![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the Law of Conservation of energy?
|
Energy is not created or destroyed in any process, it is just converted from one type to another.
|
|
|
What are the different forms of energy?
|
Thermal (heat), light, electrical, sound, kinetic, chemical, nuclear and potential (elastic and gravitational).
|
|
|
How does a TV set convert energy?
|
A TV set changes electric energy light & sound energy.
|
|
|
How does a match convert energy?
|
A match changes kinetic & chemical energy to light & heat energy
|
|
|
How does a light-bulb convert energy?
|
A light-bulb changes chemical energy to light energy
|
|
|
How does a catapult convert energy?
|
A catapult changes elastic energy to kinetic energy
|
|
|
How does a falling bucket convert energy?
|
A falling bucket changes gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy
|
|
|
How does an electrical fire convert energy?
|
An electric fire changes electric energy into heat energy
|
|
|
How does a human body convert energy?
|
A human body changes chemical energy into kinetic, heat & sound energy
|
|
|
How does a microphone convert energy?
|
A microphone changes electrical energy into sound energy
|
|
|
How does an atomic bomb convert energy?
|
An atomic bomb changes nuclear energy into sound, light & heat energy
|
|
|
How does a car engine convert energy?
|
A car engines changes chemical energy into kinetic, sound & heat energy
|
|
|
How do you calculate the efficiency of a system which converts energy?
|
Efficiency = useful energy output from the system
total energy input into the system X 100% This gives you a percentage of efficiency of the system |
|
|
What is a Sankey diagram?
|
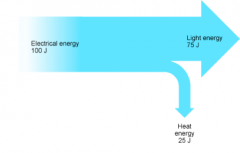
A Sankey diagram shows the level of efficiency of a scientific device or situation, and how energy is transferred and converted in that device of situation. This is a Sankey diagram (energy flow diagram) for a typical energy-saving lightbulb.
|
|
|
How can you use a Sankey diagram to calculate efficiency?
|
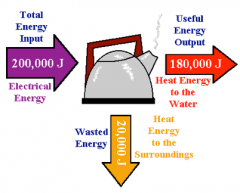
For an electric kettle:
200,000 J of electrical energy is given in in order to run the electric kettle 180,000 J of heat energy is used to boil the water 20,000 J of heat energy is lost to surroundings - Efficiency = 180,000J (180KJ) = 90% efficiency 200,000J (200KJ) X 100% |
|
|
What is conduction?
|
Thermal conduction is the transfer of thermal energy through a substance without the substance itself moving
|
|
|
What is a good thermal conductor?
|
Metals are good thermal conductors as they have free electrons that can move easily through the structure of the metal
|
|
|
What is an insulator?
|
An insulator is a poor conductor of heat (i.e. wood).
|
|
|
How does conduction occur in a metal skewer over a grill?
|
Metal skewers over a grill will become hot and heat energy is transferred along the skewer by conduction.
|
|
|
What is convection?
|
Convection is the transfer of heat through fluid (liquids and gases) by the upward movement of warmer, less dense regions of fluids. This occurs in any fluid substance.
|
|
|
How are convection heaters an example of convection?
|
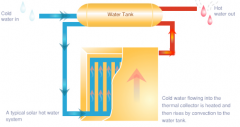
Convector heaters heat cold drawn in at the bottom air, which then floats out of the top of the heater to the top of the room.
|
|
|
What are convection currents?
|
When there is a cycle of hot fluids rising and cold fluids sinking just to be heated and rise again, this is called convection currents.
|
|
|
What is radiation?
|
Thermal radiation is the transfer of energy by infra-red (IR) waves. These waves can be reflected or absorbed.
|
|
|
What kind of surfaces reflect radiation?
|
White and shiny surfaces reflect IR waves
|
|
|
What kind of surfaces absorb radiation?
|
Black and dark surfaces will absorb IR waves.
|
|
|
How does a bathroom heater radiate thermal energy?
|
A bathroom heater will release heat through infra-red waves traveling in a straight line. This can be reflected by a shiny reflector behind a fluorescent light or torch.
|
|
|
How is a house kept insulated?
|
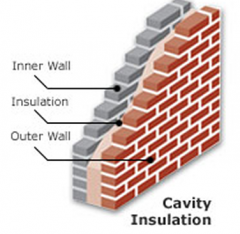
Double-glazed windows- the air in the gap of the windows is an insulator
Curtains- Trap hot air inside the house Wall cavity with wool- The air gap between the brick wall traps hot air and the glass fibre wool insulator is used to stop convection currents Roof cavities- Similarly to the walls, it traps hot air between gaps and also prevents convection current. Reflective foil is used to reduce radiation heat loss. Carpets- They are made out of thick material which are good insulators. |
|
|
How is wind energy produced?
|
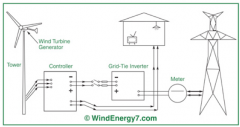
|
|
|
How is geothermal energy produced?
|
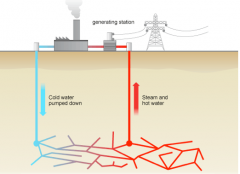
|
|
|
How is hydroelectric energy produced?
|
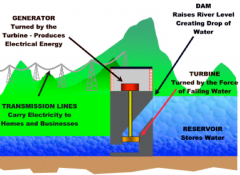
|
|
|
How is solar energy produced?
|
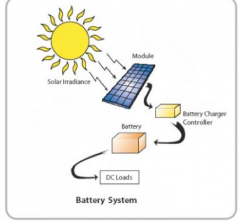
|
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of fossil fuels?
|
Advantages
-Cheap -Easy to extract Disadvantages -Global warming -Non-renewable |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear energy?
|
Advantages
-Makes clean energy -very cheap Disadvantages -risk of accidents -bad for the environment -non-renewable -uranium is in limited supply |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of solar energy?
|
Advantages
-Cheap once built -renewable Disadvantages -no energy on cloudy days -expensive to install |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of tidal energy?
|
Advantages
-Cheap once built -renewable Disadvantages -takes up a lot of space -damages habitats -requires underwater turbines |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of wave energy?
|
Advantages
-renewable -is clean energy -does not impact natural habitats Disadvantages -expensive -cannot gain a lot of power from the waves |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy?
|
Advantages
-cheap once built -clean energy -renewable Disadvantages -must find windy region -wind farms cause environmental damage -noise pollution |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of geothermal energy?
|
Advantages
-renewable -is clean energy -does not impact on natural habitats Disadvantages -potentially dangerous near volcanic areas -hard to find stable volcanic areas |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric energy?
|
Advantages
-Cheap upkeep + build -renewable -clean energy Disadvantages -spoilt landscapes may destroy natural habitats -small amounts of energy at a time |

