, storm sewers, and water mains |
|
|
|
Adjacent to road utilities |
Typ electric and communication lines either on poles or underground |
|
|
|
Either Adjacent or under the road utilities |
Gas lines |
|
|
|
Utilities precedence when installing/designing |
Sanitary and Storm Sewers b/c the use slope of land |
|
|
|
Macroclimate |
The regional weather patterns classifying an area as cool, temperate, hot arid, or hot-humid |
|
|
|
Microclimate |
Site specific modification of the macroclimate via trees, hills, bodies of water, and buildings |
|
|
|
Climatic Influences during design include: |
- Wind Patterns - Solar Orientation - Macro and Microclimate |
|
|
|
Windward side of a hill |
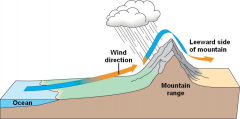
- Prevailing Winds blow directly into the hill - Moist with lush greenery |
|
|
|
Leeward side of a hill |
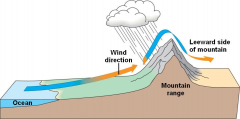
- Wind blows away from the hill - Dry |
|
|
|
Sea Breezes |
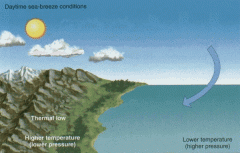
|
|
|
|
Inversion weather phenomenon |

|
|
|
|
Best wind related microclimates are |
on the south/southeast facing slope towards the middle or near the top |
|
|
|
Trees/Buildings and wind |
Groups of Trees can decrease wind speeds by 30 - 60% |
|
|
|
Solar Reflectance (Albedo) |
The amount of radiant energy from the sun received on a surface |
|
|
|
Solar Reflectance (SR) numerical expression |
0 - 1.0 albedos - 0 is a black surface that adsorbs radiation - 1 is a mirror that reflects all radiation |
|
|
|
Reflectivity and SR |
Very similar
Reflectivity is a measure of solar HEAT rejection
SR is a measure of radiant energy reflected |
|
|
|
Emmissivity |
Inverse of Albedo (SR) - Involves the emission of stored energy - Comparable to Thermal Emittance |
|
|
|
Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) |
Measure's a roofs ability to reject heat
Black roof with .05 reflectivity and .90 emittance = SRI 0
White roof with .80 reflectivity and .90 emittance = SRI 100 |
|
|
|
Heat Island Effect |
When built environments trap heat - Preventable with more vegetation |
|
|
|
Ecological Concerns During sustainable Design |
Impact on environment including air water land and wildlife
Impact on natural landforms, water runoff, vegetation etc |
|
|
|
Environmental Impact Statement (EISs) |
Requirement for federal agencies Includes analysis of how developments will impact water land air and wildlife. Instituted in the National Environmental Policy of 1969 Enforced by the EPA |
|
|
|
Site Analysis of Rural and Semirural Sites should analyze the impact on: |
- Natural landforms - Water Run-off - Wildlife - Existing Vegetation |
|
|
|
Site Analysis of Urban Sites should analyze the impact on: |
- Noise Production - Pollution - Light Pollution - Wind Conditions - Sunlight Blocking - Glare - Utility Systems - Transportation |
|
|
|
Wetlands are |
- Defined by the EPA - Areas with soil so unindated with moisture that indigenous plant life is supported |
|
|
|
Jurisdictional Wetlands |
Wetlands administered by the Army Corps of engineers |
|
|
|
Regulations protecting Wetlands |
- Clean Water Act of 1972 - Protect damage from nearby development - May allow site discharge if permitted |
|
|
|
Sustainability Issues and Site Analysis |
- Determining wetlands and sites within 100 ft of wetlands - Elevations less than 5ft above a 100 yr flood plain - Endangered Species habitats - Historic Sites including burial grounds - Prime Farmland - Existing Air Quality - Brownfields |
|
|
|
What Sustainability Guidelines May Affect a New Project? |
- Location - Building Size, Shape, and Facade - Site Disturbance - Site Development |
|
|
|
Building Location Guidelines for Sustainable Site Design |
Use Urban Sites Use sites with existing infrastructure Encourage mixed use development Locate near transportation routes Minimize vegetation clearing Use solar access to your advantage Minimize wind effects Minimize shadows on adjacent property Utilize gravity sewers |
|
|
|
Building Size, Shape, and Facade Guidelines for Sustainable Site Design |
Minimize Footprint with Multiple Floors Optimize Material Use Garden roof Include amenities for cyclists |
|
|
|
Site Disturbance Guidelines for Sustainable Site Design |
Use previously developed land Position for minimal cut/fill Plan utility installation to coincide with other digging onsite Minimal site disturbance (40 ft from bldg, 5ft from road, 25ft beyond permeable surfaces) |
|
|
|
Site Development Guidelines for Sustainable Site Design |
Parking Under bldg Minimize road, parking, and service paths Reduce heat island effect Use pervious paving Use storm water retention Minimize site lighting Use native plants Minimize high maintenance lawns |
|
|

