![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
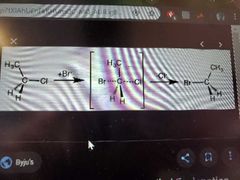
What reaction does this picture show? |
SN2 |
|
|
A group that is lost during nucleophilic substitution or elimination. Typically a halide. The less basic, the better |
Leaving group |
|
|
Rate of SN2 reaction |
Bimolecular, second order. Rate = k[reactant][nucleophile] |
|
|
What happens during a SN2 reaction? |
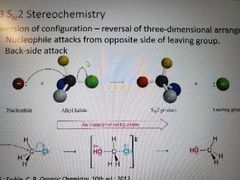
Inversion of stereochemistry at site of backside attack, nucleophile attacks from opposite side of leaving group. |
|
|
What type of reactant works best in the SN2 reaction? |
Methyl and primary carbons, because of steric hindrence. |
|
|
Measure of a Lewis base to perform a substitution. |

Nucleophilicity More basic = more nucleophilic for the same atom. The smaller the atom the better because of steric effects. |
|
|
What type of solvants are used in a SN2 reaction? |
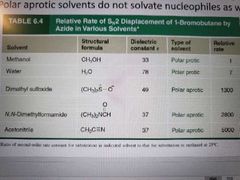
Polar aprotic solvents: polar enough to dissolve the substrate and nucleophile but do not participate in hydrogen bonding with the nucleophile. Sometimes a salt. No H bonding in an aprotic solvant, but Hs can be present. |
|
|
What type of solvant is used in an SN1 reaction? |
Polar protic, something with an H |
|
|
What is created in an SN1 reaction? |
A racemic mixture, but more of the product with the opposite stereochemistry |
|
|
What reactant preserves stereochemistry? |
OTs |
|
|
What reactant inverts stereochemistry? |
SOCl |
|
|
What kind of reaction happens with a hydrogen halide and alcohol? |
Substitution |
|
|
What kind of reactants are used in an SN1 reaction? |
Tertiary and secondary carbons |
|
|
Why are sulfonates good surrogates for alkyl halides? |
Sulfonates don't need to protonate, OH is therefore a worse leaving group than sulfonic acid, making sulfonate have an advantage in substitution reactions. |
|
|
Is there rearrangement in E1 reactions? |
Yes |
|
|
Are there rearrangements in E2 reactions? |
No, no carbocation formed |
|
|
What happens in an E1 reaction? |
Alkenes are formed, sp2 hybridized carbons. Alkenes have shorter bond lengths than sp3 carbons. No stereoisomers. Works best with 2° and 3° carbons |
|
|
What solvents are used in an E1 reaction? |
Strong acids, heat R-OH and H2SO4 |
|
|
What is the nomenclature for an alkene with higher ranked groups on the same side? |
Z |
|
|
What is the nomenclature for an alkene with higher ranked groups on opposite sides? |
E |
|
|
What happens during an E2 reaction? |
Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides An alkyl halide becomes an alkene |
|
|
What are the starting materials and solvants used in an E2 reaction? |
Alkyl halides carried out in a strong base. Works best with 2° and 3° carbons. Can work with 1° if (CH3)3OK is used. |
