![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 6 groups compounds can be classified into?
|
1. acids (formulas begin with H- except for some organic acids like acetic acid which are often written with the H- at the end, as in CH3COOH)
2. bases (formulas end in -OH except for ammonia and organic bases which are similar to ammonia and contain nitrogen) 3. metal oxides (binary compounds of a metal and oxygen) 4. non-metal oxides (binary compounds of a non-metal and oxygen) 5. salts (compounds of metals that are NEITHER bases NOR oxides) 6. other (most compounds belong here!!!!!) |
|
|
What are some strong Acids?
|
strong" acids (which exist largely as ions in solution rather than molecules) are few in number and should be learned: HCl, HBr and HI are the only strong binary acids; ternary acids are usually strong if the number of oxygens exceeds the number of hydrogens by two or more
|
|
|
What are some strong Bases?
|
LiOH, NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, Ba(OH)2
The basicity of a species depends on the reactivity of the atom with the unshared pair of electrons this atom being the basic site for accepting the H+ . the more spread out (dispersed, delocalized) is the electron density on the basic site, the less basic the species. |
|
|
What are some common salts
|
the salts which are soluble include all of the salts of lithium, sodium, potassium and ammonium cations and of nitrate and acetate anions. All chlorides are soluble except silver, lead and mercury(I) [AP H]. All sulfates are soluble except those of calcium, lead, barium, and strontium [C PBS]. All other salts should be considered only slightly soluble unless you learn otherwise.
|
|
|
What are the 6 delocalization rules
|
1. bases of binary acids (HnX) of elements in the same group the larger the basic site X, the more spread out is the charge
2. for like charged bases of binary acids in the same period the more unshared electrons the more delocalized the electronic charge 3. the more s character in the orbital with the unshared pair of electrons more delocalized 4. extended p-p bonding between the basic site and an adjacent pi resonance delocalizes 5. Extended p-d pi bonding with a atoms that can acquire more than an octet delocalizes its charge 6. inductive effect electronegative atom transmits its electron withdrawing effect through sigma bonds and they are electron donating and will localize more electron density on the basic site |
|
|
What is the oxidation number of a monoatomic ion
|
its equal to its charge
|
|
|
in compounds the oxidation number for hydrogen is
|
1 except in metal hydrides which is -1
|
|
|
in compounds the oxidation number for oxygen is
|
-2 excepts for peroxides where it is -1
|
|
|
What is the oxidation number of alkali metals
|
+1
|
|
|
The oxidation number of alkaline earth metals is
|
+2
|
|
|
What is the oxidation number for terminal halogens
|
-1
|
|
|
Pauli Exclusion Principle
|
states that each orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons providing that their spins are paired
|
|
|
Aufbau principle
|
Aufbau in german means "building up" and this principle simply states that electrons occupy and fill the lowest energy orbital this is an atoms most stable state
|
|
|
Hunds rule
|
states that when there are two or more orbitals with the sameenergy electrons will go into different orbital rather than pair up in the same orbital
|
|
|
What is the common bonding pattern for Nitrogen (neutral)
|
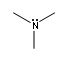
Since nitrogen has 5 val electrons will consist of 3 bonds and a lone pair
|
|
|
What is the common bonding pattern for carbon (neutral)
|
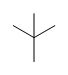
Will have four bonding pairs because carbon has four valence electrons
|
|
|
What is the common bonding pattern for carbon (negative)
|
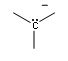
lack bonding pair instead has a lone pair
|
|
|
What is the common bonding pattern for carbon (positive)
|
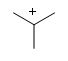
lacks a bonding pair and has a radical
|
|
|
What are the 5 general rules when drawing resonance
|
1. All the resonance structures must be valid lewis structures for the compound
2. nuclei can not be move on placement of electrons 3. number of unparied electrons must remain the same 4. major contributors are the ones with the least energy neg charges tend to go on high EN atoms 5. Resonance stabilization is most important when it serves to delocalize a charge |
|
|
Arrhenius acids and bases
|
the first scientist to classify acids and bases he proposed the idea that when acid dissolves in water it dissociates into it ions acids H+ and bases OH-
|
|
|
Bronsted Lowry Acid and bases
|
an acid donates a protone and a base acepts a proton . The strengths of the acids and bases are determined by by the extent in which they lose or gain electrons a nice rule is is acid base reactions go in the direction of forming the weaker acid and weaker base
|
|
|
Lewis Acid and bases
|
lewis acid electrophile shares an electron pair furnished by a lewis base (nuclophile) to form a covalent bond. useful in explaing the acidity of an aprotic acid like BF3 CU2+ SiF4 CO2