|
D |
|
|
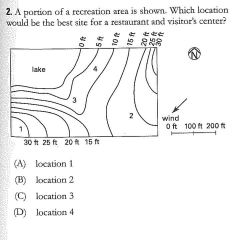
|
B |
|
|

|
C |
|
|

|
C |
|
|
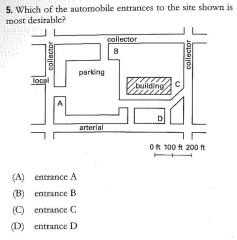
|
B |
|
|
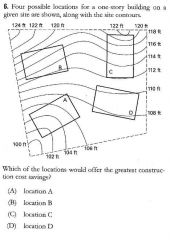
|
D |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
ABDF |
|
|
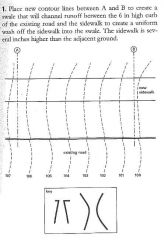
|
|
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
B |
|
|
|
B |
|
|

|
ACDE |
|
|

|
ABE |
|
|

|
ACDF |
|
|

|
ABDE |
|
|

|
ABDF |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
ACDF |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
ABDE |
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
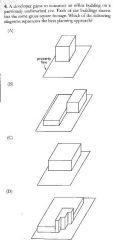
5 |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
ACDF |
|
|
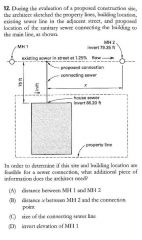
|
B |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
C |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
A |
|
|
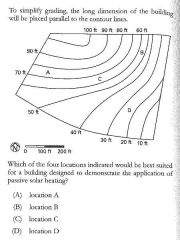
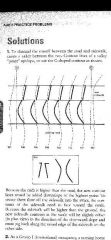
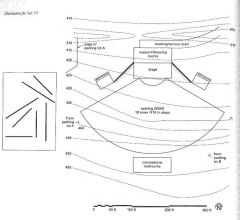
A small, three-story rectangular office building in a temperate climatic region is planned for the site shown. |
C |

|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
BCDE |
|
|

|
B |
|
|
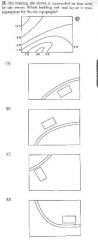
|
B |
|
|
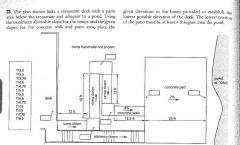
|
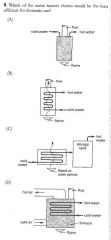
|

|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
BCDE |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
C |
|
|
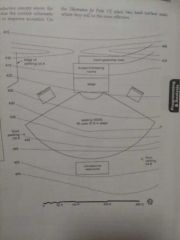
|
D |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
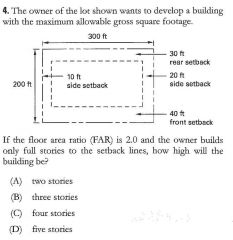
75000 sq ft |
|
|

|
ACE |
|
|

|
CDEF |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
C |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
CDEF |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
BCF |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
C |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
ABDF |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
ADEF |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
ADEF |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
C |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
C |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
A |
|
|

|
B |
|
|

|
D |
|
|

|
ACDF |
|
|

|
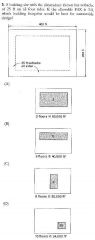
47 |
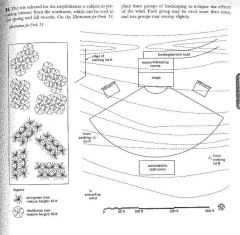
|
|

|
C |
|
|
|
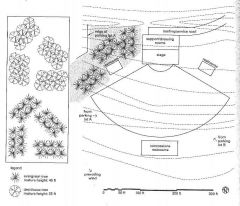
|
|
|
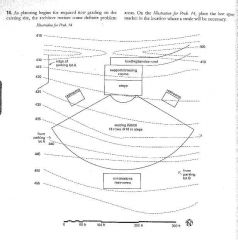
|
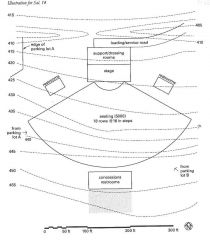
|
|
|
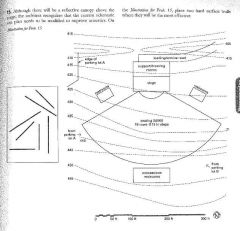
|
|
|
|