|
|
Why is regioselectivity and stereoselectivity important in E2 reactions? |
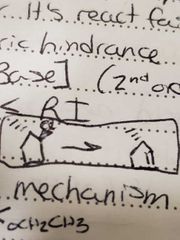
To react, axial halides and anti hydrogen's react faster, because of less steric hindrence. Products favor trans and more substituted. |
|
|
What is the rate of an E2 reaction? |
Second order Rate = k[Alkylhalide][Base] |
|
|
What types of products are created in E1 and E2 reactions? |
Zaitev products |
|
|
What happens in a Markovnikov Addition reaction? |
A cation is formed in breaking the double bond of an alkene. |
|
|
In a Markovnikov reaction, where does the nucleophile attack? |
The more substituted carbon |
|
|
What is used to catalyze the hydration of alkenes? |
Strong acid, H2SO4 |
|
|
What reactants and solvents are used in the electrophilic addition of HX to alkenes? |
A strong acid (HBr, HCl) and acetic acid |
|
|
What are the reactants and catalysts in ether synthesis? |
An alkene, HxCxOH, and H2SO4 as the catalyst. |
|
|
What solvents are used in oxymercuration and demercuration? |
Hg(OAc)2, THF-H2O NaBH4, OH- |
|
|
What happens in an oxymercuration/demercuration reaction? |
A mercury cation intermediate is formed, and there is Markovnikov Addition of H and OH across a double bond. |
|
|
How are alkenes named? |
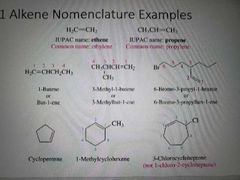
|
|
|
Stability of alkenes |
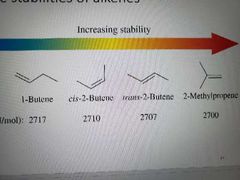
Energy difference gets bigger between trans and cis the larger the group attached. Trans more stable. For cycloalkenes: small and medium rings are more stable as cis, reduced steric strain |
|
|
What is the temperature of a dehydrohalogenation reaction? |
Very high |
|
|
"The most branched alkene will form" |
Zaitsev's Rule |
|
|
Has to do with which product is easier to make. Is related to either energetic pathway or stability of product. 'Preference' to product made. |
Stereoselection |
|
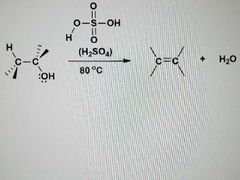
What is this reaction? |
E1: Dehydration of alcohols |
|
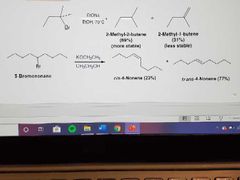
What reactions are these? |
E2: Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides |
|
|
What do stereoelectronic effects have to do with the E2 reaction? |
Axial halides and anti halogens react faster |
|
|
What reaction do 2° alkyl halides go through with a strong base? |
Elimination: E2 |
|
|
1° alkyl halides only go through substitution unless: |
A bulky base, KOC(CH3)3, is used |
|
|
What type of reaction do 2° alkyl halides go through with weakly basic nucleophiles? |
Substitution, SN1 |
|
|
What type of reactions do 3° alkyl halides go through with strong bases? |
E2 |
|
|
What type of reactions do 3° alkyl halides go through in the absence of anionic nucleophiles? |
SN1/E1 |
|
|
Rate of reaction for electrophilic addition of HX to alkenes |

|
|
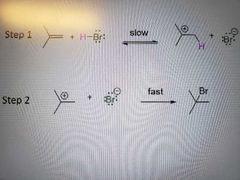
