![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
130 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
System for nomenclature of ethers |
list two alkane groups in alphabetical order and add ether to end |
|
|
Oxane |

|
|
|
oxirane |

|
|
|
oxitane |

|
|
|
oxolane |

|
|
|
thiirane |

|
|
|
diglyme |

|
|
|
What is a special characteristic of cyclo ethers? |
Under extreme ring strain |
|
|
What is a characteristic of the boiling points of ethers? |
They have low boiling points similar to alkanes |
|
|
What is the solubility of an ether in water? |
Highly soluble due to oxygen being able to bond a hydrogen from the water molecule |
|
|
What characteristics allow ethers to bond with metals and become complexes? |
-The polar carbon-oxygen bond -Lone electrons |
|
|
Draw 12-crown-4 molecule |

|
|
|
Draw 18-crown-6 molecule |

|
|
|
What is the first number in a crown molecule? Second? |
1. Number of atoms in ring 2. Number of oxygens in ring |
|
|
Draw a methoxy group |
O-CH3 |
|
|
What are crown molecules used for? |
The isolation of cations from difficult to extract compounds such as sodium from KOH |
|
|
Host-guest chemistry |
-Crown molecules are an example -Help us understand biological processes |
|
|
What is special about the structure of crown molecules? |
The diameter of the interior of the molecule exactly matches a specific ion |
|
|
REACTION: Acid catalyzed ether preperation |

|
|
|
Williamson ether synthesis |
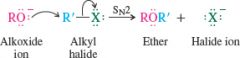
Works best with methyl and primary alkyl halides
-Does not work with secondary and tertiary alkyl halides |
|
|
Why are ethers good solvents? |
-Very unreactive -Dissolves nonpolar substances |
|
|
REACTION: Acid catalyzed cleavage of ethers |
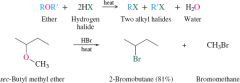
Produces 2 Alkyl halides -SN2 |
|
|
REACTION: Epoxidation of Alkenes |
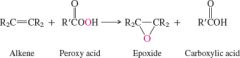
-Stereospecific -Syn addition -Produces enantiomers |
|
|
REACTION: Sharpless epoxidation |
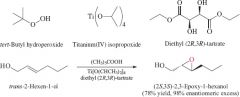
-Allylic alcohols to epoxides -Enantioselective -R,R yields S,S vice versa -Syn addition |
|
|
What compound is used to protect OH? |
Tertbutyl group |
|
|
REACTION: Vicinal halohydrins |
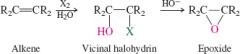
-Cis yields cis |
|
|
REACTION: Nucleophile + Epoxide |
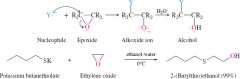
-Similar to grignard reaction with epoxides |
|
|
REACTION: Nucleophile + Epoxide Ring Opening Special Characteristc |
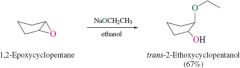
-Inversion at carbon attacked by nucleophile -Nucleophile attacks less substituted carbon |
|
|
REACTION: Acid catalyzed epoxide ring opening |
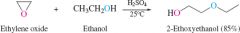
-Reaction occurs at more substituted carbon |
|
|
REACTION: Preparation of Sulfides |

|
|
|
Oxidation of sulfides |

|
|
|
REACTION: Oxidation of Sulfide to Sulfoxide |

NaIO4 best reagent to use because it doesnt oxidize all the way to sulfone |
|
|
REACTION: Oxidation of Sulfide to Sulfones |

-1 equivalent gives sulfoxide -2 equivalents gives sulfone |
|
|
REACTION: Production of sulfonium salts |
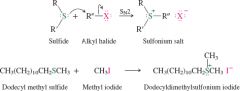
- Sulfur is more nucleophilic than oxygen causing it to react better with alkyl halides |
|
|
What will be produced from a Williamson reaction with secondary or tertiary halide? |
An alkene + an alcohol |
|
|
Partial mechanism of halohydrin involving alcohol and primary alkyl halide. |

|
|
|
How should you draw epoxides when drawing molecules? |
With the filled or dashed lines so you know that both bonds are cis |
|
|
Reactions of sulfides stereochemistry is... |
inversed |
|
|
Carbonyl group resonance structures |

|
|
|
What do more substituents do to carbonyl group? |
Increase stability |
|
|
REACTION: Ozonolysis of Alkene |
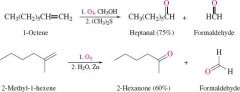
-Alkene produces aldehyde or ketone -Must be in a reducing agent |
|
|
REACTION: Hydration of Alkynes |
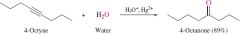
-Follows M's rule -produces Ketone |
|
|
REACTION: Friedel Craft Acylation |
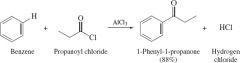
-No rearrangement -Electriophilic aromatic substitution |
|
|
Draw an acyl group |