|
D |
|
|
|
Local Municipalities and States may or may not choose to adopt... |
the ICC set of building codes |
|
|
|
Local Municipalities and States may... |
Adopt, partially adopt, or amend the ICC building codes |
|
|
|
IBC Chapter 3 |
Use and Occupancy Classification A, B, E, F, H, I, M, R, S, U |
|
|
|
IBC Chapter 5 |
General Building Heights and Areas General Height and Area Unlimited Area Buildings Mixed Use and Occupancy |
|
|
|
IBC Chapter 6 |
Types of construction |
I, II, III, IV, V |
|
|
IBC Chapter 7 |
Fire Rated Construction Firewalls/Barriers/partitions Smoke Barriers/Partitions |
|
|
|
IBC Chapter 10 |
Means of Egress
Occupant load Egress Width Accessible Means of Egress Doors/Stairs/Ramps/Signs |
|
|
|
The Major model building code for USA |
The IBC, |
|
|
|
The IBC is prescriptive in that... |
It describes specific means and methods of design and construction for building components and systems. |
|
|
|
Least Acceptable Risk |
The minimum level of risk needed for building and occupant safety. |
|
|
|
Separation of use groups is governed by which code? |
IBC |
|
|
|
Setbacks from property lines are governed by which code? |
Zoning codes |
|
|
|
Minimum green spaces are governed by which code? |
Zoning codes |
|
|
|
Storm water from roof drains is governed by which code? |
IPC |
|
|
|
Loading Spaces and Parking are governed by which code? |
Zoning |
|
|
|
Accessible Paths of Travel are governed by which code? |
IBC |
|
|
|
Standards have no legal standing until |
They are adopted by a governmental jurisdiction |
|
|
|
ASTM Standards standardizes... |
Testing of materials and assemblies over a specific testing period |
|
|
|
NFPA Standards standardize... |
All testing and approval of material and assemblies related to fire protection |
|
|
|
ASHRAE standardizes.. |
HVAC equipment and assembly testing standards |
|
|
|
ANSIs Function... |
To approve the standards developed by other organizations. They also help to prevent standards duplication |
|
|
|
Items that are listed as ANSI approved |
Have been reviewed by several relevant organizations related to the applicable trade and agreed upon with ample debate |
|
|
|
NRTLs are |
Nationally recognized testing laboratories |
|
|
|
NRTLs are recognized by OSHA to |
Test products to spec and product safety standards |
|
|
|
UL (Underwriters Laboratory) is an |
NRTL |
|
|
|
UL tests... |
Product safety |
|
|
|
UL labels |
Listed label - product or assembly passes safety testing Classified label - parts or certain aspects of a product or assembly passes safety testing |
|
|
|
Testing Fire Resistance of Construction Assemblies |
ASTM E119 NFPA 252 NFPA 257 |
|
|
|
Testing Flammability of Construction Materials |
ASTM E84 NFPA 265 NFPA 286 |
|
|
|
Flammability Tests determine... |
- Whether a material is flammable and or combustible - How fast for spreads across the material - Smoke and fumes emitted from a material |
|
|
|
Steiner Tunnel Tests AKA ASTM E84 tests for |
Rates of surface burn of materials |
|
|
|
Flame Spread Index Classifications |
Class A(I): 0 - 25 FSI Most Fire Resistant Class B(II): 26 - 75 FSI Class C(III): 75 - 200 FSI |
|
|
|
The First Zoning Ordinance |
NYC as an attempt to curb crowding, industrial encroachment of living areas, blocking of light and air |
|
|
|
Purposes of Zoning Ordinances |
- Land use - Open space - Structure size - Setbacks - Parking and Loading Spaces |
|
|
|
Easements extends rights... |
Of ones land for another use |
|
|
|
Utility Easements allow |
A utility to use private land, maintain their equipment, and restricts the landowners ability to build on the property without consent |
|
|
|
Access Easements allow... |
The public to cross an adjacent property that blocks access to a parcel |
|
|
|
Rights of Way |
Legal right of an entity to cross another's property. Usually with roads and sidewalks |
|
|
|
Restrictive Covenants |
Restrict the use of a property (Think homeowner's associations rules) |
|
|
|
Affirmative Covenants |
Require a buyer to perform a specific duty in the future |
|
|
|
Conditional Covenants |
Permits a title to revert back to its original owner restrictions are not followed |
|
|
|
The influences of solar orientation are |
- Building Orientation - Outdoor Space Location - Building Entry Location |
|
|
|
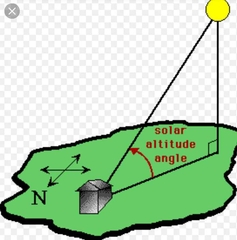
Solar Altitude |
The angle of the sun above the horizon |
|
|
|
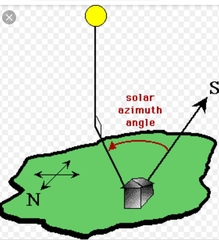
Solar Azimuth |
