![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Multiple Choice |

|
|
|
Coral Bleaching |
When water is too warm, corals will expel the algae living in their tissues causing the coral to turn completely white. This is called coral bleaching. When a coral bleaches, it is not dead. If conditions do not improve the animals can be overtaken and die out |
|
|
3 Types of adaptations |
Structural- Are the physical features of the organism. (Things you can see like shape,body coverings, internal organs) Physiological- Related to how an organisms metabolism works. (Regulate their bodily functions like breathing,temperature) Behavioural- Are learned or inherited behaviours that help organisms to survive |
|
|
Ocean Acidification |
A reduction in the pH of the ocean over an extended period of time, caused primarily by uptake of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Mainly caused by carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere dissolving into the ocean. |
|
|
Biotic and Abiotic factors |
Biotic Factors- Living things Abiotic Factors- Non Living things |
|
|
Symbiotic Relationships |
Mutualism-both benefit Ex: (the clownfish feed on small fish, call Martin vertebrae’s, that have the potential to harm to sea anomie) Commensalism-one benefits while the other is unaffected Ex: (Remora fish attaches itself to the leopard shark without hurting the shark) Parasitism-one benefits at the hosts expense Ex: (leeches can attach themselves to loggerhead turtles and use the turtle to lay their eggs within them as well as use them for food. The loggerhead turtles can suffer from diseases caused by the leeches) |
|
|
Matching definitions of biomes |

|
|
|
Ecology Definitions |
Species: a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring Population: a group of individuals that belong to the same species and share the same habitat Community: a combination of different populations that live together in a defined area Ecosystem: a combination of all the living organisms that live in a place, together with their physical environment Biome: a group of ecosystems that share the same climates and typical organisms Biosphere:our entire planet with all its organisms and physical environments, is known as the biosphere |
|
|
Compare and contrast (bubble diagram) |
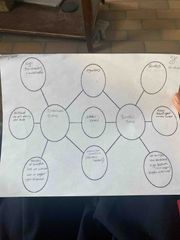
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Who am I? Identify the correct biome |

Rocky shore intertidal zone:
Rocky shore subtidal zone: Mud flat: Estuary: Deep sea floor: Hydrothermal vent: Sandy beach: Cobble beach: Salt marsh: Mangrove forest: |
|
|
Interpret a graph |

Identify what information the chart is meant to convey. Identify information contained on each axis. Identify range covered by each axis Look for patterns or trends. Read the specific data. Data is typically read as [number of Y's per X]. |
|
|
Ecology |
the study of organisms and how they interact with the environment around them |
|
|
How do oysters, barnacles and clams feed? |
They are filter feeders, since they can’t move they fillter the water for any living organisms floating in it. |
|
|
What types of organisms do estuaries support? |
Fish, shellfish, lobsters, sea grasses |
|
|
What did dolphin seals and other mammals eat? |
Fish, squid, jellyfish |
|
|
What two ingredients make estuaries suitable for plants and animals? |
Nutrients and light |
|
|
What two ingredients make estuaries suitable for plants and animals? |
Nutrients and light |
|
|
How many of the world's 10 largest urban areas are built on estuaies? What concerns might this cause for wildlife |
6, pollution in the water from automobiles that could harm the wildlife |
|
|
What are the main limiting factors of aquatic organisms? |
The avilability of Sunight, concentration of dissolved oxygen and nutrients |
|
|
Aquatic biomes are divided into zones based on the amount of —— they receive? |
Sunlight |
|
|
What defines where the aphotic zone begins |
It begins where there’s less 1% of sunlight reaches |
|
|
Would you expect to find algae in the aphotic or photic zone of an aquatic biome? Why? |
The photic zone as phytoplankton carry out the photosynthesis providing the base of the food web |
|
|
Would you expect to find more dissolved nutrients near the shore of a lake or the middie of a lake? Why? |
Near the shore as most nutrients enters the water from the land through runoffs |
|
|
Aquatic biomes in the ocean are called ——- biomes |
Marine |
|
|
You find an organism that has special organs for excreting excess salt. Were you expect this organism to be from |
The ocean because the ocean has more salt in it than a river or lake |
|
|
The narrow strip along the coastline covered by water at high tide, and exposed to air at low tide is known as the —— zone |
Intertidal zine |
|
|
What is a chemoautotroph? Where do we find them in the ocean? |
An organism that makes its own food through the use of chemical energy They are mostly found by deep sea vents in areas with no sunlight |

