![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is leptin? |
an anti obesity and energy sufficiency signal. Produced from fat cells and is correlated to amount of fat, works on neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. Decreases food uptake and increases expenditure. prevents starvation response |
|
|
What is the implication of agouti in obesity? |
Encodes a protein that normally antagonises melanocortin receptor to control pigment. Obesity results from expression of agouti in the CNS, antagonises melanocortin 4 receptors |
|
|
What is glycogen |
stored from of glucose |
|
|
Risk factors of T2D |
FA, inflammatory and cytokines, mito dysfunction, amyloid protein deposists in pancrease |
|
|
Name three genes linked to MODY |
HNF1A, HNF4A, HNF1B |
|
|
What do alpha and beta cells of the pancreas produe |
alpha - glucagon and beta - insulin |
|
|
What is glucolipotoxicity |
deleterious effects of increased glucose and FA on beta cells. decrease in insulin secretion, gene expression but still apop due to influx of glucose. Causes oxidative stress which decreases glucokinase and secretion of insulin. PDX decreases |
|
|
Explain inflammation on islet cells |
the inflam response is caused by dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia and increased adipokines. modulation of IL-1b is a therapeutic agent |
|
|
What are inflammasomes |
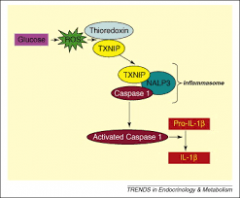
multiprotein danger sensing strucutres activated by hyperglycemia. Eventually produce active IL-1beta |
|
|
What is the effect of IL1 receptor signalling |
Creates a signalling cascade activating NFkB and AP-1, a transcription factor for differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis. NFkb then enhance B cells, controls DNA , cytokine production and cell survival. responds to oxidised LDL, a regulator of the immune system |
|
|
What cytokines are targeted |
anti-TNF, anti-IL1, anti-IL6, anti-TNFR5 |
|
|
What are the stages of plaque formation |
1. Calcification 2. Plaque rupture 3. Heamoraghe 4. Fragmentation 5. Weakening of the arterial wall |
|
|
Define familial hypercholesterolemia |
Congenital disease where LDL are not synthesised and chol in blood increases. Cuases athero, xanthomas |
|
|
what are the effects of oxidised LDL on endothelial cells |
promotes: adhesion molecules, oncoyte chemotactic protein, marcophage stimulating factor, matrix metalloproetinase I reduces: NO, prostaglandins, protein C, plasminogen activator |
|
|
what are the effects of oxidised LDL on monocyte and macrophages |
scavenger receptor increasing uptake of ox LDL, cytokines, APC |
|
|
what are the effects of ox LDL on muscle cells |
prolif, platelet derived growth factor, metalloporteinase expression, apop |
|
|
what is atherogenesis and what is it caused by? |
Disorder of the artery wall and is in response to injury, retention, altered permeability, oxlipid, LDL with proteoglycan, endothelial function, infection, inflammation |
|
|
Name three adipocytokines |
leptin, TNFa, IL6, adiponectin |
|
|
How does lipoprotein change in obesity |
LDL size: inccreases, density increases, more susceptible to oxidation |
|
|
What is TNFalpha |
inhibits adipocyte differentiation, stimulates lipid mobilisation, could reduce NO by decreasing arginine. reduces eNOS. Increases NADPH leading to increased superoxide anion and decreases NO |
|
|
What is IL6 |
increases expression of adhesion molecules and secretion of cytokines by endothelial cells, MCP-1 from macrophages, regulating migration, |
|
|
what is adiponectin |
reduced in obesity. It increases FA oxidation, it increases glut4, and decreases acetyl coA carboxylase. it reduces NFkB |
|
|
What is the lipoprtoein profile in diabetics |
increased LDL, less HDL, |
|
|
three effects of insulin |
decreases VLDL secretion - enhances aopB degradation as normlaly it is targetted by it Stimulates LPL - lipoprtoien lipase which hyrodlyses TAG stimulates PPAR alpha which increases HDL asscaited aopA1 |
|
|
Why is omega 3 important |
an essential fatty acid that regulates plasma cholesterol by modulating VLDL secretion, steroyl coA desatruase (FA metab, steroic acid produced from oleic acid) apo B, and HDL |
|
|
What is glycation |
covalent boding of a protein/lipid with a sugar. Glucose reacts with amino acids to form a schiff base = ketomaine. Produces AGE's |
|
|
What are the effects of glycation |
LDL are more susceptible to oxidation as the lipops have been glycated, and reduces the activity of paraoxonase (anti ox) |