The angle from Due North or Due South |
|
|
|
Climate Zones in the US |
8 Different Set by The department of Energy |
|
|
|
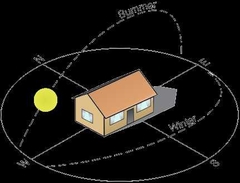
Optimal Building Position in the Northern Hemisphere |
South Facing Entry (or slightly angled east or west)
|
|
|
|
Sun Control Devices |
Window/Roof Overhangs (South) Vertical Sun Baffles (East/West) Louvers Trees |
|
|
|
Four Basic Climate Zones |
Cool Temperate Hot-Humid Hot-Arid |
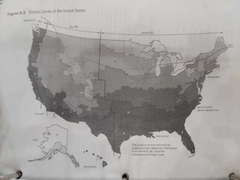
|
|
|
Cold climate Zones and Building Design |
- Partially Underground - Minimal Northern Exposure - South Facing Doors and Windows - Little to no North Facing windows/doors - Landscaping and orientation to block winter winds - Cube Shaped - Avoid passive heating - Include summer shading - Dark colors to absorb heat - Insulate |
|
|
|
Temperate climate Zones and Building Design |
- Maximize Southern Exposure *- Minimize Northern Exposure *- Landscaping and orientation to block winter winds but allow summer winds- Rectangular Shaped*- Passive and Active solar heating*- Include summer shading*- Medium colors to minimally absorb heat- Evening ventilation* |
|
|
|
Hot-Humid Climate Zones and Building Design |
- Maximize Openings - Landscaping and orientation to allow for cross ventilation - Narrow Floor Plans - Passive and Active solar cooling - Include shading for all openings - Light colors to reflect heat - Material with minimal thermal Mass |
|
|
|
Hot-Arid climate Zones and Building Design |
- Minimize Openings* - Use pools to reduce local air temp* - Compact Floor Plans* - Active solar cooling* - Include shading for all openings* - Light colors to reflect heat* - Material with high thermal Mass* |
|
|
|
Alternative Energy systems |
- Passive Solar Heating - Natural Cooling - Active Solar - Photovoltaics |
|
|
|
Passive Solar heating |
Maximize Southern Exposure Works best in long narrow building Incorporate Thermal Mass Deciduous Trees to block summer sun and allow winter sun |
|
|
|
Natural Cooling Includes |
Shading natural ventilation Radiative cooling Evaporative cooling Ground Coupling |
|
|
|
Radiative Cooling |
Materials are used so that Heating is stored during the day and released at night |
|
|
|
Ground Coupling |
Uses the stable coolness of the Earth to cool a building using a ground source heat pump |
|
|
|
Design for natural cooling by... |
Using trees for shade Use fixed shading devices on south Use large overhangs Minimize East West windows Use water and wind elements Use light colored or reflective materials Minimize impervious surfaces Take advantage of winds (add courtyards and maximize cross ventilation)
|
|
|
|
Active Solar Collectors |
Hide with parapets and sloped roof Careful of glare on other buildings |
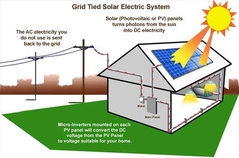
|
|
|
Photovoltaics |
Optimize by use on large, flat roof or sloped roof Use pvs in building materials |
|
|
|
1 acre = |
43,560 sqft |
|
|
|
1 hectare = |
10,000 sq meters |
|
|
|
US PLSS Public Land Survey System |
Subdivision of land into smaller townships and sections |
|
|
|
PLSS system uses |
Principal Meridians and Standard Parallels to create 24mi square checks divided into 16 6mi square townships (labeled by North/South East/West) divided into
divided into divided into 36 1mi square sections (labeled by township and range) divided into 4 1/4s (labeled by direction of corner, section number, township and range number) |
|
|
|
PLSS plot label explanation SE 1/4 of the NW 1/4 of section 12, T. 1N, R. 7W |
The Southeast corner of the northwest corner of the subdivided section 12 located at the intersection of the 1st North township and the 7th west range |
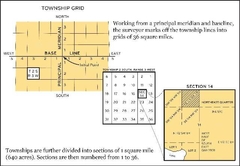
|
|
|
Metes and Bounds Survey |
Bearing lines angling from the NEWS in degrees/minutes/seconds with the distance of the plot line |
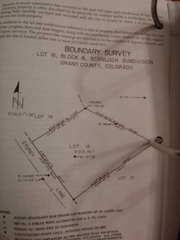
|
|
|
Evaluation of Existing Structures during programming involves evaluation of... |
All the components of a building's site, systems, structure, cladding, roof, finishes, and code compliance |
|
|
|
Site Features to analyze during an existing building survey |
Parking - Service Access - Pedestrian Access - Adjacent Properties - Microclimate - Views - Water features, etc |
|
|
|
Building Configuration Qualities to analyze during an existing building survey |
- Building Size - Building Shape - Building Orientation - Basic Structure Configuration - Basic Systems - Basic Room Configurations |
|
|
|