|
|
|
amphoteric substances
|
the word comes from greek ampho means both substances that can act either as a base or an acid depending on the conditions
|
|
|
binary acids
|
the simplest acids composed of only two elements when naming them the ending of the second atom (the non metal) js changes to an 'ic' and the prefix hydro is used
|
|
|
what are some of the strong acids
|
HCl
H2SO4 HNO3 HClO4 HBr HI |
|
|
What are the structural effects on acidity
|
a more electronegative element bears a negative charge more easily, giving a more stable conjugate base and a stronger acid
C<N<O<F stability CH3<NH2<OH<F Size negative charge of an anion is more stable if it spread over a larger region of space |
|
|
A nucleophile
|
donates electrons
|
|
|
an electrophile
|
accepts electrons
|
|
|
acidic protons
|
may serve as electron acceptors
|
|
|
Name the element that corresponds to the electron configuration 1s2 2 s2 2 p2
|
carbon
|
|
|
Name the element that corresponds to the electron configuration
1s2 2s2 2p4 |
oxygen
|
|
|
Name the element that corresponds to the electron configuration 1s2 2 s2 2 p2
|
carbon
|
|
|
Name the element that corresponds to the electron configuration
1s2 2s2 2p4 |
oxygen
|
|
|
There is a small portion of the periodic table that you must know to do organic chemistry, make a list of the elements in the first two rows of the periodic table
|
H, He
Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F, Ne P, S, Cl Br I |
|
|
Explain the relative energies when two hydrogen 1s orbitals overlap
|
when the two 1 s are in phase the result is a molecular orbital is a sigma bonding with a lower energy than the 1 s atomic orbital then out of phase form an antibonding orbital with an higher energy that that of 1 s
|
|
|
Explain the bonding of a Cl2 molecule
|
p and p overlap constructive overlap forms a sigma bonds
|
|
|
a pi bond
|
results from overlap between two p orbitals oriented perpendicular to the line connecting the nuclei
|
|
|
a double bond
|
requires the presence of four electrons in the bonding region the first is a strong sigma bond the other goes into a pi bond MO with its electron density centered above and below the sigma bond
|
|
|
sp Hybrid Orbitals
|
a pair of directional sp hybrid orbitals results from two orbitals s and p to enhance electron density in the bonding region to form sigma bonds this results in a linear bond with a bond angle of 180
|
|
|
sp2 Hybrid Orbitals
|
to orient three bonds as far apart as possible 120 is required when 1 s and two p orbitals the resulting three hybrid orbitals oreinted at 120 angles to each other they are called sp2 hybrid trigonal geometry, the remaining p orbital is perpendicular to the plane of the three hybrid orbitals
|
|
|
sp3 Hybrid orbitals
|
by combining one s orbital and three p orbitals 4 orbitals are called sp3 hybrid orbitals with angles of 109.5 and a tetrahedral geometry
|
|
|
Constitutional isomers
|
isomers that differ in their bonding sequence atoms are connected differently
|
|
|
Stereoisomers
|
differ only how thier atoms are oriented in space
|
|
|
Dipole- Dipole Forces
|
polar bonds have a positve end and a negative end the most stable is when the positve end is close to the negative end of another molecule generally attractive this attraction must be overcome when a liquid vaporizes resulting in larger heats of vaporization and higer boiling points for strongly polar compunds
|
|
|
The London dispersion force
|
non polar molecules can be decribed as a temporary dipole dur to electrons be displaced slightly symmetrical arrangement this attraction depends on surface area
|
|
|
Hydrogen bonding
|
is not a true bond but a strong attractive dipole to dipole interaction can occur when a hydrogen atom is bonded to oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine
|
|
|
How many possible structural isomers can Butane have and what are the names ?
|
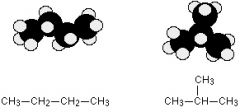
only two are possible
n- butane isobutane |
|
|
How many possible structural isomers is there for pentane and what are the names?
|
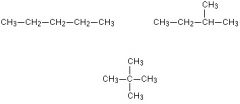
3 possible
names n- pentane iso pentane neo pentane |
|
|
How many structural isomers does hexane have
|
5 possibilities
|
|
|
What is a constitutional isomer
|
isomers whose atoms are connected differently, they differ in their bonding sequence
|
|
|
What are the conformations of cyclohexane
|
Chair, half chair, boat, twisted boat
|
|
|
define stereoisomerism
|
In stereoisomerism, the atoms making up the isomers are joined up in the same order, but still manage to have a different spatial arrangement. Geometric isomerism is one form of stereoisomerism
|
|
|
Chair conformation
|
the most stable conformation for cyclohexane with both parts puckered upward and the other downward
|
|
|
boat conformation
|
the less stable puckered conformation most stable boat structure is the twisted boat
|
|
|
half chair
|
the unstable conformation half way bettwen a chair and boat configuration
|
|
|
What is the structure of isobutyl
|
...
