![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
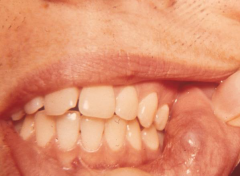
Mucocele
|
* AKA: Mucus Extravasation Cyst
* Description: Mucin retained in surrounding tissue * Cause: Trauma and Severing of a Salivary Excretory Duct * Found in: Younger groups * Location: Lower/Upper Lip, Palate, Retromolar area, Ventral Tongue, Buccal Mucosa Floor of Mouth, or Lingual Frenum * Color: Skin-tone, blue in color * Treatment: Removal of damaged duct or blockage (sialolith). Caution Pt. to avoid trauma to area. * Clinical Characteristics: Movable, Soft, Painless, Dome-shaped |
|
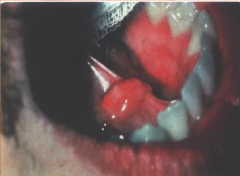
Sialolith
|
* Description: Salivary gland stone that causes obstruction. May cause retention cyst.
* Location: Floor of mouth * Treatment: Surgical removal. |
|
|
Infectious Viral Diseases: Cytotoxic
|
* Replicate within the host cells and DESTROY them.
* Release viral particles into adjacent tissue then move into and destroy other host cells. |
|
|
Infectious Viral Diseases: Non-cytotoxic
|
* NO or INTERMITTENT cellular destruction.
* May lie dormant for long periods of time (ie. herpesvirus) * May replace host DNA and become part of the cell. |
|
|
Infectious Viral Diseases: Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
|
* At least 8 HHV
* May occur in primary or systemic forms |
|
|
Infectious Viral Diseases: What are HHV-1 associations?
|
* Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis, recurrent oral herpes, and herpes labialis.
-- May cause genital lesions due to genital-oral contact. |
|
|
Infectious Viral Diseases: What are HHV-2 associations?
|
* Genital Herpes
-- Type 2 may cause oral lesions due to oral-genital contact |
|
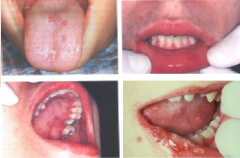
Infectious Viral Diseases: Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
|
* Description: (before rupture) Multiple vesicles w/ red margins, (after rupture) multiple ulcers surrounded by erythema.
* Cause: HHV-1 * Characteristics: migrates along trigiminal nerve and remains latent in the ganglion until triggered by event. Painful lesions, possible temperature, generalized malaise, cervical lymphadonopathy and sore throat. * Treatment: Soft diet, non acidic/carbonated liquids, cold foods (ie. ice-cream), Topical Benadryl elixir and Kaopectate (for pain). * Postpone Dental Care Course: 10-14 days. * Initial Exposure is called a primary infection (often subclinical) |
|
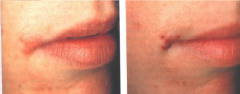
Infectious Viral Diseases: Secondary/Recurrent Herpes Simplex
|
* Description: (Before rupture) Clusters of vesicles on vermillion border, perioral skin or keratinized intraoral surface; (after rupture) crusted ulcers
* Cause: Event reactivated Latent Virus --Event is often immune compromising: Cold/fever, Sunburn, Emotional stress, Trauma, Infection, Menstruation, Systemic disease, Allergy, Pregnancy, Debilitation, Scaling/Root planning/Periodontal Surgery. * 20-40% affected after primary infection * Postpone Dental Care |
|
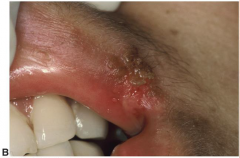
Infectious Viral Diseases: Herpes Labialis
|
* Description: (Before rupture) Clusters of vesicles on vermillion border, ; (after rupture) crusted ulcers
* Treatment of outbreak: Antiviral topical ointments or creams reduce duration or stop lesion formation. + USE APPLICATOR + Avoid Sunburns, Avoid triggers. Take acyclovir orally (EXPENSIVE) |
|
|
Infectious Viral Diseases: Herpetic Lesions vs Aphthous Ulcers
|
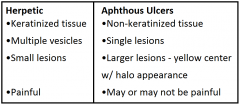
|
|
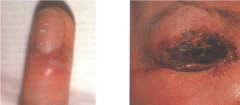
Infectious Viral Diseases: Herpetic Whitlow
|
* Cause: HSV-1 on finger - usually a primary infection but can recur.
