![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
652 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Understand the differences between authoritative (decisive), democratic (inclusive), and laissez-faire (hands-off) leadership. |
Leadership Styles Comparison |
|
|
Interactional vs. Transformational Leadership |
Interactional is about how leaders and followers interact, while transformational is about inspiring positive change. |
|
|
These theories say that the right leadership style depends on the situation or context. |
Situational and Contingency Theories: |
|
|
Combining leadership (inspiring) and management (organizing) skills is crucial for the success of healthcare organizations. |
Integration of Leadership and Management: |
|
|
Situation: You're a BSN-prepared nurse in a hospital. You notice a recurring issue with medication errors due to poor communication between nurses and doctors.Application: |
You take the lead in implementing a standardized communication system that improves patient safety and reduces errors. |
|
|
Situation: You're working in a community health clinic with various healthcare professionals (doctors, social workers, pharmacists) caring for a diabetic patient.Application: |
You regularly meet with the team to discuss the patient's progress, adjust the care plan, and ensure everyone is on the same page to improve the patient's health outcomes. |
|
|
Situation: As a BSN nurse, you're assigned to care for a diverse group of patients in a general medical-surgical unit.Application: |
Your broad nursing knowledge allows you to provide comprehensive care to patients with various conditions, from post-surgery recovery to chronic disease management. |
|
|
Situation: You're a nurse manager in a busy emergency department. The department is facing resource allocation challenges during a surge of patients.Application |
Your leadership involves optimizing staffing, streamlining processes, and ensuring the department operates efficiently during high-demand periods. |
|
|
Situation: You're an MSN-prepared nurse working in population health. You're coordinating a community vaccination program.Application: |
You collaborate with public health officials, community organizations, and volunteers to ensure the program reaches as many people as possible, improving both patient and population health. |
|
|
Situation: You're working in a specialized area, such as nurse anesthesia or nurse practitioner, and you're managing complex patient cases.Application |
Your advanced knowledge and skills enable you to provide expert-level care, diagnose and treat patients, and contribute to improved health outcomes. |
|
|
Situation: You're a nurse executive in a large hospital. There's a need to build stronger relationships between nursing staff and hospital administration.Application: |
You initiate regular meetings, listen to concerns, and foster open communication to build trust and collaboration among the teams. |
|
|
emphasizes control, leaders or managers |
Manager |
|
|
increases productivity by maximizing workforce effectiveness, leadership or management |
leadership |
|
|
look forward and imagine the possibilities that the future may bring in order to set direction , leaders or managers |
leaders |
|
|
inspires change , leadership or management |
leadership |
|
|
requires vision, leadership or management? |
leadership |
|
|
requires imagination, leadership or management |
leadership |
|
|
requiresabstract thinking, leadership or management |
leadership |
|
|
requires ability to articulate , leadership pr management? |
leadership |
|
|
an aptitude to self, leadership or management |
leadership |
|
|
understanding the external environment, leadership or management |
leadership |
|
|
requires risk taking, leadership or management |
leadership |
|
|
requires confidence in the face of uncertainty, leadership or management |
leadership |
|
|
is accountable to the entire organization , leadership or management |
leadership |
|
|
manages transformation , leadership or management |
management |
|
|
requires tenacity , leadership or management |
management |
|
|
requires specific, leadership or management |
management |
|
|
requires concrete data, leadership or management? |
management |
|
|
requires ability to interpret, leadership or management |
management |
|
|
requires an aptitude to teach, leadership or management |
management |
|
|
requires understanding of how work gets done inside the organization, leadership or management? |
management |
|
|
requires self discipline, LEADERSHIP or management |
management |
|
|
requires blind commitment to completing the task at hand , leadership or management |
management |
|
|
is accountable to the team , leadership or management |
management |
|
|