|
|
|
REACTION: Oxidation of alcohols |
-Occurs with primary or secondary alcohols not tertiary -PCC/PDC in CH2I2will reduce to aldehyde -Na2Cr2O7 in H2SO4, H2O will reduce to ketones |
|
|
REACTION: Aldehyde from Carboxylic Acid |
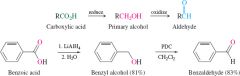
-Can only be done indirectly |
|
|
REACTION: Ketone from Aldehyde |
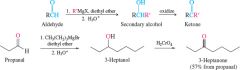
-Indirectly using Grignard reagents |
|
|
REACTION: Reduction of Ketones/Aldehydes to Hydrocarbons(1) |
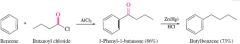
-Acylation produces ketone/aldehyde -Clemmenson reduction -REAGENT Zn(Hg) in HCl |
|
|
REACTION: Ketones/Aldehydes to Hydrocarbons(2) |

-Acylation produces ketone/aldehyde -Wolff Kischner reduction produces hydrocarbon -REAGENT H2NNH2, KOH in Triethylene glycol heated |
|
|
REACTION: Reduction of Aldehydes/Ketones to Alcohols |
-H2 with metal catalyst makes primary alcohol -NaBH4 in ethanol makes 1°or 2° -LiAlH4 in diethyl ether makes 1° or 2° (can reduce carboxylic acid) |
|
|
REACTION: Reduction of Aldehydes/Ketones to Alcohols using Grignard reagents |
Can produce 1°(formaldehyde), 2°(aldehyde), 3°(ketones) alcohols
|
|
|
REACTION: General mechanism of carbonyl nucleophilic addition |

|
|
|
What do substituents do to the reaction rate of carbonyl groups with water? |
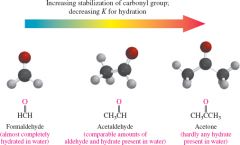
-More substituents increases stability which decreases reaction rate |
|
|
What effect do electronegative atoms have on reaction rate of carbonyl groups? |
They increase it because they destabilize the group |
|
|
What effect does the size of a molecule have on the reaction rate? |
Larger size decreases reaction rate |
|
|
What is the RDS of hydration of aldehyde/ketones in basic solution? |
The first step |
|
|
Draw the mechanism of acid catalyzed hydration of aldehyde/ketone |
Find |
|
|
Draw the mechanism of base catalyzed hydration of aldehyde/ketone |

|
|
|
What is the rate determining step of acid catalyzed hydration of ketone/aldehyde? |
The second step. |
|
|
REACTION: Formation of cyanohydrin |

|
|
|
Which compounds react most readily with hydrogen cyanide? |
The least substituted carbonyl groups. |
|
|
Cyanohydrin |

|
|
|
Hemiacetal |

|
|
|
Acetal |

|
|
|
REACTION: Carbonyl group with Alcohol |

|
|
|
In what form are ketals more stable? |
Cyclic form |
|
|
REACTION: Diols + 1,2 or 1,3 aldehydes |
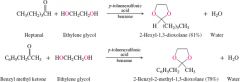
reversible |
|
|
Groups used for carbonyl protection |
Acetals and ketals |
|
|
REACTION: Protection step of carbonyl group |

-produces ketal |
|
|
REACTION: Alkylation of ketal |

|
|
|
REACTION: Removal of protecting group |

|
|
|
Hemiaminal group |

|
|
|
Imine |
R2C=NR |
|
|
aldimine |

|
|
|
Ketimine |

|
|
|
REACTION: Primary amine + aldehyde |

|
|
|
Draw primary amine + aldehyde mechanism |
See 17.5 Mechanism |
|
|
Enamine |
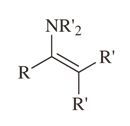
-Produced by reaction of secondary amine with aldehyde or ketone -Alkenyl substituted amine |
|
|
Draw mechanism of enamine formation |
See Mechanism 17.6 |
|
|
What are Witting reactions used for? |
-Regiospecific synthesis of alkenes from aldehydes and ketones |
|
|
Wittig reagent and its resonance |

|
|
|
Wittig intermediate and product |

|
|
|
What type of steroisomers do simple ylides yield? |
Z dominates |
|
|
What type of stereoisomers are formed when an ylide contains a strong withdrawing group? |
E dominates |
|
|
REACTION: Oxidation of aldehyde to carboxylic acid |

