![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
high energy electrons are where with respect to the atomic nucleus?
|
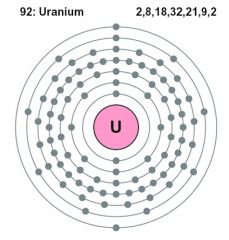
further from the Atomic nucleus = higher energy
|
|
|
A period of the periodic table is the _____
|
Columns (up-down on table) of elements to represent
1s 2s 2p 3s 3p .... Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells; with each group across a period, the elements have one more proton and electron and become less metallic. |
|
|
a group in the periodic table is the _____
|
rows (left to right). They share similar electron numbers in their outer shell
The elements in a group have similar physical or chemical characteristic of the outermost electron shells of their atoms (i.e., the same core charge), as most chemical properties are dominated by the orbital location of the outermost electron. |
|
|
Characteristics of metallic elements and the reason for metallic bonds
|
Atoms of metals readily lose their outer shell electrons, resulting in a free flowing cloud of electrons within their otherwise solid arrangement. This provides the ability of metallic substances to easily transmit heat and electricity. While this flow of electrons occurs, the solid characteristic of the metal is produced by electrostatic interactions between each atom and the electron cloud
The lower the values of ionization energy, electronegativity and electron affinity, the more metallic character the element has |
|
|
atomic number represents?
|
the number of protons in its nucleus
|
|
|
atomic weight
|
protons and neutrons
|
|
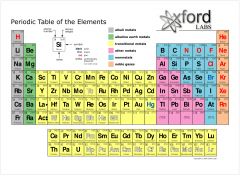
what is the electron configuration of Silicon? Iodine? Chlorine? Potassium?
|
Silicon - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2
Iodine - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p5 Potassium - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 etc |
|
|
Where is there more metallic character? Higher atomic radius? Ionization energy? Electron affinity?
|
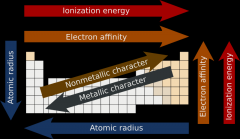
|
|
|
what is ionization energy?
|
The first ionization energy is the energy it takes to remove one electron from an atom, the second ionization energy is the energy it takes to remove a second electron from the atom, and so on. Electrons in the closer orbitals experience greater forces of electrostatic attraction; thus, their removal requires increasingly more energy. Ionization energy becomes greater up and to the right of the periodic table
|
|
|
what is electronegativity?
|
In easy terms, the desire for the atom to steal an electron. Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus.
In a covalent bond, the atom that is more electronegative will hog the electron more than the atom that is less electronegative. |
|
|
Electron affinity
|
The electron affinity of an atom is the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom to form a negative ion. Although electron affinity varies greatly, some patterns emerge. Generally, nonmetals have more positive electron affinity values than metals. Fluorine most strongly attracts an extra electron.
|
|
|
Ions are? Cations and Anions?
|
atoms with different number of electrons compared to protons. they can have more or less and are denoted by their ionic number
Cations are positive, hence t = + Anions are negative, hence n = negative Al3+, Cl− |
|
|
The ionization energy is?
|
of an atom or molecule describes the minimum amount of energy required to remove an electron (to infinity) from the atom or molecule
|
|
|
First column in periodic table is?
|
Alkali metals, know SODIUM and POTASSIUM
lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr) readily lose their outermost electron to form cations with charge +1. |
|
|
second column of periodic table?
|
Alkali earth metals, know CALCIUM and MAGNESIUM
beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra) readily lose their two outermost electrons to form cations with charge 2+ and an oxidation state, or oxidation number of +2. |
|
|
last column in periodic table?
|
Noble gases
very LOW chemical reactivity. know HELIUM and NEON The six noble gases that occur naturally are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn). |
|
|
second to last column in periodic table?
|
Halogens, FLUORINE, CHLORINE, IODINE
fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). This HIGH REACTIVITY is due to the high electronegativity of the atoms due to their high effective nuclear charge. They can gain an electron by reacting with atoms of other elements. |
|
|
How many electrons can be held in a shell?
|
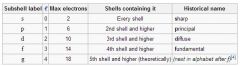
4ℓ + 2
4(1)+2= 6 etc etc |
|
|
shielding effect describes ?
|
the attraction between an electron and the nucleus in any atom with more than one electron shell.
|
|
|
What is unique about D block electron configurations in comparison to S and P block?
|
The D block backfills a shell configuration, so if you already have 3p6 4s2, then you have 3d next.
The outermost energy shell is still the 4s2 because the D block is backfilling the previous shell. However, the D block are still the highest energy state electrons if they are the final ones in the electron configuration. |
|
|
What does the metallic nature of an element mean?
|
It means it wants to give away electrons. they have a low ionization energy
|
|
|
what is 2nd ionization energy?
|
the energy required to remove the second electron
elements like Lithium (alkali metals) that have only one valence electron have a very high 2nd ionization energy |
|
|
what is somewhat counterintuitive about the size of an element in reference to its electron radius and placement on the periodic table?
|
although the element is generally larger the lower you get on the periodic table as it contains more protons, neutrons, and electrons, the electrons actually get pulled closer to the nucleus the further filled the electron valence shells are and further right the element is on the periodic table.
|
|
|
Covalent Bond
|
Strongest bond, an atom which wants to give an electron bonds with an atom that wants to take an electron. Electron is shared.
The atom that is more electronegative will hog the electron more than the atom that is less electronegative. ie O2, Oxygen has 6 valence electrons and two of the electrons are shared among the space between them so the atoms can pretend like they each have 8 (double bond) More common with atoms that are similarly electronegative or the same element altogether, as in O2 |
|
|
Ionic Bond
|
An atom which wants to give an electron gives its electron to an atom that wants to take an electron. The donor atom is now positively charged, having more protons than electrons, and the receiver atom is now negatively charged. The charge of the two atoms draws them together.
ie NaCl, Na becomes a cation and Cl becomes an anion. |
|
|
Diatomic Molecules
|
Molecule consisting of only 2 atoms, considered homonuclear if both the atoms are the same element and generally share as a covalent bond.
Picture of atoms that commonly present as homonuclear |
|
|
Polar Covalent Bond
|
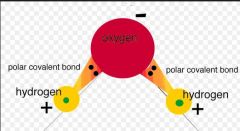
A covalent bond where, as in H2O, there is an atom that is more electronegative which causes a slight imbalance in charges on the atoms. In H2O, Oxygen is more electronegative and hogs Hydrogen's electrons, leaving Oxygen with a slightly negative charge. The two hydrogens are then slightly positive.
|
|
|
Metallic Bond
|
Several atoms who like to give up their electrons all share electrons in a communal electron area.
i.e. 4 Fe atoms together will become more positively charged as they give off electrons to be in this shared zone Makes these elements more conductive to electricity because their electrons can move around much easier, also makes element more malleable. |

