![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
126 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Hematocrit |
percentage of erythrocyte in a volume of blood |
|
|
|
Hemoglobin tests |
Total amount of hemoglobin in a sample of peripheral blood |
|
|
|
Platelet count |
Number of platelets per cubic millimeter or microliter of blood |
|
|
|
Prothrombin time |
Test of ability of blood to clot |
|
|
|
Red blood cell count |
Number of erythrocyte per cubic millimeter or microliter of blood |
|
|
|
Red blood cell morphology |
Microscopic examination of a stained blood smear to determine the shape of individual red cells |
|
|
|
White blood cell count |
Number of leukocytes per cubic millimeter or microliter of blood |
|
|
|
White blood cell differential |
Percentage of different types of leukocytes in the blood |
|
|
|
Apheresis |
Separation of blood into component parts and removal of a portion from the blood |
|
|
|
Anemia |
Deficiency in erythrocytes or hemoglobin 1. Aplastic 2. Hemolytic 3. Pernicious 4. Sickle cell 5. Thalassemia |
|
|
|
Aplastic anemia |
Failure of blood cell production in the bone marrow |
|
|
|
Hemolytic anemia |
Reduction in red cells due to excessive destruction |
|
|
|
Pernicious anemia |
Lack of mature erythrocytes caused by inability to absorb vitamin B12 into the bloodstream |
B12 |
|
|
Sickle cell anemia |
Hereditary disorder of abnormal hemoglobin producing sickle -shaped erythrocytes and hemolysis |
|
|
|
Thalassemia |
Inherited defect in ability to produce hemoglobin, leading to hypochromia |
|
|
|
Hemochromatosis |
Excess iron deposits throughout the body |
|
|
|
Polycythemia vera |
General increase in red blood cells |
|
|
|
Hemophilia |
Excessive bleeding caused by hereditary lack of blood clotting factors necessary for blood clotting |
|
|
|
Pupura |
Multiple pinpoint hemorrhages and accumulation of blood under the skin |
|
|
|
Leukemia |
Increase in cancerous white blood cells |
|
|
|
Granulocytosis |
Abnormal increase in granulocytes in the blood |
|
|
|
Mononucleosis |
Infectious disease marked by increased number of mononuclear leukocytes and enlarged cervical lymph nodes |
|
|
|
Multiple myeloma |
Malignant neoplasm of bone marrow |
|
|
|
Antiglobulin test |
Test for the presence of antibodies that coat and damage erythrocytes |
|
|
|
Bleeding time |
Time required for blood to stop flowing from a tiny puncture wound |
|
|
|
Coagulation time |
Time required for venous blood to clot in a test tube |
|
|
|
Complete blood count |
Determination of numbers of blood cells, hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit, and red cell values |
|
|
|
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
Speed at which erythrocytes settle out of plasma |
|
|
|
Blood transfusion |
Whole blood or cells are taken from a donor and infused into a patient |
|
|
|
Bone marrow biopsy |
Microscopic examination of a core of bone marrow removed with a needle |
|
|
|
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
Peripheral stem cells from a compatible donor are administered to a recipient |
|
|
|
Ab |
Antibody |
|
|
|
ABO |
Four main blood types - A, B, AB, O |
|
|
|
BMT |
Bone marrow transplantation |
|
|
|
CBC |
Complete blood count |
|
|
|
diff |
Differential count |
|
|
|
EPO |
Erythropoietin |
|
|
|
ESR |
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
|
|
|
Hct |
Hematocrit |
|
|
|
Hgb or HGB |
Hemoglobin |
|
|
|
PT, pro time |
Prothrombin time |
|
|
|
RBC |
red blood cell; red blood cell count |
|
|
|
sed rate |
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
|
|
|
SMAC |
Sequential multiple analyzer computer - an automated chemistry system that determines substances in serum |
|
|
|
WBC |
White blood cell; white blood cell count |
|
|
|
WNL |
within normal limits |
|
|
|
Bas/o |
Base |
|
|
|
Chrom/o |
Colour |
|
|
|
Coagul/o |
Clotting |
|
|
|
Cyt/o |
Cell |
|
|
|
Eosin/o |
Red, dawn, rosy |
|
|
|
Erythro/o |
Red |
|
|
|
Granul/o |
Granules |
|
|
|
Hemoglobin/o |
Hemoglobin |
|
|
|
Is/o |
Same, equal |
|
|
|
Kary/o |
Nucleus |
|
|
|
Mon/o |
One |
|
|
|
Leuk/o |
White |
|
|
|
Morph/o |
Shape |
|
|
|
Myel/o |
Bone marrow or spinal cord |
|
|
|
Neutr/o |
Neutral |
|
|
|
Nucle/o |
Nucleus |
|
|
|
Phag/o |
Eat, swallow |
|
|
|
Poikil/o |
Varied, irregular |
|
|
|
Sider/o |
Iron |
|
|
|
Spher/o |
Global, round |
|
|
|
Thromb/o |
Clot |
|
|
|
-apheresis |
Removal, carry away |
|
|
|
-blast |
Immature, embryonic |
|
|
|
-cytosis |
Abnormal cell condition (increase usually) |
|
|
|
-emia |
Blood condition |
|
|
|
-gen |
Giving rise to, producing |
|
|
|
-globin, -globulin |
Protein |
|
|
|
-lytic |
Destruction, separation |
|
|
|
-oid |
Derived from |
|
|