* Location: on finger but may infect mouth, nose,e eyes, or other mucosal lining. |
|
|
Infectious Viral Diseases: Herpes Simplex Virus - 2
|
* AKA: Genital Herpes
* Transmission: Genital secretions * Cannot visually differentiate between type 1 or 2 * Oral sex increases likely hood of type-1 (oral) on genitellia and type-2 (genital) on mouth. Also implicated in certain head and neck cancers caused by HPV. |
|
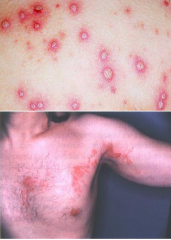
Infectious Viral Diseases: Primary Varicella-Zoster HSV-3
|
* AKA: Chickenpox (varicella -Original infection) and Shingles (zoster - Reactivated infection)
* Transmission: air droplets or direct contact w/ lesions. |
|
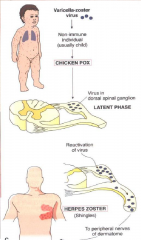
Infectious Viral Diseases: Chickenpox to Shingles: Order and Differences
|
* Chickenpox - more often in children
-- NO pain (itchy instead) -- Only Treatment is relief of itching (pruritus) * Shingles - more often in elderly -- Pain and paresthesia lasting 2-3 weeks -- can cause chickenpox in not-prevously-exposed people -- May also cause fever, malaise and lymphadenopathy. -- Prevention includes vaccination or isolation. -- Treatment includes management of skin lesions, pain control, and antiviral meds ( oral acyclovir 800mg 5xday for 7-10 days - Effects may include: post-herpetic neuralgia for years, facial paralysis, diminished hearing, vertigo, tooth exfoliation (rare) and necrosis of the mandible (rare). |
|
Infectious Viral Diseases: Entrovirus 71
|
* AKA: Coxsackie Entrovirus
* Can cause Hand-foot-and-mouth disease, Herpangia, and acute lymphonodular pharyngitis. |
|
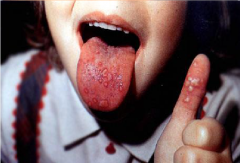
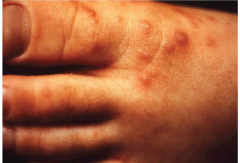
Infectious Viral Diseases: Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease
|
* Transmission: airborne and oral/fecal
* Mostly in children under age 5 * Description: Rash on soles of feet and palms, vescifles that may or may not rupture, fever, sore throat, malaise and lymphadenopathy. |
|
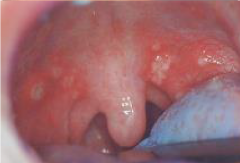
Infectious Viral Diseases: Herpangia from Coxsackie A-16
|
* Transmission: oral/fecal
* Description: Oral lesions in posterior, soft palate, pillars and tonsils. Sore throat, fever, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, and vomiting, reddened tissues and vesicles that rupture and ulcerate. * May be mistaken for strep throat. * Treat for discomfort. |
|
|
Infectious Viral Diseases: Acute Lymphonodular Pharyngitis
|
* Vary rare condition *
* Description: Fever Oral appearance may vary. Includes fever, sore throat, headache, and inflamed lymphoid tissue. * Lasts several days to weeks. |
|
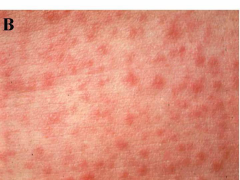
Infectious Viral Diseases: Measels
|
* AKA: Rubeola
* Family: Paramyxoviridae * Transmission: airborne and droplets. * Description: Fever, malaise, upper respiratory congestion, cough, conjunctivitis, and a rash that can be found on buccal/labial mucosa before extraoral. * Rash may last 7-24 days. |
|
|
Infectious Viral Diseases: Koplik's Spots
|
* AKA: "Grains of salt on a wet background."
* Description: small, irregular red spots w. bluish white spec in each center, found on buccal and lingual mucosa often associated w/ measles. * Pathognomonic of early stage measles, appearing a few days before rash arrives. |
|
|
Word of the day: Pathognomonic
|
* A sign or symptom that is so characteristic of a disease that it makes the diagnosis.
* Comes from the Greek "pathognomonikos'" meaning "skilled in judging diseases." |
|
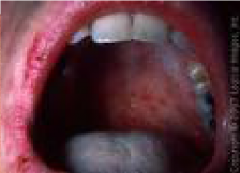
Infectious Viral Diseases: Rubella
|
* AKA: German Measles
* Cause: Toga virus * Transmission: respiratory droplets **HIGHLY CONTAGIOUS** * Description: Mild erythematous rash w/ low grade fever, malaise, nausea, poor appetite, lymphadenopathy, w/ red and pink papules on the body. * Forchheimer's signs (small, discrete, dark red papules) may be visible in soft palate region and are considered an early sign of infection. |
|
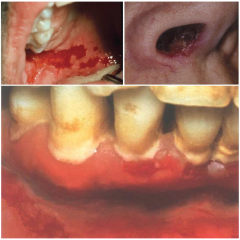
Noninfective Vesiculobullous (Autoimmune) Diseases: Pemphigus Vulgaris
|
* Transmission: no modes
* Occurrence: Most often in 40-60 years of age, and of Jewish or Mediterranean descent. * Description: Begin as bulla greater than 1cm that rupture quickly, form shallow ulcers covered by gray pseudomembrane. |
|
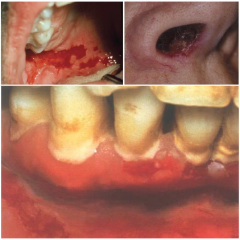
Microscopic Events of Pemphigus Vulgaris
|
* Acantholysis (separation of epithelial cells) caused by autoantibodies that attack protein components of desmosomes.