What mechanism is this? |
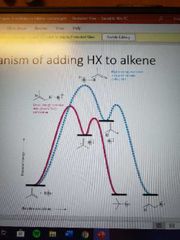
Electrophilic addition of HX to alkenes |
|
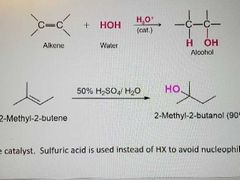
What kind of reaction is this? |
Acid catalyzed hydration of alkenes |
|

What mechanism is this? |
Acid catalyzed hydration of alkenes |
|
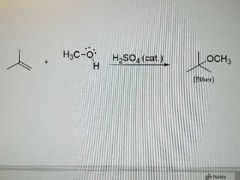
What reaction is this? |
Acid catalyzed ether synthesis from alkenes |
|
|
A system at equilibrium adjusts so as to minimize any stress applied to it |
Le Châtelier's |
|
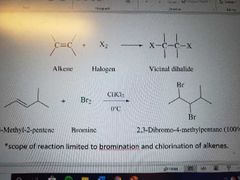
What rection is this? |
Halogenation of alkenes to form vicinal dihalides. Stereospecific reaction, anti addition. Only works with bromine and chlorine |
|
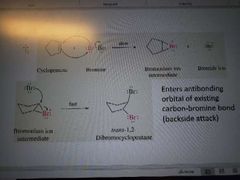
What mechanism is this? |
Halogenation of alkenes to form vicinal dihalides |
|
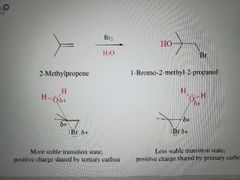
What reaction is shown here? |
Halogenation of alkenes in the presence of water to make vicinal halohydrins with OH on the Markovnikov position |
|
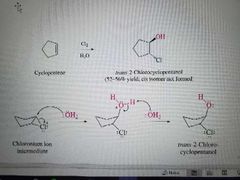
What mechanism is shown? |
Halogenation of alkenes in the presence of water |
|
|
What products are made in the halogenation of alkenes reaction? |
Trans with the second group on the backside and the enantiomer. |
|
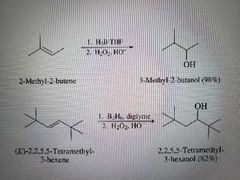
What reaction is shown here? |
Hydroboration oxidation |
|
|
What kind of reaction is hydroboration oxidation? |
Anti Markovnikov |
|
|
What reactants and solvents are used in a hydroboration oxidation reaction? |
An alkene, a strong base (OH-), H2O2, and a compound with B and H. |
|
|
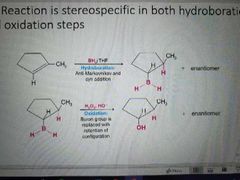
Hydroboration oxidation mechanism |
|
|
|
What is the stereospecific product in hydroboration oxidation? |
Syn |
|
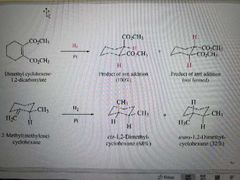
What reactions are shown here? |
Hydrogenation of alkenes with the same substituent ( in this case H2) |
|
|
Based on starting materials, which product will be made |
Stereoselection |
|
|
What compound would have the highest heat of hydrogenation? |
The least stable |
|
|
What products are made in a hydrogenation reaction? |
The syn product and enantiomer if chirality centers are made
|
|
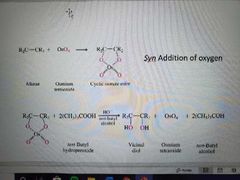
What reaction is shown here? |
Preparation of vicinal diols by OsO4 dihydroxylation |
|
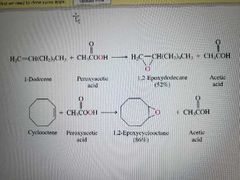
What reactions are shown here? |
Alkene epoxidation. Enantiomers are made |
|
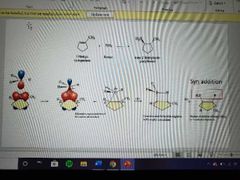
What mechanism is this? |
Hydroboration |
|
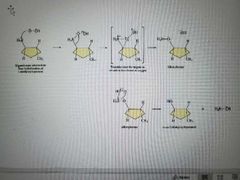
What mechanism is this? |
Oxidation |
|
|
What reactant is needed in a hydrogenation reaction? |
A metal, Pt, Pd, Ni, or Rh |
|
|
What products are favored in an E2 reaction? |
Trans and more substituted |
|
|
