![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
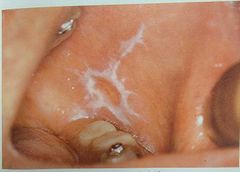
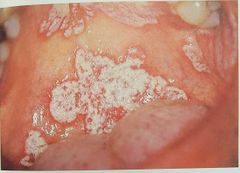
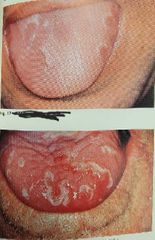
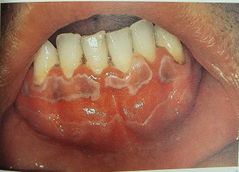
All White lesions |

|
|
|
|
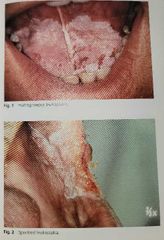
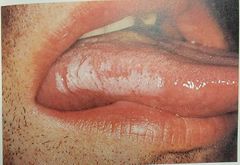
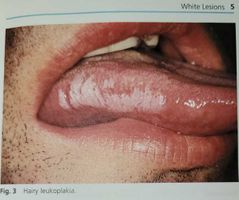
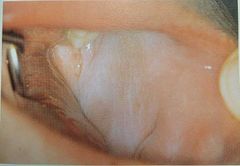
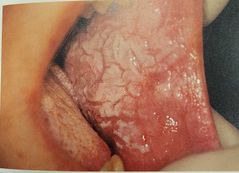
Leukoplakia |

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
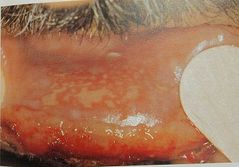
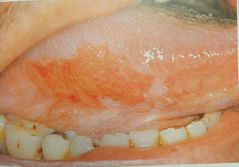
Cancer patient receiving radiation therapy |
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|

|

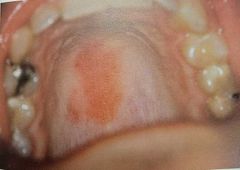
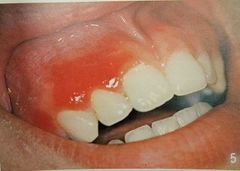
Differential: herpetiform |
|
|

