![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pathology
|
The study of abnormal conditions
|
|
|
Define Etiology
|
Causative factors of disease
|
|
|
What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic?
|
Intrisic is from inside, like genetics or hormones. Extrinsic is outside, like cigarettes
|
|
|
What are examples of risk factors?
|
Genetics, immune system, lifestyle, age, stress, pre-exhisting conditions
|
|
|
Define Sequela
|
A conditions happens due to disease
|
|
|
Define Atrophy
|
Shrinking
|
|
|
Define Hypertrophy
|
An inlargement of the individual cells leading to an increase in size of the tissue or organ. Think of the muscle man.
|
|
|
Hyperplasia
|
An increase in the number or cells in a tissue or organ. Like when you move to altitude.
|
|
|
Metaplasia
|
One cell turns into another cell and then can go back.
|
|
|
Dysplasia
|
The creation of abnormal cells from normal cells
|
|
|
What is another name for Free Radicals?
|
Oxidents
|
|
|
What are some risk factors of oral cancer?
|
Smoking, chewing tobacco, alcohol, excessive UV
|
|
|
What is the most common site for cancer on the tongue?
|
The lateral border
|
|
|
Where else other than the tongue might you see cancer?
|
Vermillion Boarder, and the floor of the mouth are most common.
|
|
|
If you find a varrient of normal when performing the IO/EO what do you do?
|
Document, document, document! Take pictures and note the charts, possibly refer.
|
|
|
What types of questions do you ask for a varrient of normal?
|
Has the lesion changed? Did you know you had it? Is it causing pain? Be sure to dialog with your patient.
|
|
|
How would you measure a lesion?
|
Use your probe.
|
|
|
Pustule
|
Pus filled lesion
|
|
|
Papule
|
>5mm and not fluid filled
|
|
|
Nodule
|

<5mm and not fluid filled
|
|
|
Sessile base
|
No defined base of the lesion
|
|
|
Pedunculated
|

A raised lesion connected by a narrow stem
|
|
|
Plaque
|

Covers a broad area, looks painted on, flat surface
|
|
|
Ulcerative
|
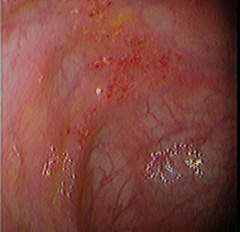
Tissue looks "angry", is wearing away
|
|
|
What is Differential Diagnosis
|
Playing detective to find the probable cause of a disease. The goal is to establish a definitive diagnosis.
|
|
|
What is the process of differential diagnosis?
|
Describe the abnormality. Determine a list of similar diseases. Eliminate. Rank what is most or least possible. Decide what additional info may be necessary.
|
|
|
What is Leukoedema?
|
It looks like you're looking through a fogged mirror. African American prevalence. When you stretch the tissue is disappears. No TX!
|
|
|
What is a Lingual Thyroid Nodule?
|
Thyroid tissue that never descends. Its more prevalent in Females. TX may involve a referral as PT may have items caught in the nodule or there may be Thyroid issues.
|
|
|
How would you TX Hairy Tongue?
|

Brush/scrape the tongue, use an antimicrobial rinse.
|
|
|
What is Epidemiology?
|
Those who are susceptible to a condition or disease
|
|
|
What is Pathogenesis?
|
The progression of the disease
|
|
|
Hyperplastic
|
Excessively moveable tissue in the MX or MN, from an increase of normal cells.
|