Managers used to mainly focus on making sure everyone did their jobs efficiently (like checking off tasks on a to-do list). Now, to achieve their goals, they also need to be good at (3) |
1. VISIONING 2. MOTIVATING 3. INSPIRING
|
|
|
This means having a clear picture of where they want their team or company to go in the future. |
VISIONING |
|
|
It's about getting their team excited and willing to work hard. |
MOTIVATING |
|
|
Leaders show by example and create a positive work atmosphere. |
INSPIRING |
|
|
OFTEN DO NOT HAVE DELEGATED AUTHORITY BUT OBTAIN THEIR POWER THROUGH OTHER MEANS SUCH AS INFLUENCE, leaders or managers |
LEADERS |
|
|
HAVE A WIDER VARIETY OF ROLES, leaders or managers? |
LEADERS |
|
|
MAY OR MAY NOT BE PART OF A FORMAL ORGANIZATION, leaders or managers |
LEADERS |
|
|
EMPHASIZE INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS, leaders or manager? |
LEADERS |
|
|
DIRECT WILLING FOLLOWERS, leaders or managers? |
LEADERS |
|
|
HAVE GOALS MAY OR MAY NOT REFLECT THOSE OF THE ORGANIZTION, leaders or managers |
LEADERS |
|
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TIuMMwsSg-Y |
note:12:02
|
|
|
BOOK |
NOTE |
|
|
BOOK |
NOTE |
|
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=64d9X7KT2vk |
NOTE |
|
|
https://quizlet.com/501475847/31qwexp-nclex-questions-for-leadership-and-management-flash-cards/ |
Note: which behaviour demonstrates the nurse's competency as an emotionally intelligent leader? |
|
|
https://quizlet.com/530627956/leadership-and-management-nclex-type-questions-flash-cards/ |
N: a nurse manager considers yhat there are five rights of delegation in... |
|
|
https://nurseslabs.com/leadership-management-nursing-test-bank-nclex-questions/ |
NOTE: QUIZ #1 > #7 |
|
|
https://quizlet.com/489867408/nursing-leadership-and-management-nclex-questions-flash-cards/ |
N: registered nurse is discussing the characteristics of anorexia... |
|
|
https://quizlet.com/576434366/leadership-nclex-questions-flash-cards/ |
NOTE : Leadership is the process of influencing people to accomplish goals by inspiring confidence and support among followers. |
|
|
https://www.rnpedia.com/practice-exams/nclex-exam/nclex-practice-exam-leadership-management-bioethics-research-1/ |
N: q#5 she knows that there are external |
|
|
https://www.scribd.com/document/399852477/Ncm-119-Midterm-Exam |
NN |
|
|
BOOK |
NOTE |
|
|
BOOK NOTE |
NN |
|
|
BOOK NOTE |
NNN |
|
|
BOOK NOTE |
BOOK NOTE |
|
|
THE NURSE MANAGER AXPANDING RESPONSIBILITIES AND DEMANDS 1 |
GOOGLE DRIVE NOTE |
|
|
THE NURSE MANAGER AXPANDING RESPONSIBILITIES AND DEMANDS 2 |
google drive note |
|
|
are assigned a position by the organization , leaders or managers? |
managers |
|
|
have a legitemate source of power due to delegated authority that accompanies their position |
managers |
|
|
have specific duties and responsibilities they are expected to carry out, Leaders or managers |
managers |
|
|
emphasize control, decision making, decision analysis and results, leaders or managers? |
managers |
|
|
manipulate people , the environment, money, time, and other resources to achieve the goals of the organization, leaders or managers |
managers |
|
|
have a greater formal responsibility and accountability for rationality and control, manager or leaders |
managers |
|
|
direct willing and unwilling subordinates leaders or mabagers? |
managers |
|
|
direct willing and unwilling subordinates, leaders or managers |
managers |
|
|
often do not have delegated authority but obtain power through other means, such as influence. Leaders or managers |
leaders |
|
|
have a wider variety of roles leaders or managers |
leaders |
|
|
focus on group process, information gathering, feedback and empowering others, leaders or managers |
leaders |
|
|
may or may not be part of the formal hierarchy of the organization, leaders or managers |
leaders |
|
|
emphasize interpersonal relationships, leaders or managers |
leaders |
|
|
direct willing followers, leaders or managers? |
leaders |
|
|
have goals that may or may not reflect those of the organization, leaders or managers? |
leaders |
|
|
novice means |
beginner |
|
|
aptitude means |
talent; ability |
|
|
leadership means |
motivating people to do something |
|
|
motivate their followers to do the right things,leader or manager |
leader |
|
|
WE NEED TO DO THINGS RIGHT, MANAGER OR LEADER |
manager |
|
|
change agent, always aim for change and development. LEADER OR MANAGER |
leader |
|
|
continuity: more firm agent, being spontaneous on what you do. Leaders or managers |
manager |
|
|
It is the process of coordination and integration of resources to accomplish specific goals. , leadership or management |
management |
|
|
It includes the activities of planning, organizing, coordinating, directing, and controlling. Management functions or leadership roles |
management |
|
|