Building Structure Qualities to analyze during an existing building survey |
- Type of Structure - Load Capacity - Condition of Structure including Foundation and Structural Frame - |
|
|
|
__________ performs the structural survey during the Existing Building Survey |
A structural engineer |
|
|
|
Roof Qualitiesto analyze during an existing building survey |
- Type - Condition - Useful Life Span |
|
|
|
___________ is used to determine the composition and condition of an existing roof assembly. |
Core Drilling |
|
|
|
____________ is used to find weakened areas in a roof assembly. |
Infrared Testing |
|
|
|
Exterior Envelope Qualitiesto analyze during an existing building survey |
- Type - Condition (including insulation, windows, openings) |
|
|
|
_____________ is used to find air leaks and failures in a building envelope. |
Infrared Testing |
|
|
|
Mechanical Systems to analyze during an existing building survey |
- Type of Heating and Cooling - Capacity of Central Plant - Condition of Distribution systems |
|
|
|
__________ performs the HVAC survey during the Existing Building Survey |
Mechanical Engineer |
|
|
|
__________ performs the plumbing survey during the Existing Building Survey |
Mechanical Engineer |
|
|
|
__________ performs the electrical survey during the Existing Building Survey |
Electrical Engineer |
|
|
|
__________ performs the fire protection survey during the Existing Building Survey |
Mechanical OR Fire Protection Engineer |
|
|
|
Plumbing systems to analyze during an existing building survey |
- Capacity of Service to Bldg - Sewer Capacity - Condition of Pipes and Fixtures - Number of Fixtures |
|
|
|
Electrical systemsto analyze during an existing building survey |
- Capacity of Service to Bldg - Primary and Secondary Service - Condition of Wiring and Devices - Condition of lighting - Other electrical Components |
|
|
|
Fire Protection Systems to analyze during an existing building survey |
- Condition of System - Condition of Pipes - Spacing of Heads |
|
|
|
Equipment to analyze during an existing building survey |
Major Equipment like - Refrigeration - Food Service Equipment - Lab Equipment |
|
|
|
Finishesto analyze during an existing building survey |
- Condition - Useful Life |
|
|
|
Accessibility Requirementsto analyze during an existing building survey |
- Egress condition - Fire Rated Elements |
|
|
|
Building Surveys document... |
building conditions including interior partitions, doors, equipment, casework, elevations of floors, noted systems etc |
|
|
|
Building surveys can be illustrated using the following methods... |
Hand Sketch OR CAD - Site Prepared OR As-Builts - Existing Site Surveys/Geotech/Soils Reports
|
|
|
|
Electromagnetic Distance Measurement (EDM) Reflectorless Electromagnetic Distance Measurement (REDM) Rectified Photography Orthophotography Stereo Photogrammetry Convergent photogrammetry Laser Scanning |
Advanced Field Measuring Methods |
|
|
|
When examining an existing structure, inquire about... |
Site Configuration Appearance Structure Code Updates Systems Upgrades Construction Type and Allowable Area Time and Budget Extent of Renovation required |
|
|
|
Economic Feasibility is analyzed during existing structure survey and includes |
Comparison of new structure Costs vs renovation costs |
|
|
|
The _________ provides guidelines for Historic Preservation of existing structures. |
National Park Service |
|
|
|
Four approaches to historic preservation |
Preservation Rehabilitation Restoration Reconstruction |
|
|
|
Preservation of existing structure includes |
Retaining all the historic character through conservation, maintenance, or repair |
|
|
|
Rehabilitation of existing structures includes |
Retaining AND Repair where repair is acceptable within limits Usually with a delapidated building |
|
|
|
Restoration of existing structure includes |
A period specific renovation including removal of inapplicable materials |
|
|
|
Reconstruction of existing structure includes |
Recreation of a historic site to a specific time period. The least historic method |
|
|
|
The Secretary of the Interiors Standards for Rehabilitation |
A set of 10 guidelines used for the Federal Historic Preservation Tax Incentive Program |
|
|
|
Guidelines used for the Federal Historic Preservation Tax Incentive Program |
1. Same use or new use with minimal change 2. Preserve the character 3. Preserve the time period. 4. Retain historical evolutions 5. Preserve the construction. 6. Repair elements if possible. Replace if not. 7. Use least destructive cleaning methods. 8. Preserve site. 9. New construction must respect old. |