* Protein component binds the epithelial cells together wich leads to bulla and ulceration of affected tissues. * Immunofluorescence aids in diagnosis. |
|
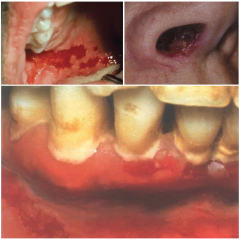
Nikolsky's Sign of Pemphigus Vulgaris
|
* First described by Russion dermatologist Pyotr Valilyewich Nikolsky in 1896.
*Initially described sign as appearing after rubbing skin with pemphigus foliaceus, causing a blistering or denudation of epidermis w/ glistening, moist surface underneath. *Shows positive response in all phemphigus disorders. * used to diagnose pemphigus. *Pressure is applied to skin w/ finger or paperclip to blistered, perilesional or normal skin in pt suspected of having pemphigus. Positive response = extension of blister and/or removal of epidermis in area immediately surrounding blister or lesion. |
|
Treatment for Pemphigus Vulgaris
|
* Good oral hygiene and Medical treatment is crucial
* Systemic corticosteroids and immunosupressive agents * Topical steroids DO NOT USE: -- alcohol based products -- abrasive dental products -- tooth whitening products |
|
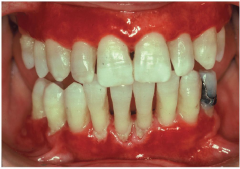
Noninfective Vesiculobullous (Autoimmune) Diseases: Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
|
* AKA: Desquamative gengivitis
* Description: Bulla form and break, leaving raw or ulcerated surface. * Cause: Often contact allergy * Location: Often oral cavity, especially gingiva. * Treatment: Discontinue contact with aggravating product. -- spicty foods, cinnamon, sodium laurel sulfate (in toothpaste) flavoring agents (in foods like salsa), processed foods, and soft drinks. |
|
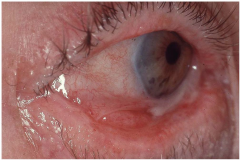
Noninfective Vesiculobullous (Autoimmune) Diseases: Ocular Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
|
Eyes should be examined and patient should be referred to an eye professional for evaluation.
|
|
|
Noninfective Vesiculobullous (Autoimmune) Diseases: Bullous Pemphigoud
|
* Affects elderly 70-80 years of age
* Rarely affects intraoral areas - would be found on gingiva. * Cutaneous bullae develop slowly - may last for weeks to months before breaking, causing painful, erythematous and ulverative lesions * Treatment: Systemic corticosteroids w/ other immunosuppressants. |
|
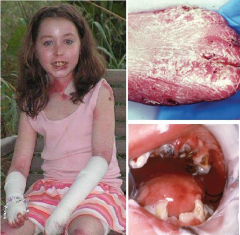
Congenital or Genetic Diseases: Epidermolysis Bullosa
|
* Fragility of the skin and mucosa which blister
* Four groups: Simplex, Junctional, Dystrophic, and Mixed (Kindler Syndrome). * Can have enamel hypoplasia with a high rate of caries. * Fluoride and non-cariogenic soft diet. * Affected Organs: Eyes, Blood (poor iron absorption), skin-tails, esophagus, intestine, and musculoskeletal. |
|
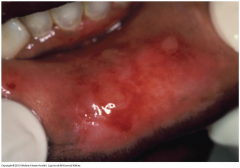
Congenital or Genetic Diseases: Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita
|
* Chronic Subepithelial Blistering Disease.
* Affects the dermal-epidermal junction. * Classic form is characterized by fragility of the skin, including nikolsky's sign. * affects 0.2 million people. |
|
|
Congenital or Genetic Diseases: Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita - Dental Procedures
|
* Hand-scale (low-power ultrasonic in less severe cases)
* Low abrasive polish * NO AIR POLISHERS * Limited contact w/ tissue. NEVER fulcrum on tissue. * Apply medications w/ cotton swab. NO soft tissue contact. |