What reactants and catalysts are used in the preparation of vicinal diols by OsO4 dihydroxylation? |
(CH3)3COOH, OsO4 (cat), tertbutanol, -OH |
|
|
Are intermediates formed in the SN2 and E2 reactions? |
No, no rearrangement possible. Called a concerted reaction |
|
|
What are the best nucleophiles? |
Iodides and sulfides. Sulfides the best because they are conjugate bases of strong acids. |
|
|
What way to retrosynthesis arrows face? |
Towards starting materials |
|
|
Memorize |
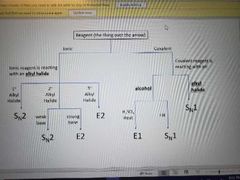
|
|
|
What reagents are used in an ozonolysis of alkene reaction? |
Ozone (O3) and H20 or Me2S |
|
|
What happens when H2O is a reagents in the ozonolysis reaction? |
Oxidative conditions, carboxylic acid formed |
|
|
What reagents are used in the Simmons-Smith (or cyclopropanation) reaction? |
CH2I2 and ZnCu and diethyl ether |
|
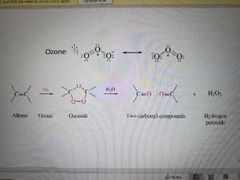
What reaction is shown? |
Ozonolysis of alkenes |
|
|
What happens when zinc is a reagent in ozonolysis? |
The second step is reductive, an aldehyde and formaldehyde are made |
|
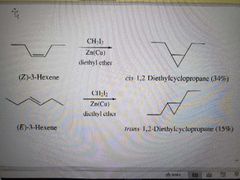
What reaction is shown? |
Simmons-Smith Reaction |
|
|
What products are made in a Simmons-Simon Reaction? |
Carbenoid, syn addition |
|
|
What are the properties of alkynes? |
Pretty acidic Linear, short bond lengths Low water solubility Similar bpts to alkanes |
|
|
What happens to alkynes in the presence of water and amide ions? |
They can be protonated. This is useful in making long chains through the SN2 mechanism. |
|
|
What happens in reactions with alkynes and secondary or tertiary carbons? |
E2 |
|
|
Mechanism of E2 using alkynes |
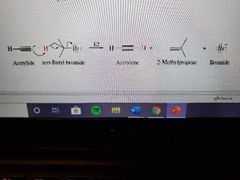
|
|
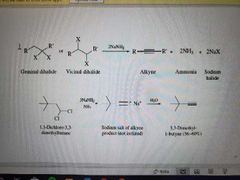
What reaction is shown? |
Formation of alkynes via elimination |
|
|
What reagents are used in the formation of alkynes via elimination? |
NaNH2, NH3, H2O |
|
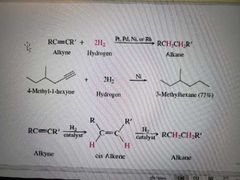
What reaction is shown below? |
Hydrogenation of alkynes |
|
|
What reagents create alkenes from alkynes during hydrogenation? |
H2 and Lindlar Pd |
|
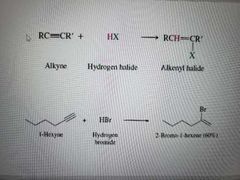
What reaction is shown? |
Addition of hydrogen halides to alkynes. Reaction can occur again to make a alkane with geminal dihalides. |
|
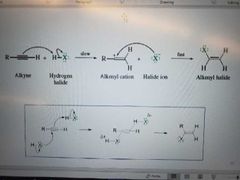
What mechanism is shown? |
Addition of hydrogen halide to alkyne. Markovnikov reaction |
|
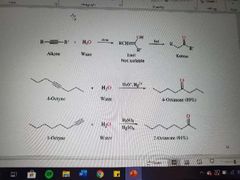
What reaction is shown here? |
Hydration of alkynes |
|
|
What products are created in the hydration of alkynes? |
Ketones |
|
|
What reagents are used in the hydration of alkynes when ketones are formed? |
Water, acid, and mercury |
|
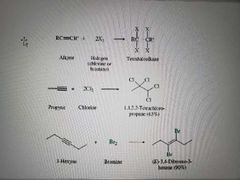
What reaction is shown? |
Addition of dihalogen to alkynes. Markovnikov reaction |
|
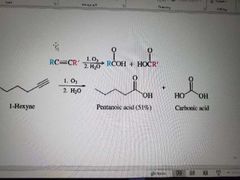
