![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
HORMONES
|

|
|
|
|
Carbohydrates (CHO)
|
organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen in various combinations.
|
|
|
|
Simple Carbohydrates
|
are usually known as sugars, can be subdivided into 2 groups:
disaccharides & monosaccharides. (think of saccharine as a non caloric sweetner). |
usually refers to table sugar, or sucrose, a disaccharide and the monosaccharides.
|
|
|
Complex carbohydrates
|
commonly known as starches, are generally formed when 3 or more glucose molecules combine.
a.k.a Polysaccharides |
foods high in starch, such as bread, cereals, fruits, & veggies.
|
|
|
Digestion
|
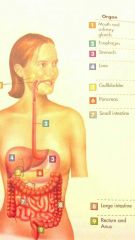
|

|
|
|
Carb Loading
|
also called glycogen loading and glycogen super compensation, is a dietary technique designed to promote a significant increase in the glycogen content in the liver & the muscles in an attempt to delay the onset of fatigue.
|
|
|
|
Dietary Fiber
|
Non digestible carbohydrates and lignin that are intrinsic and intact in plants.
|
|
|
|
Types of Fat
|

|
|
|
|
Cholesterol
|
one of the lipids known as sterols. It is not a fat, but is a fat-like pearly substance found in animal tissues.
|
It is not an essential nutrient for humans BC it is manufactured naturally in the liver.
|
|
|
What are the major functions of the body lipids?
|
•Structure
•Metabollic Regulation •Energy Source |
|
|
|
(EAA) Essential Amino Acids
|
amino acids that must be obtained in the diet, and can not be manufactured in the body.
|
|
|
|
Protein Needs Based on Age
|

|
|
|
|
Function of Protein
|

|
|