|
|
|
Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids |
-Count longest chain of carbons that include the carboxylic acid -Replace -e ending of alkane with -oic acid -Numbering of chain begins at the carboxylic acid |
|
|
Double bonds in main chain of carboxylic acid name |
-enoic acid |
|
|
Two carboxylic acids in a group nomenclature |
-dioic acid or dicarboxylic acid -e of alkane is retained |
|
|
Resonance structures of carboxylic acids |
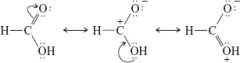
-stabilizes group -sp2 hybridization |
|
|
WHich is more electrophilic aldehyde/ketone or carboxylic acid? |
Aldehyde/Ketone |
|
|
Relative melting and boiling points of carboxylic acids. |
Relatively high compared to hydrocarbons and oxygen containing compounds due to strong intermolecular forces |
|
|
Relative acidity of carboxylic acids. |
Most acidic group that contain hydrogen, oxygen and carbons |
|
|
Average pKa of carboxylic acids |
5 |
|
|
Henderson Hasselbach equation |

|
|
|
Equation for determining relative quantities of acid or base at given pH |

|
|
|
Alkyl substituent effect on carboxylic acid acidity |
Negligible all around 5 pKa |
|
|
Alpha halogen effect on carboxylic acid acidity. |
Increase acidity, the more electronegative atoms the more acidic. pKa ranges from 3-1 |
|
|
Electron attracting groups effect on carboxylic acidity. |
Increase acidity pKa 2-4 |
|
|
WHat is the relationship between number of bonds and inductive effect? |
Inductive effect decreases as the number of sigma bonds in between carbon and other atom increases. |
|
|
Relative acidities of acetic to benzoic acid. |
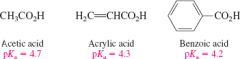
Benzoic acids are slightly more acidic than other carboxylic acids due to sp2 hybridzed carbons |
|
|
What increases with s character? |
-Electron withdrawing effects and therefore acidity increases |
|
|
When are benzoic acids the most acidic? |
When strong electron withdrawing groups are ortho. |
|
|
Are carboxylic groups hydrophilic or phobic? |
Philic |
|
|
What can carboxylic acids due to hydrophobic molecules? |
They can cause them to become more hydrophilic and dissolve in water |
|
|
Micelle definition |
A spherical aggregate of species such as carboxylate salts of fatty acids that contain a lipophilic end and a hydrophilic end. Micelles containing 50–100 carboxylate salts of fatty acids are soaps. |
|
|
In dicarboxylic acids which pK is larger? |
The first pKa because -more sites to attack -one carboxylic acid electron withdraws from the other allowing easier dissociation |
|
|
What happens to the acidity of a dicarboxylic compounds when the amounts of bonds between them increases? |
The acidity of the compound decreases |
|
|
IUPAC name of NaHCO3 |
Sodium hydrogen carbonate |
|
|
REACTION: Formation of carbonic acid and bicarbonate |

|
|
|
Which is a stronger acid bicarbonate or carboxylic acid? |
Bicarbonate is a weaker acid than carboxylic acids but a stronger acid than water and alcohols |
|
|
REACTION: Side chain oxidation of alkylbenzens |

|
|
|
General mechanism for reacting grignard reagents with CO2 |
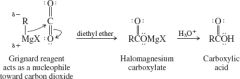
Grignard + CO2= Carboxylic acid |
|
|
REACTION: Grignard Reagent + CO2 |
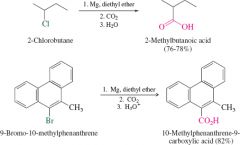
Reagent cannot have OH, NH, SH, or CO groups |
|
|
General reaction of nitrile with carboxylic acid |
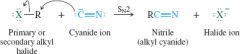
Primary or secondary alkyl halides |
|
|
REACTION: Nitrile + Carboxylic Acids |

|
|
|
REACTION: Conversion of Carboxylic acid to Acyl Chlorides |

|
|
|
Acid catalyzed esterification mechanism |
See Mechanism 18.1 |
|
|
Lactone definition |
Cyclic ester |
|
|
REACTION: Intramolecular esterification to produce lactones |
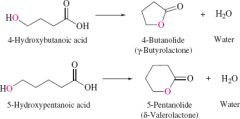
-Produces 5-6 six membered rings -much have hydroxyl and carboxylic acid group |
|
|
Decarboxylation |

|
|
|
REACTION: Decarboxylation reaction |
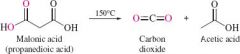
-only one carboxyl group is lost |
|
|
In Williamson sythesis what type of alkyl halides can be used? |
Primary only |
|
|
In Williamson synthesis what type of alkoxide can be used? |
Any |
|
|
List reactions to produce epoxides |
1. Alkene + Peroxyacid 2. Conversion of vicinal halohydrin to epoxide in basic conditions |
|
|
What is the difference between epoxide reaction in basic then acidic conditions? |
Basic conditions adds to least substituted carbon Acidic adds to most substituted |
|
|
HNMR of H on epoxide ring |
2.5 |
|
|
Chemical shift of ether hydrogen |
3.2-4 |
|
|
HClO4 vs OsO4 dihydroxilation |
HClO4 anti OsO4 syn |
|
|
Ether boiling point relative to water and alkanes. |
Lower than water and alkanes |
|
|
LiAlH4 + epoxide |
Makes same product as acid catalyzed epoxide opening |

