![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
(1) Six Sigma is a methodology for _________.
(2) Six Sigma uses _______ and _______ to rationalize processes. (3) Six Sigma changes companies from fixing broken products to fixing broken _______. (4) What kinds of processes can be addressed by Six Sigma? (5) What can be simultaneously obtained with Six Sigma? (6) The best arguments in favor of Six Sigma are... (7) In order to success in a Six Sigma project is is mandatory to ____ |
(1) process improvement
(2) statistical techniques ; rigorous scientific method (3) Processes (4) Production, Administration, Services (5) Cost reduction, quality improvement, customer satisfaction (6) the results obtained 7. rigorously follow the methodology in all phases |
|
|
How do we work with six sigma?
|
(1) Detect opportunities for improvement
(2) Create a multi-discipline group (3) Apply methodology (4) Follow and control the project (5) Results variation (6) Apply new process |
|
|
What is the Six Sigma Methodology?
|
DMAIC cycle!
1 - Define 2 - Measure 3 - Analysis 4 - Improve 5 - Control |
|
|
What is the main thing you do in each phase of the six sigma methodology?
|
1 - Define - set project boundaries
2 - Measure - calculate process capability 3 - Analysis - discover sources of variation 4 - Improve - determine cause and effect relationships 5 - Control - keep variation sources controlled |
|
|
Give more details on phase 1.
|
DEFINE
1. Understand “WHAT” does the “CUSTOMER” need. 2. Translate this into “HOW” our product or service satisfies these requirements. 3. Determine those characteristics of the product or service that are critical to quality and cost. |
|
|
Give more details on phase 2
|
MEASURE
1. Understand the process’ real performance. 2. Gather objective data: |
|
|
What is a statistical problem with process centering?
|
Production processes are random in nature
|
|
|
We need to talk about what process sigma is
|
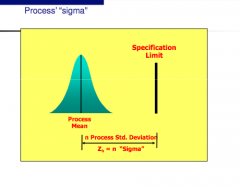
see image abbove
|
|
|
Give more details on phase 3.
|
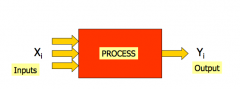
ANALYSIS
Identify which input factors are the ones with the largest effect in process output. |
|
|
Give more details on phase 4
|
IMPROVE
Conceive and validate change sin the process aimed at: reducing/eliminating inefficiencies reducing/eliminating defects |
|
|
Give more details of phase 5.
|
Conceive mechanisms that guarantee the long lasting of improvements
|
|
|
ASIDE FROM KNOWING THESE, WOULD BE HELPFUL IF YOU ALSO LOOK AT IMAGES IN THE SLIDES.
1. Which Six Sigma tool answers the question, which are the characteristics critical to quality (CTQ)? 2. ....how does the actual process look and what are the variables involved? 3. ....which variables are responsible for cost and quality? 4....what is the importance of these variables (e.g. defect per product type)? 5....how to define the variables of interest? 6. ...How can the variables of interest be measured? 7. ...is the measurement system adequate? 8. ...What do the measurements tell us? 9. ...how good is the actual process? 10. ...What are the causes responsible for process centering and variability? 11. ...What the relations between the variables that determine the performance of the process? |
1. Critical characteristics map
2. process diagram 3. cause and effect diagram 4. Trivial and Vital causes chart 5. variable definition tools 6.Measurement system analysis 7. Measurement system capability 8. Data gathering (e.g. probability plot) 9. Product capability analysis 10. Graphical Analyses (scatterplots) and Numerical analyses (e.g. numerical analysis of variance) 11. Process modeling (e.g. pareto chart, interaction plot, main effects plot) |
|
|
(1) What are the limitations to the tools / models?
(2) What tells us the variation that is allowable to the critical input variables? |
(1) Determining whether the errors of the model are acceptable
(2) operative tolerances |
|
|
Finally, what does stage 5 of the six sigma process look like?
|
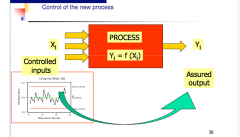
see image above
|
|
|
What are the general pre-requirements to work with Six Sigma?
|
Clear knowledge of the customer, process oriented management, clear knowledge of process performance
|
|
|
What are the specific requirements to work with Six Sigma?
|
1. Specific training at different levels (e.g. champions, black belts, etc)
2. Operative structure clearly established for 6 sigma (procedures for selecting, working, an devaluating improvement projects) 3. Management commitment 4. Key improvement projects are carried out with 6 sigma 5. customer focus, fact based decisions, scientific method, continuous improvement |
|
|
What are the general roles in Six Sigma methodology?
|
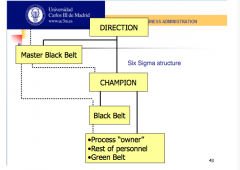
see image above
|
|
|
General idea of each role:
1. Champion 2. Master Black Belt 3. Black belt 4. Process owner |
1. lead improvement program
2. gives advice / training 3. assist champion 4. control process |
|
|
When implementing Six Sigma, what is the firs thing you should do?
|
1. send a clear message throughout org about implementation and why / benefits. Explain the advans and disadvans of the ways of discpline and what's to be expected in the short and long term.
|
|
|
How do you work with Six Sigma (e.g. continuous improvement)?
|
1. Write down the Continuous Improvement Programme.
2. Develop/update a business metrics system. 3. Set upcriteris for project selection. 4. Develop/update a project management system. 5. Apply the “improvement process” to the selected projects. |
|
|
What is the process for project selection?
|
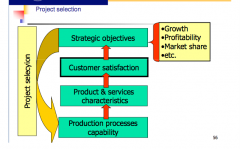
see image above
|
|
|
How do you determine cause and effect relationships to the updated processes?
|
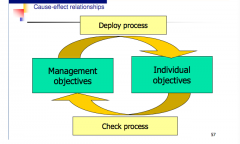
see image above
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of a Six Sigma project? (6 things!)
|
(1) Strategic objectives oriented ...and...
(2) Multi-departmental (3) Limited extension (4) Not atomized (5) Not obvious solutions (6) Related to other projects (sinergy) → aww, look how he spelled synergy! |
|
|
Project selection:
1. Choose with rational and ________ criteria. 2. Never put out subjects "________" 3. Choose a _______ number of projects. 4. Pay special attention to the selection of ________. |
1. objective - oriented
2. from the pocket 3. manageable 4. team-members |
|
|
PROJECT LAUNCH!
1. Clarify the team specific __________. 2. Specify all the ______ and ________ to be considered by the team. 3. Set up the date when the project is _________. 4. Establish the available _________. |
1. objectives
2. restrictions and guidelines 3. to be finished 4. budget |
|
|
PROJECT FOLLOW-UP
1. Control the adequate compliment with : ______ |
1. Project schedule
|
|
|
PROJECT EVALUATION
1.Evaluation as a compendium of the _______ follow up performed. 2. Objective versus subjective evaluation. Carefully check the following: |
1. continuous
2. Carefully check: |
|
|
NEW PROCESS APPROVAL
1. Formalize new process with the following: |
1.
Documentation |