|
|
|
Existing Conditions Survey of a Historic Structure includes... |
All from a non historic survey (structure, site, cladding, openings, building systems, roof, fire protection, etc) and: - structural integrity of structural members - alteration/removal of historic elements |
|
|
|
Treatment of Masonry in Historic Buildings |
- ID, retain, preserve - Protect and maintain - Repair - Replace - Remove - Recreate |
|
|
|
Protection and maintenance of masonry in historic buildings |
- Correct drainage issues - Clean using the gentlest method possible - Remove paint to the next sound layer using the gentlest method possible |
|
|
|
Repairing of masonry in historic buildings |
- Hand rake, don't use electric methods, to remove mortar. - replace damaged masonry dispatchin with patching, or reinforcing masonry - deteriorated masonry units maybe replace with similar substitute |
|
|
|
Replacing of masonry in historic buildings |
Reproduce the feature using economically and technically feasible substitute materials |
|
|
|
The Process of Programming Includes... |
- establishing goals - collecting facts - uncovering concepts - determining needs - stating the problem |
|
|
|
Four considerations during programming |
Function Form Economy Time |
|
|
|
Programmatic concepts |
Abstract solutions to a client's needs without the physical means to achieve them |
|
|
|
The four elements of cost |
Quantity Quality Budget Time |
|
|
|
Problem statements during programming |
A bridge between programming and Design where the most important aspects of design problem are summarized. There should be four statements that link to function, form, economy, and time. |
|
|
|
Programmatic concepts occurring before design |
General, abstract solutions to a client's problems |
|
|
|
24 programmatic concepts |
Priority Relationships Hierarchy Character Density Service groupings Activity grouping People grouping HomeBase Communications Neighbors Accessibility Separated flow Mixed flow Sequential flow Orientation Flexibility Tolerance Safety Security controls Energy conservation Environmental controls Phasing Cost control |
|
|
|
Determining Space Needs are dependent on one of 3 factors |
- The number of Occupants in space - The equipment required in the space - The activity taking place in the space |
|
|
|
Benchmarking in programming |
Common Space Standards for rooms, spaces, and activities |
|
|
|
Net Assignable Area |
the space in a building taken by the main rooms and functional spaces also called net area |
|
|
|
Non-assignable Area |
the space in a building occupied by support spaces like circulation, walls, restrooms, mech, elec, and telephone/server rooms. |
|
|
|
Efficiency of a Building or Efficiency Ratio |
Net area : Gross Area |
|
|
|
Gross Area |
net area + non-assignable areas |
|
|
|
Typical Building Efficiency Range |
60 - 80% |
|
|
|
High Efficiency Building Types |
Offices, Retail, Libraries, Museums |
|
|
|
Low Efficiency Building Types |
Theaters, Hospitals |
|
|
|
Net Rentable Area |
Calculated by BOMA standards Sum of the occupant space and a prorated amount of the shared tenant spaces |
|
|
|
BOMA International |
Building Owners and MAnagers Association International - Used for calculating rentable space |
|
|
|
For a floor shared by multiple tenants, area calculations are measured... |
to the center of demising walls and inner surface of all others (inner surface of glass walls too) |
|
|
|
ANSI/BOMA Z65.1 has 2 methods for measuring rentable area |
Method A - Legacy Method Method B - Single Load Factor Method |
|
|
|
Legacy Method for measuring rentable area |
R/U ratio rentable area / usable area |
|
|
|
Single Load Factor Methodfor measuring rentable area |
R/O ratio net area/ usable area |
|
|
|
rentable area = |
load factor * necessary occupant area |
|
|
|
Graphically Showing Adjacency |
Adjacency Matrix Adjacency Diagram (Bubble Diagram) |
|
|
|
Adjacency is determined by the immediate needs of |
People Products Information |
|
|
|
Construction Budgets are usually based on 4 interrelated constraints |
Quality Quantity Available Funds Time |
|
|
|
Debt Service |
Ongoing Finance costs or long-term interest No included in the project development budget |
|
|
|
3 Budget Preparation Methods |
- Project Comparison Method - Area or Volume Method - Assembly or System Method |
|