|
|
|
What is the structure for sec-butyl
|
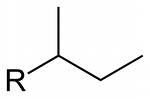
|
|
|
What is the structure of tert-butyl
|
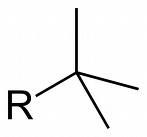
|
|
|
what is the structure of isopentyl
|
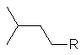
|
|
|
Structure for neopentyl
|
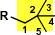
|
|
|
When giving IUPAC names for cycloalkanes what is the rule for naming functional groups that are long alkane chains?
|
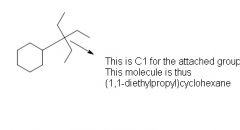
Name functional group seperately
The Carbon that is directly attached to the cycloalkane is carbon #1 and name the rest with the same rules |
|
|
Alkanes C1-C4 is at what phase and STP
|
methane ethane propane and butane are gases at room temperature but propane and butane can be liquified easily under modest pressure
|
|
|
Alkanes C5- C8 is at what phase at STP
|
free flowing volatile liquids isomers of pentane hexane and octane are the primary constituents of gasoline
|
|
|
Alkanes C9- C-16
|
higher boiling points usually viscous kerosene, jetfuel and diesal fuel
C16 and up are called sometimes mineral oils |
|
|
What are some general rules when discussing the boiling points of alkanes
|
High BP -higher molecular weights
linear molecules boil higher than branched molecules higher intermolecular forces will have higher boiling points |
|
|
What are the 8 different five carbon alkyl groups
|
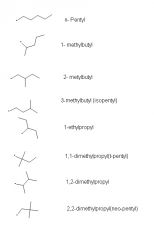
|
|
|
Explain the initiation step in the free radical chain reaction
|
Radicals are formed: Light supplies the energy to split a Cl, Br
|
|
|
Explain the propagation step in the free radical chain reaction
|
A radical reacts to form another radical
|
|
|
Explain why free radical halogenation usually gives mixtures of products
|
free radical halogenation substitutes a halogen atom for a hydrogen. only if a molecule has only one type of hydrogen, substitution of the first of these hydrogens form a new compound for ex. chloronation of methane can produce CH3Cl, CH2Cl2 CHCl3 and CCl4
|
|
|
Name 3 mechanism that can account for a termination step
|
radicals combine with other radicals ...
reactions of radicals withthe vessels or other contaminants when the concentration of radicals are low usually towards the end of the reaction |
|
|
explain the problem solving hint to be sure if a reaction is a valid free radical chain reaction
|
initiation steps usually creates new radicals
propagation steps usually combine a free radical and a reactant to give a product and another free radical termination steps generally decrease the number of free radicals |
|
|
Enantiomers
|
mirror image isomer; pair of compounds that are nonsuperimposable mirror images
|
|
|
Asymmetric carbon atom or chiral carbon atom
|
is a carbon that is bounded to four different groups
|
|
|
A stereo center
|
any atom at with the interchange of two groups gives a stereoisomer
|
|
|
How can you tell whether or not a molecule is Chiral or Achiral?
|
Generally speaking the ultimate test is whether or not its mirror image is the same or different
1. If a compound has no asymmetric carbon it is usually achiral 2. If a compound has just one asymmetric carbon atom, it is chiral 3. If a compound has more than one asymmetric carbon it may or may not be chiral |
|
|
Cahn- Ingold- Prelog convention
|
when a carbon atom is assigned a letter based on its three dimensional configuration
Rules 1. Assign a priority to each group bonded to the asymmetric Carbon. Atoms with higher atomic numbers receive higher priorities I>Br>Cl>S>F>O>N>C-13>C-12>Li>H-3>H-2>H-1 2. In case of ties, use the next atoms along the chain of each group as tiebreakers 3. Treat double and triple bonds as if each were to a separate atom 4. Using a three- dimensional drawing or a model, put the fourth priority group in back and view the molecule along the bond from the asymmetric Carbon to the fourth priority group draw an arrow from the first priority group through the second to the third if the arrow points counterclockwise it is called S if clockwise R |
|
|
Dextrorotatory
|
rotate planes of polarized light toward the right or clockwise
|
|
|
Levorotatory
|
rotate planes of polarized light toward the left of counterclockwise
|
|
|
specific rotation (Sigma)
|
Sigma (observed)/ (c*l)
c= concentration in grams per mL l= length of sample cell (path length) in decimeters (dm) |
|
|
Racemic mixture
|
a solution with equal amounts of two enantiomers so that the mixture is optically inactive
|
|
|
Optical purity
|
is defined as the ratio of a mixture of its rotation to the rotation of a pure enantiomer
O.P= Observed rotation/ Rotation of pure enantion X 100% |
|
|
Diasteromers
|
are stereoisomers that are not mirror images
|
|
|
Meso compund
|
a achiral compound that has chirality
|

