![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Three-Component Model of |
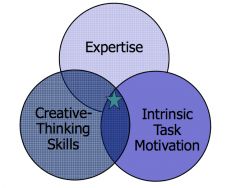
|
|
|
What Is Motivation? |
The processes that accounts for an individual’s intensity, direction, and |
|
|
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory |
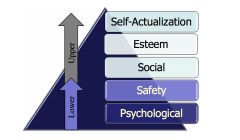
|
|
|
Douglas McGregor’s X & Y |
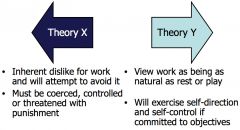
|
|
|
Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory |
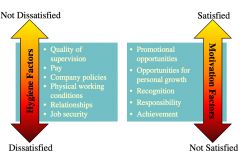
|
|
|
McClelland's Theory of Needs |
Need for Achievement (nAch) |
|
|
Contemporary Theories of Motivation: Self-Determination Theory |
People prefer to have control over their actions so when they feel they are forced to do something they previously enjoyed motivation will decrease
Verbal rewards increase intrinsic motivation, while tangible rewards undermine it |
|
|
Contemporary Theories of Motivation: Goal-Setting Theory |
Goals increase performance when the goals are: |
|
|
Contemporary Theories of Motivation: Management by Objectives (MBO) |
Converts overall organizational objectives into |
|
|
Contemporary Theories of Motivation: Self-Efficacy or Social Learning Theory |
Individual’s belief that he or she is capable of performing a task |
|
|
Contemporary Theories of Motivation: Equity Theory |
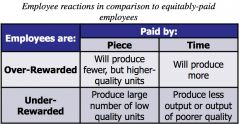
Employees weigh what they put into a job situation (input) against what they get from it (outcome).
|
|
|
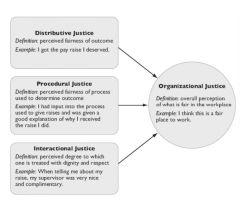
Equity Theory: Forms of Justice |
|