|
|
Project Comparison method of estimation project costs |
Uses project of similar scope, size, and complexity estimate Accurate to 15 - 25% |
|
|
|
Area (or Volume) Method of estimation project costs |
Uses area or volume derived from a preliminary design Accurate to 5 - 15% |
|
|
|
Assembly method of estimation project costs |
- Derived from the known subsystems a project will include - Accurate to within 10% |
|
|
|
Land value are influenced by |
location, market conditions, and profitability |
|
|
|
Land values are calculated using |
- The Market Approach - The Income Approach - The Cost Approach |
|
|
|
The Market Approach for calculating land values |
value is determined based on comparable properties sold |
|
|
|
The Income Approach for calculating land values |
value is determined based on the potential profitability of the land net value = gross value - various expenses |
|
|
|
The Cost Approach for calculating land values |
V = C - D + L |
|
|
|
Mill Levy |
How property taxes are expressed as thousandths of a dollar ($.001) |
|
|
|
49.31 mills = |
49.31/1000 |
|
|
|
Public Works Financing Types |
- General Sales and Property Taxes - Special Sales Taxes - General Obligation Bonds - Revenue Bonds - Public Enterprise Revenue Bonds - Tax-Increment Financing - Development Impact Fees - Subdivision Exactions - Special District Assessments |
|
|
|
General Obligation Bonds issued by a public entity are... |
backed by general tax revenues, recollected by property tax revenues, and voted on by tax payers |
|
|
|
Revenue (Rate Supported) Bonds issued by a public entity are... |
backed by general tax revenues, recollected by revenues collected by the facility's use, and voted on by tax payers ie sewer improvements |
|
|
|
Public Enterprise Revenue Bondsissued by a public entity are... |
backed by general tax revenues, recollected by charges imposed by the facility's use, and voted on by tax payers ie parking garages, hospitals, airports |
|
|
|
Tax Increment Financingissued by a public entity are... |
intended to encourage private development which over time will lead to increased property values then increased property taxes. No public vote required |
|
|
|
Development Impact Fees imposed by a public entity are... |
fees paid by a developer to extend public services to a new site. - controversial as calculation is subjective and who benefits is unclear |
|
|
|
Subdivision Exactions |
requirements satisfied by a developer. include land for public use or a cash contribution for purchase of land/facilities |
|
|
|
Special District Assessments |
Areas are defined by a public entity and agreed upon by a majority of taxpayers in the district. Taxes are assessed among the taxpayers in the district to fund an improvement, usu a park or public space Does not encourage private development |
|
|
|
Types of Project Financing |
- Mortgage - Balloon Mortgage - Bond - Bridge Loan - Construction Loan - Hard Money Loan - Mezzanine Loan |
|
|
|
Mortgage |
A project financing type that grants a lien on the property to the lender as collateral until the full loan is repaid |
|
|
|
Blanket Loan |
A project financing type that allows a borrower to sell parcels of a property, satisfying that part's mortgage, while the remainder of the loan remains due. |
|
|
|
Bonds |
A project financing type that is issued by a government entity to a individual investor or investment company to raise money for a construction project |
|
|
|
Bridge Loan |
A project financing type that is used on a short term basis to finance a purchase until a permanent funding method is set |
|
|
|
Construction Loan |
A project financing type that funds the building process and is converted when construction ends |
|
|
|
Hard Money Loan |
A project financing type that is used on distressed properties, for short-term quick sale. Usu interest is high |
|
|
|
Mezzanine Loan |
A project financing type that uses the development company as collateral for a loan Usu used by developers on large projects |
|
|
|
Pro Forma |
A statement of all the expected expenses compared the the expected income and appreciation Used to determine a project's feasibility |
|
|
|
Abatement |
Reduction of property value due to discovery of a problem |
|
|
|
Aquifer |
A natural underground reservoir from which wells draw water |
|
|
|
Bedroom Community |
A region containing mainly housing and few employment opps |
|
|
|
Boilerplate |
A standard portion of a written document |
|
|
|