|
-osis |
Abnormal condition |
|
|
|
-penia |
Deficiency |
|
|
|
-phage |
Eat, swallow |
|
|
|
-philia |
Attraction for (increase in cell number) |
|
|
|
-phoresis |
Carrying, transmission |
|
|
|
-poiesis |
Formation |
|
|
|
-stasis |
Stop, control |
|
|
|
Albumin |
Protein in blood; maintains the proper amount of water in the blood |
|
|
|
Antibody |
Specific protein produced by lymphocytes in response to bacteria, viruses, or other antigens. An antibody is specific to an antigen and inactivates it |
|
|
|
Antigen |
Substance, usually foreign, that stimulates the production of an antibody |
|
|
|
Basophils |
White blood cells containing granules that stain blue; associated with release of histamine and heparin |
|
|
|
Bilirubin |
Orange-yellow pigment in bile; formed by the breakdown of hemoglobin when red blood cells are destroyed |
|
|
|
Coagulation |
Blood clotting |
|
|
|
Colony-stimulating factor |
Protein that stimulates growth of white blood cells ( granulocytes) |
|
|
|
Differentiation |
Change in structure and function of a cell as it matures; specialization |
|
|
|
Electrophoresis |
Method of separating serum proteins by electrical charge |
|
|
|
Eosinophil |
White blood cell containing granules that stain red; associated with allergic reactions |
|
|
|
Erythroblast |
Immature red blood cell |
|
|
|
Erythrocyte |
Red blood cell. There are about five million per microliter or cubic milliliter of blood |
|
|
|
Erythropoietin |
Hormone secreted by the kidneys; stimulates red blood cell formation |
|
|
|
Fibrin |
Protein that forms the basis of a blood clot |
|
|
|
Fibrinogen |
Plasma protein that is converted to fibrin in the clotting process |
|
|
|
Globulin |
Plasma protein |
|
|
|
Granulocytes |
White blood cell with numerous dark staining granules; eosinophil, neutrophil, and basophil |
|
|
|
Hematopoietic stem cell |
Cell in the bone marrow that gives rise to all types of blood cells |
|
|
|
Hemoglobin |
blood protein containing iron; carries oxygen in red blood cells |
|
|
|
Hemolysis |
Destruction or breakdown of blood |
|
|
|
Heparin |
Anticoagulant found in blood and tissue cells |
|
|
|
Immune reaction |
Response of the immune system to foreign invasion |
|
|
|
Immunoglobulins |
Protein with antibody activity |
|
|
|
Leukocytes |
White blood cells |
|
|
|
Lymphocytes |
Mononuclear leukocyte that produces antibodies |
|
|
|
Macrophage |
Monocyte that migrates from the blood to tissue spaces. As a phagocyte, it engulfs foreign material and debris. In the liver, spleen, and bone marrow macrophages destroy worn out blood cells |
|
|
|
Megakaryocytes |
Large platelet precursor cells found in the bone marrow |
|
|
|
Monocyte |
Leukocyte with one large nucleus. It is a cell that engulfs foreign material and debris. Monocytes become macrophages as they leave the blood and enter body tissues |
|
|
|
Mononuclear |
Pertaining to a cell with a single round nucleus; lymphocytes and monocytes or mononuclear leukocytes |
|
|
|
Myeloblasts |
Immature bone marrow that gives rise to granulocytes |
|
|
|
Neutrophil |
Granulocytic leukocyte formed in bone marrow. It is a phagocytic tissue fighting cell. Also called a polymorphonuclear leukocytes |
|
|
|
Plasma |
Liquid portion of blood; contains water, protein, salts, nutrients, lipids, hormones, and vitamins |
|
|
|
Plasmapheresis |
Removal of plasma from withdrawn blood by centrifuge. Collected cells are re transfused back into the donor. Fresh frozen plasma or salt solution is used to replace withdrawn plasma |
|
|
|
Platelet |
Small blood fragment that collects at site of injury to begin the clotting process |
|
|
|
Polymorphonuclear |
Pertaining to a white blood cell with a multilobed; neutrophil |
|
|
|
Prothrombin |
Plasma protein; converted to a thrombin in the clotting process |
|
|
|
Reticulocyte |
Immature erythrocyte. A network of strands is seen after staining the cell with special dyes |
|
|
|
Rh factor |
Antigen on red blood cells of rh-positive individuals. The factor was first identified in the blood of rhesus monkey |
|
|
|
Serum |
Plasma minus clotting proteins and cells. Clear, yellowish fluid that separates from blood when it is allowed to clot. It is formed from plasma, but does not contain protein coagulation factors |
|
|
|
Stem cell |
Unspecialized cell that gives rise to mature, specialized forms. A hematopoietic stem cells is the progenitor for all different types of blood cells |
|
|
|
Thrombin |
Enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin during coagulation |
|
|
|
Thrombocyte |
Platelet |
|
|
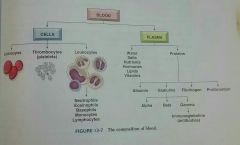
|
Know this |
|
|
|
How does a clot form? |
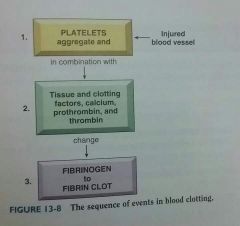
|
|