|
|
|
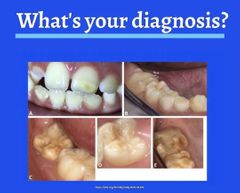
|

|
|
|
|
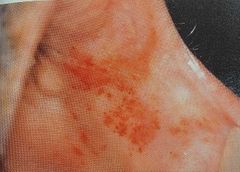
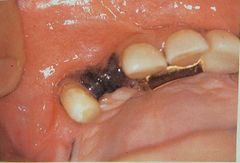
Palatal cyst of newborn |
Epstein pearls -- From islands of epithelium trapped from shelves
Bohn nodules -- from epithelial remnants of salivary glands
Dental lamina cyst -- keratin filled cyst |
|
|
|
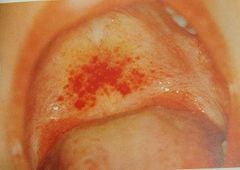
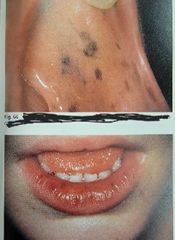
Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy |
Benign pigmented lesion from neutral crest cells (rare) Location: Anterior maxilla Age: infants younger than 1yr old Test: urine (vanillyl-mandelic-acid) |
|
|
|
Congenital epulis of newborn |
Benign gingival granular cell tumor Location: Alveolar ridges of newborns |
|
|
|
Hemangioma |
Infantile Hemangioma most common tumor of infancy Present at birth (if present at birth, will be Hemangioma not congenital vascular malformation) |
|
|
|
Natal teeth |
Natal: present at birth Neonatal: erupt within first 30 days after birth Not supernumerary Usually hypermobile Check vitamin K |
|
|
|
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis |
Cankers Age: teenagers and older NOT in areas heavily keratinized
Major: 1cm or greater Minor: <1cm (most common) Herpetiform: small like herpes No gingivitis |
|
|
|
Coxsackie A |
RNA virus Associated with: -Hand foot mouth --- school age, limb lesions -Herpangina --- soft palate, tonsils |
|
|
|
Erythema multiform |
Recurring targetoid mucocutaneous lesions of skin and mucous membranes Age: 7-21 Etiology: HSV Steven-Johnson syndrome |
|
|
|
Herpes |
DNA virus HSV 1 - latent in nerves Transfer through saliva or gentital secretions Marginal gingivitis Acyclovir but controversial |
|
|
|
Localized Juvenile Spongiotic Gingival Hyperplasia |
Inflammatory gingival hyperplasia in young patients usually in max anterior region. Not plaque related (hygiene won't help) Etiology is unknown Gingivectomy |
|
|
|
Gingival overgrowth causes |
Medications/drug induced Leukemia Idiopathic Gingival fibromatosis Plaque/hygiene |
|
|
|
Drug induced gingival overgrowth |
Immunosuppressants: - cyclosporine Anticonvulsants: - phenytoin Ca Channel Blockers: - nifedipine |
|
|
|
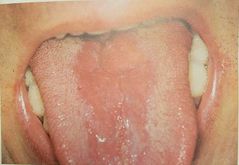
Geographic tongue |
Associated with psoriasis Unknown etiology Erythema migrans |
|
|
|
Median rhomboid glossitis |
Central papillary atrophy Fungal infection (candidiasis) Use antifungal Etiology: taking antibiotics for a long time |
|
|
|
Crohn's disease |
10% have oral mucosal ulcers Indurated borders (different from cankers) |
|
|
|
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura |
Autoimmune destroying own platelets by spleen. Purple oral lesion Splenectomy |
|
|
|
PT Test of hemostasis |
Extrinsic pathway, Normal = 10-12 seconds Prolonged by deficiencies in factor VII, X, V, prothrombin, and fibrinogen Monitor warfarin, evaluate liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, and DIC INR |
|
|
|
PTT test |
Intrinsic pathway Normal = 25 - 35 seconds Prolonged by deficiency in plasma -clotting factors except VII and XIII |
|
|
|
PFA-100 test of hemostasis |
Platelet function (not number) (CBC looks at platelet number) |
|
|
|
Selective IgA deficiency |
One of most common type of primary immunodeficiency When children have oral candidiasis not from overuse of medications. |
|
|
|
Behcet's disease |
Eyes, mouth, and genital sores Idiopathic rheumatoid condition |
|
|
|
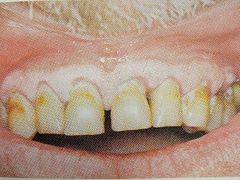
Pre-eruptive intrinsic staining |
Fluorosis - Dentinogenesis imperfecta Amelogenesis imperfecta Hematologic disorders - hyperbilirubinemia - green Meds |
|
|
|
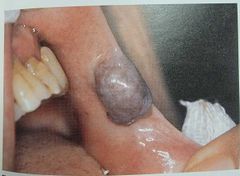
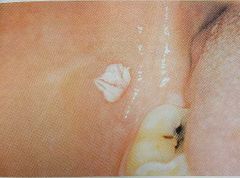
Mucocele |
Ruptured Salivary glad spillage of mucin to surrounding soft tissue Usually due to trauma |
|
|
|
Which comes with bone changes radiographically? Pyogenic granuloma Peripheral ossifying fibroma Peripheral giant cell granuloma |