Buffer zone |
A piece of land used to separate 2 incompatible uses |
|
|
|
Capital Expenditure |
Money used to improve a property to enhance its value over time |
|
|
|
CC&Rs |
Conditions, Covenants, and Restrictions - Rules that apply to property owners in a subdivision, condo, or co-op housing |
|
|
|
Cluster Housing |
Housing development where housing is close each other and near common open spaes |
|
|
|
Conditional Use Permit (CUP) |
Zoning Allows a normally unpermitted use in an area |
|
|
|
Conveyance |
Transferring interest in a property to another person Also the document name |
|
|
|
Dedication |
The donation of a parcel of land by a developer for public use |
|
|
|
Despoil |
To remove items of value from a site |
|
|
|
Discount Rate |
a rate of interest adjusted for inflation to calculate the value of future cash flow |
|
|
|
Downzoning |
Change in zoning which decreases allowable density |
|
|
|
Ground Lease |
Long term property lease that allows improvements on the land but reverts back to owner at lease end |
|
|
|
Improvement Ratio |
improvement value : All Value |
|
|
|
Inverse Condemnation |
Court ordered remedy to a property owner whose property was taken by eminent domain |
|
|
|
Land Sale Leaseback |
Developer sells property then immediately leases it back |
|
|
|
modified uniform present worth factor |
Discount factor to convert a variable annual amount to a present value |
|
|
|
Net Leaseable Area |
The Area of a bldg available to rent not including common areas |
|
|
|
Occupancy Permit |
Certificate of Occupancy issued by Govt stating that a building may be occupied |
|
|
|
Restriction |
AKA Restrictive Covenant restricting how a property owner may use their property |
|
|
|
Riparian |
refers to land adjacent to a river |
|
|
|
Riparian Rights |
Rights to the water use bordering your property |
|
|
|
Special Use PErmit |
Exemption from Zoning regs in a jurisdiction |
|
|
|
Spot Zoning |
Applying zoning regs to specific properties when nearby land is under different zoning |
|
|
|
Uniform Capital Recovery |
Process of converting future value into present value using a discount rate |
|
|
|
Uniform Present Worth Factor |
Discount factor to convert a uniform annual amount to a present value |
|
|
|
Uniform sinking fund |
The amount of money that needs to be invested at the discount rate to attain a specific amount in the future |
|
|
|
Usury |
The illegal practice of charging exorbitant interest rates on a loan |
|
|
|
Variance |
permission granted by the govt to deviate from the zoning ordinance where strict adherence would cause undue hardship |
|
|
|
Standard Structural Systems - Wood |
Wood Joist System Plank and Beam Glulam Beams Wood I-Joists Wood Trusses Box Beams |
|
|
|
Standard Structural Systems - Steel |
Beam and Girder System Open Web Steel Joists |
|
|
|
Standard Structural Systems - Concrete |
Precast vs Cast-In-Place Prestressed Concrete - Beam and Girder System - Concrete Joist - Two Way Systems - Flat Plate - Flat Slab - Waffle Slab PreCast Structural Members - Rectangular Beams - T Beams - L Beams - Single Tee - Double Tee - Precast Column - Hollow Core Slab |
|
|
|
Standard Structural Systems - Masonry |
- Single Wythe - Double Wythe - Cavity |
|
|
|
Slenderness Ratio |
Deals with the ratio of the unsupported height a member to its width |
|
|
|
Flexural Strength |
Deals with the ability of a member to resist lateral forces |
|
|
|
Standard Structural Systems - Composite Construction |
Reinforced Concrete - Composite Decking w/ Steel Beams - Steel Beams with Concrete Decking |
|
|
|
Standard Structural Systems - Walls Systems |
Need to account for creep of concrete and thermal expansion of different materials |
|
|
|
Creep |
Deformation of Concrete under a continuous dead load |
|
|
|
Premanufactured buildings vs Built on site |
Premans are faster and more cost economical to construct with less material and labor costs |
|
|
|
Silt |
Soil type classified by Small Particles High Water Retention Poor Drainage Expands Bad for Foundations |
|
|
|
Types of Soils |
Peat Sand Silt Clay Loam Rock |
|
|
|
Sand |
Soil type classified by Medium Particles Low Water Retention Excellent Drainage Good For Foundations |
|
|
|
Clay |
Soil type classified by Tiny Particles High Water Retention Poor Drainage High Expansion Bad For Foundations |
|
|
|
Loam |
Soil type classified as a mix of Sand, Silt, and Clay Mix of Particles Low Water Retention Excellent Drainage Good For Foundations |
|

