![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
How do chemical bonds move according to IR spectroscopy? And how are they detected? |
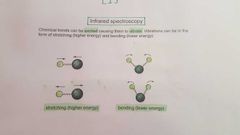
Only vibrations producing a change in dipole moment are observed i.e. 'large' electronegativity differences. |
|
|
|
How can frequency of an IR spectrum be calculated? |

|

|
|
|
What are the two main regions on an IR spectrum and what are they called? |

|
|
|
|
How does 'OH' stretch and 'NH' appear in an IR spectrum? |
They have a very large due to hydrogen bonding. The peaks for both normally occur at 3500 cm^-1 because of hydrogen bonding. A monomeric hydroxyl has a sharper peak at 3600 cm^-1 and NH2 can give two separate peaks. |
|
|
|
What are the general rules of IR? |

|
|
|
|
What happens at the 3300-2700 region in an IR spectrum? |

|
|
|
|
What happens at the 2500-1900 region in an IR spectrum? |

|
|
|
|
What happens at the 1900-1500 region in an IR spectrum? |

|

|
|
|
What are the different types of C=O and what properties do they have in an IR spectrum? |
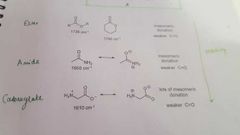
|
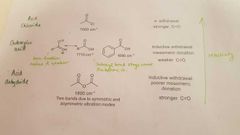
|
|
|
How does ring strain relate to IR? |

|
|
|
|
What is the basic schematic of mass spectrometers? |

|
|
|
|
What are the two types of mass analysers? |

|

|
|
|
How does ion detection work for MS? |
It amplifies signals and only detects charged species. |
|
|
|
What are the different ionisation methods for MS? |

|
|
|
|
How does 'electron impact (EI)' work? |

EI causes fragmentation to stable cationic daughter peaks. |
|
|
|
How does 'chemical ionisation (CI)' work? |

|
|
|
|
How does 'electrospray ionisation (ESI)' work? |

|
|
|
|
How does 'MALDI ionisation' work? |

|
|
|
|
How are the methods of organic structure determination used to ID unknown compounds? |

|

|
|
|
How can isotopic data be identified from MS? |

|

|
|
|
What is the theory behind NMR? |

|

|
|
|
How can resonance frequency be observed? |

|
|
|
|
How would an NMR experiment be carried out? |
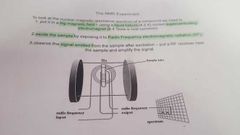
|
|
|
|
How is the resonance frequency calculated? |

|
|
|
|
How can we identify which nuclei are NMR active? |

|
|
|
|
How does the fourier transform NMR experiment work? |
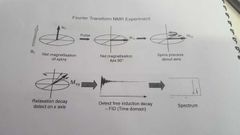
|
|
|
|
What does a NMR spectrum look like? |

|
|
|
|
What are the practical considerations of NMR? |

|
|
|
|
How does chemical shift work in NMR? |

|

|
|
|
How are the integrals calculated in a NMR spectrum? |

|
|
|
|
What are the general trends for chemical shift in NMR? |

|
|
|
|
Apply knowledge of NMR to carbonyl groups. |

|
|
|
|
How do anisotropic effects work in NMR? |

|

|
|
|
How do anisotropic effects occur in aromatic compounds? |

|
|
|
|
What are the effects of proton change? |

|

|
|

|

|
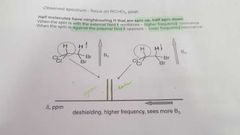
|
|
|
Give some coupling terminology. |

|
|
|
|
What are the sizes of coupling dependent on? |
• Number of bonds • Angles between the bonds • Substituents on the coupling path |
|
|
|
What do 2 bond coupling and 3 bond coupling look like? |

|
|
|
|
How much distance is allowed for coupling to occur? |
Anything 20 H2 or under |
|
|
|
How is angular dependence on coupling calculated? |
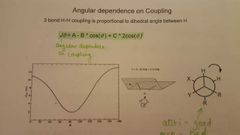
|
|
|
|
How can the configuration of cyclohexanes be determined using coupling rules? |

|
|
|
|
Explain how 3 bond coupling can be used to differentiate between alkenyls. |

|
|
|
|
How are the number of lines for couplings determined? |

|
|
|
|
How do coupling patterns look like? |

|

|
|
|
What are the typical patterns for 2 couplings? |

|
|
|
|
What are the typical patterns for 3 couplings? |
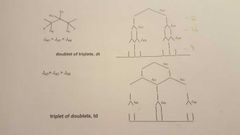
|

|
|
|
What are the two criteria that prevent H from coupling? |

|
|
|

How would the proton nmr spectra look liked for these? |
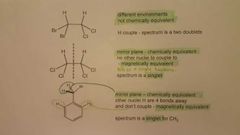
|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|

|
|
|
How can first and second order spectra be determined? |

|

|
|
|
How can chemical equivalence state the relation between two molecules with regards to chiral centres? |

|
|
|

|
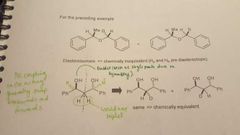
|
|
|
|
What issues are associated with 13C NMR and what could be done to resolve these issues? |

|
|
|

The schematic in this diagram is similiar to proton NMR, what makes carbon NMR different? |

|

|
|
|
What happens to carbon NMR when H-C coupling occurs? |

|
|
|
|
How can coupling be removed in carbon NMR? |

|
|
|
|
What are the general features of carbon NMR? |

|
|
|
|
What structures are anomalies in carbon NMR? |
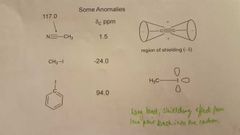
|
|
|
|
How are the numbers of spins determined in carbon NMR? |
2 x I + 1 where I is spin quantum number |
|
|
|
What is the DEPT experiment in 1D carbon NMR? |

|
|
|
|
How should organic structure determination occur? |

|
|
|
|
Explain the difference between the 1D experiment and the 2D experiment? |

|
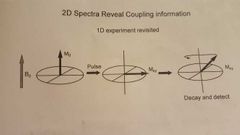
|
|

|
. |
|
|
|
What are the different 2D experiments? |
• 1H-1H COSY • HMQC • HMBC |
|
|
|
Explain how 1H-1H COSY works. |

|
|
|
|
Explain how HMQC works. |

|
|
|
|
Explain how HMBC works. |

|
|