What reaction is shown here? |
Ozonolysis of alkynes. Ketones also made during demercuration. |
|
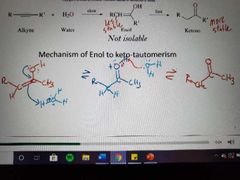
|
Memorize |
|
|
Stability of alkyl radicals |
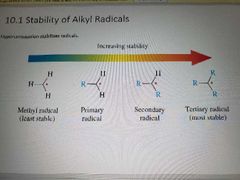
|
|
|
How are radicals formed? |
Homolytic cleavage (homolysis) |
|
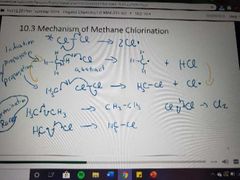
What mechanism is this? |
Methane chlorination |
|
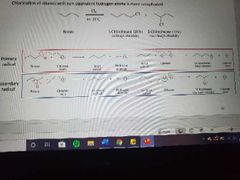
What mechanism is shown? |
Halogenation of higher alkanes |
|
|
What happens in a free radical HX addition to alkenes and alkynes with and without peroxides? |
No peroxides, X adds in the Markovnikov position. With peroxides, X adds to anti Markovnikov position |
|
|
Mechanism of free radical addition of HX to alkenes and alkynes with peroxides |
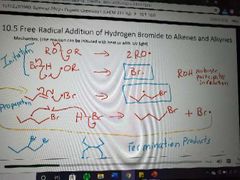
|
|
|
What product is made when an alkyne reacts with HX in free radical addition? |
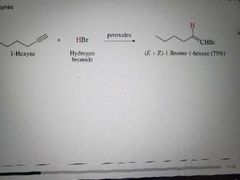
|
|
|
What reagents are used to hydrogenate alkynes using free radicals? |
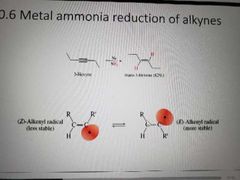
Na, NH3. Metal ammonia reduction |
|
|
Mechanism for Na-ammonia reduction |
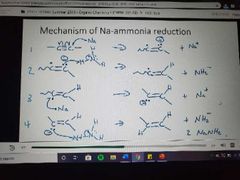
|
|
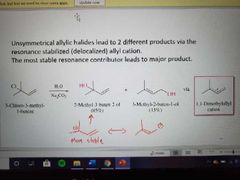
What reaction is shown here? |
SN1 of allylic halides |
|
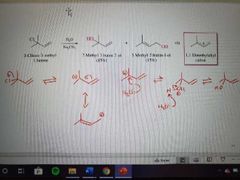
What mechanism is this? |
SN1 of allylic halides |
|
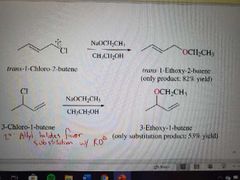
What reaction is shown here? |
SN2 of allylic halides |
|
|
What reagents are used in an SN1 of allylic halides reaction? |
H2O and Na2CO3, or alcohol for ether synthesis |
|
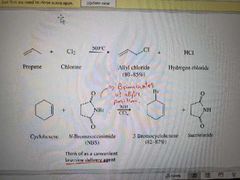
What reaction is shown here? |
Allylic free radical halogenation |
|
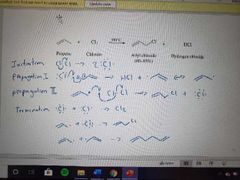
What mechanism is shown here? |
Allylic free radical halogenation mechanism |
|
|
What is the stability of dienes? |
Conjugated > isolated > cumulated |
|
|
How are sigma bonds affected my pi bonds? |
They become shorter |
|
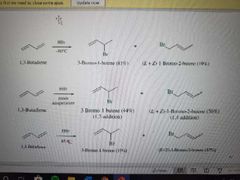
What reaction is shown here? |
Addition of HX to conjugated dienes. If cold temps, no rearrangements occur |
|
What reaction is shown? |
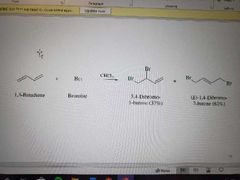
Halogen addition to conjugated dienes. Leads to mixture but 1,4 dominating |
|
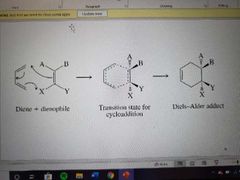
What reaction is shown? |
The Diels-Alder reaction |
|
|
How is the Diels-Alder reaction both stereospecific and stereoselecive? |
If a trans groups on the dienophile, groups off cyclohexane have opposite stereochemistry. If cis groups on the dienophile, same stereochemistry and Endo preferred. |
|
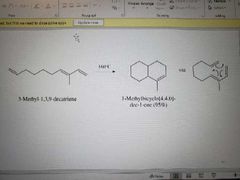
What reaction is shown here? |
Intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction |
|
|
The Cope and Claisen Rearrangement |
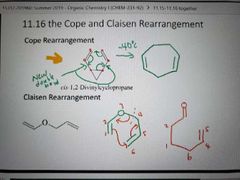
|

