![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Optically Active |
At least 1 carbon connected to 4 groups, and no plane of symmetry. |
|
|
Enantiomer |
Mirror images that are not super-imposed |
|
|
Diastereomers |
Non super-imposable non mirror images |
|
|
Meso compound |
Super-imposable mirror image |
|
|
Regioselective reaction |
Out of 2 constitutional isomers, only 1 is observed, or 1 is formed in higher ratio compared to the other. |
|
|
Markovnikov Rule |
In H-X reaction, H attaches to carbon with most hydrogens. - Most stable carbocation intermediate |
|
|
Carbocation stability |
More substituted carbocations (least amount of hydrogens attached) is most stable |
|
|
Hyperconjunction |
Interaction between vacant p orbital on C+ and a filled sp3 hybrid on an adjacent carbon - Stabilizing interaction |
|
|
Inductive effects |
Alkyl groups can donate electron density towards C+, stabilizing the positive charge. |
|
|
When will a carbocation not rearrange? |
It will not rearrange if the product is less stable |
|
|
Halogenation |
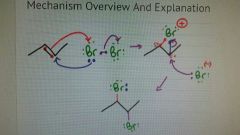
When an alkene reacts with a diatomic halogen. - halogen goes on either side of the pi bond in an anti config (one up, one down) |
|
|
Halohydrin |
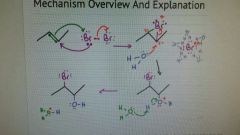
Same as halogenation, but H2O is the attacking nucleophile. Therefore one halogen is replaced with an OH molecule which goes on the carbon with less hydrogen. |
|
|
Industrial hydration |

Addition of water to form alcohol. |
|
|
Alcohol addition to alkene |

Same as industrial hydration but with an alcohol except for water. Alcohol goes on carbon w/ least hydrogens. |
|
|
Oxymercuration |

Addition of an acid (minus 1 H) and H on either side of pi bond. The acid adds to carbon with less amount of hydrogen. |
|
|
Hydroboration (Anti-Markovnikov) |
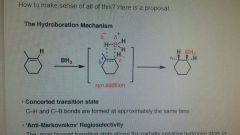
Addition of BH2 to carbon w/ most hydrogen, and hydrogen to other carbon (anti-markovnikov) which results in a transition state sterically and electronically more favourable. Both will be same side (syn addition). |
|
|
Hydrogenation (reduction) |
Addition of H2. Hydrogen attaches to each carbon connected to the pi bond. Will be syn reaction, same face. |
|
|
Stability of Alkenes |

- The more carbon groups connected to carbon double bond = more stable. - This is the smallest heat of hydrogenation. |
|
|
Stability of substituted alkenes |
- The less hydrogen on the alkene, the more stable. - Trans substituents are most stable, then cis, and when 2 substituents are on the same carbon, it is the least stable. |
|
|
Alkene Epoxidation |

Reacts in non-polar solvent. Both carbons connect with one O. Single step. |
|
|
Ozonylsis |

Break every double bond in half and replace each end with oxygen. |
|
|
Planar carbocation |
A carbocation with an sp2 hybridization. It can be attacked by either side and forms a racemic mixture. |
|
|
Stereoselective reaction |
Out of 2 stereoisomers, only 1 is formed or 1 has a higher ratio |
|
|
Racemic mixture |
When 2 stereoisomers are formed in equal amounts. It must have a chiral centre and not be symmetrical. If it does have symmetry, it will be meso. |

