![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Weak activators and their direction |
Alkyl groups; o/p (Methyl, ethyl, i-propyl, t-butyl) |
|
|
Moderate activators and their direction |
Carbonyl groups (esters, 2° and 3° amides ATTACHED BETA to carbonyl) Ethers All o/p |
|
|
Strong activators and their direction |
Alcohols Alkoxides Amines (1°,2°,3°) All o/p |
|
|
Weak deactivators and direction |
Halides, o/p |
|
|
Moderate deactivators and directions |
All carbonyl groups (carbonyl is BENZYLIC) Sulfonic acid, SO3H Cyanide All meta |
|
|
Strong deactivators and their direction |
Nitro groups Quaternary ammonium group (N+) Alkyl trihalides All meta |
|
|
What are two limitations of EAS reactions on substituted rings? |
1. Nitration cannot be done on a ring with an amino group already present 2. Friedel-Crafts reactions don't work if a ring or moderately / strongly deactivated 2. Friedel-Crafts reactions don't work if a ring or moderately / strongly deactivated |
|
|
What are 3 considerations for EAS reactions on a substituted ring? |
1. For monosubbed rings, the para product tends to dominate (sterics) 2. For 1,4 rings, substitution will occur at the less sterically hindered site (if more than one site is favored by directing effects) 3. For 1,3 rings, substitution generally doesn't occur between the existing subs |
|
|
What are 3 requirements for NAS to occur? |
1. A strong e- withdrawing group must be present (ring must be e- poor) 2. Ring must have a good LG 3. The LG must be ortho or para to the withdrawing group |
|
|
What nucleophiles require acidic conditions? |
Those attacking carbonyls - form negative alkoxide intermediates which are protonated during acidic workup |
|
|
Protonation of a carbonyl makes it a better ________ |
Electrophile |
|
|
Under acidic conditions, mechanisms will only be reasonable if they avoid the formation of _______ |
Strong bases |
|
|
Under basic conditions, mechanisms will only be reasonable if they avoid the formation of _______ |
Strong acids |
|
|
Under acidic conditions, reagents should either be _______ or have a _______ |
Neutral or +1 formal charge |
|
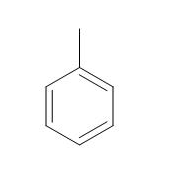
|
Toluene |
|
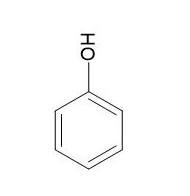
|
Phenol |
|
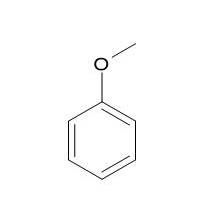
|
Anisole |
|
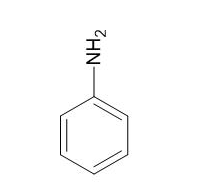
|
Aniline |
|
|
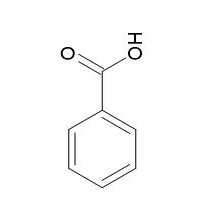
Benzoic acid |
|
|
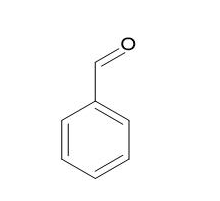
Benzaldehyde |
|
|
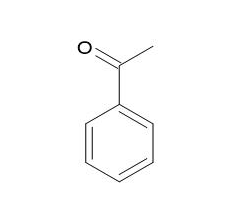
Acetophenone |
|
|
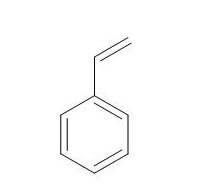
Styrene |
|
|
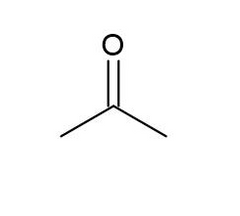
Acetone |
|
|
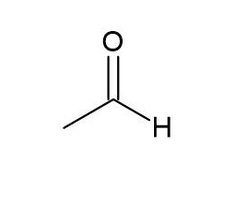
Acetaldehyde |
|
|
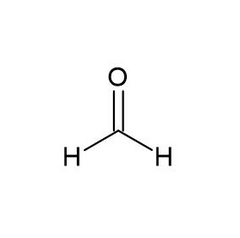
Formaldehyde |
|
|
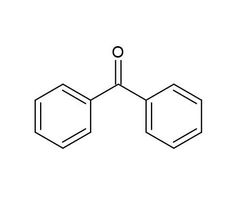
Benzophenone |
|
|
Reagents to reduce a benzylic ketone to an alkane (leaving the benzene) |
Zn(Hg), HCl, heat |
|
|
Reagents to reduce NO2 to NH2 |
1. Zn, HCl 2. NaOH |