Peripheral ossifying fibroma AND Peripheral giant cell granuloma |
|
|
|
Pyogenic granuloma |
Unrelated to infection and granulomas Response to irritation |
|
|
|
Peripheral ossifying fibroma |
Inflammatory Hyperplasia of gingiva in response to trauma or irritation Common bone involvement |
|
|
|
Peripheral giant cell granuloma |
Only in gingiva Distal to incisors May cause bone resorption |
|
|
|
Eruption cyst |
Usually under age 10 |
|
|
|
Giant cell fibroma |
Uncommon Differential: papilloma Palate |
|
|
|
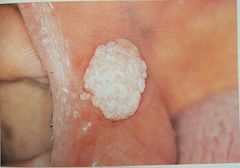
HPV |
DNA virus Spreads through sexual contact and autoinoculation Squamous Papillomas Verruca vulgaris Condyloma acuminata Multifocal epithelial hyperplasia-heck |
|
|
|
Squamous papilloma |
Induced by HPV. Usually tongue, lips, soft palate |
|
|
|
Verruca vulgaris |
Most common on hands |
|
|
|
Condyloma acuminata |
STD Cauliflower like growth |
|
|
|
Multifocal epithelial hyperplasia - Heck's disease |
Associated with HPV 13 and 32 Multiple flat lesions |
|
|
|
Supernumerary teeth syndromes (video) |
Cleidocranial dysplasia Gardner's syndrome |
|
|
|
Gemination |
Increases tooth number Single tooth chamber |
|
|
|
Tooth Fusion |
Reduced number of teeth Adjacent tooth germs combined with dentin or enamel Two separate chambers |
|
|
|
Concrescence |
Fusion after root formation Roots of two or more teeth are united by cementum |
|
|
|
Taurodontism |
Normal crown size Long chamber Trisomy 21 |
|
|
|
Dens in dente |
Infolding of outer enamel into interior Coronal: folds into dental papilla Radicular: invagination of Hertwig's sheath |
|
|
|
Amelogenesis imperfecta types |
1. Hypoplastic 2. Hypomaturation 3. Hypocalcified 4. Hypomaturation-hypocalcified with Taurodontism |
|
|
|
Amelogenesis imperfecta type 1 |
Hypoplastic
Thin enamel, pitted, rough, or smooth surface Undersized yellow-brown |
|
|
|
Amelogenesis imperfecta type 2 |
Hypomaturation Normal thickness of enamel, mottled Cloudy white, yellow, brown Softer enamel |
|
|
|
Amelogenesis imperfecta type 3 |
Hypocalcified Normal thickness enamel Normal size/shape at eruption Increases permeability, darkened/stained |
|
|
|
Amelogenesis imperfecta type 4 |
Hypomaturation-hypocalcified with Taurodontism |
|
|
|
Dentinogenesis imperfecta |
1. With osteogenesis imperfecta 2. Isolated type 3. With brandywine Brown to black Bulbous crown, short splendor roots Don't see pulp chamber/ chamber obliteration |
|
|
|
Dentin dysplasia |
Type 1 - Radicular: normal color, short/abnormal roots, vital tooth, canals filled in. Type 2 - coronal: primary dentition shows but permanent is normal. Canals full in after eruption. Normal roots |
|
|
|
Regional odontodysplasia |
Ghost teeth Only a few teeth in quadrant affected Hypoplastic and hypocalcified enamel and dentin |
|
|
|
Turner's tooth |
Enamel hypoplasia Extension of periapical infection or trauma from deciduous tooth |
|
|
|
Congenital syphilis |
Hutchinson's teeth Mulberry molars |
|
|
|
Hypercementosis |
Excessive deposition of cementum Paget's disease Hyperpituitarism |
|
|
|
Sensitivity |
(+) result in the test when disease is present |
|
|
|
Specificity |
(-) result when disease is NOT present |
|
|
|
Macrocytic anemia |
Hypoproliferative Vit B12 deficiency Folate deficiency |
|
|
|
Microcytic anemia |
Iron -> + common Thalassemia
Hypoproliferative |
|
|
|
Normocytic anemia |
Anemia is chronic disease Bone marrow aplasia Hypoproliferative |
|
|
|
Hemolytic anemia |
Immune hemolysis Mechanical hemolysis Sickle cell anemia G6PD deficiency |
|
|
|
Normal WBC |
4,500 - 10,000/mm3 High = infection (leukocytosis) Low = drugs, viral infection (leukopenia) |
|
|
|
Platelets normal |
150,000 - 300,000 cells/mm3 High = inflammatory rxn Low = immune/idiopathic, drugs Most common platelet function disorder: Bernard Soulier syndrome |
|
|
|
Blood clot = |
Platelets + fibrin |
|