. It is a process of planning and directing human effort to achieve established objectives.leadership or management? |
management |
|
|
It is the directing of the organizations' money, facilities, and supplies to achieve results.leadership or management |
management |
|
|
Surveys their followers' needs and sets goals for them. |
transactional leader? |
|
|
who are focused on maintenance and management of ongoing and routine work. |
transactional leader? |
|
|
Leadership is founded on trust. Behaviors that build trust include (3) |
1. sharing relevant information 2. reducing controls 3. meeting expectations. |
|
|
Inspiring a vision is a management function.Leadership or management? |
leadership |
|
|
is focused on task accomplishment leadership or managemnet |
management |
|
|
is more focused on human relationships.leadership or managament? |
leadership |
|
|
The role of the _____ is to provide leadership and direction for all aspects of nursing services with a focus on integrating the system and building a culture. |
nurse executive |
|
|
concentrate on long-term administration of an institution or program that delivers nursing services, focusing on integrating the system and building a culture |
nurse executive |
|
|
A medical-surgical unit reports higher rates of patient satisfaction coupled with high rates of staff satisfaction and productivity. Which of the following is attributed to the data findings: |
effective leadership |
|
|
A nurse is caring for an elderly patient who was admitted after sustaining a fall at home. When creating a care plan for the patient, she requests that the doctor order a home health visit to assess for home safety and medication compliance. In addition, the nurse is concerned about the nutrition of the patient and requests a dietitian evaluation. The nurse is demonstrating which of the following leadership skills: |
care coordination |
|
|
is the delivery of nursing services that involves the organization and coordination of complex activities. The nurse uses managerial and leadership skills to facilitate delivery of quality care. |
care coordination |
|
|
During a staff meeting, a group of RNs has complained that medications are not arriving to the unit in a timely manner. The nurse manager suggests that the group resolve this issue through the development and work of a multidisciplinary team led by one of these RNs. This scenario demonstrates |
empowerment |
|
|
is the giving of authority, responsibility, and the freedom to act. |
empowerment |
|
|
father of scientific management |
frederick W. taylor |
|
|
where workers achieved minimum standards doing the least amount of work possible |
systematic soldiering |
|
|
means of organizing work mst be replaced with scientific methdods
|
traditional rule of thumb |
|
|
Ms. Caputo is newly promoted to a patient care manager position. She updates her knowledge on the theories in management and leadership in order to become effective in her new role. She learns that some managers have low concern for services and high concern for staff. Which style of management refers to this? |
Country Club Management |
|
|
This term typically refers to the overall process of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling an organization's resources and activities to achieve its goals and objectives efficiently and effectively. It encompasses various management functions and approaches to ensure the smooth functioning of an organization. |
organizaton management |
|
|
also known as "indifferent management" or "laissez-faire management," is a style where the manager has low concern for both the tasks at hand and the welfare of the team. In this approach, the manager minimally involves themselves in decision-making and often allows situations to take their own course with little intervention. |
Impoverished Management |
|
|
is a leadership style where the manager focuses on both the welfare of the team members and the accomplishment of tasks. It involves fostering a collaborative and supportive work environment while also striving for high levels of productivity and achieving organizational objectives. This style is often considered effective in balancing both employee satisfaction and goal attainment. |
team management |
|
|
Her former manager demonstrated passion for serving her staff rather than being served. She takes time to listen, prefers to be a teacher first before being a leader, which is characteristic of: |
Servant leader |
|
|
where the former manager demonstrates a passion for serving the staff, takes time to listen, and prefers to be a teacher first before being a leader |
servant leadership |
|
|
is someone who inspires and motivates their team by creating a compelling vision of the future and encouraging innovation and positive change. They focus on developing the potential of their team members and often lead by example. |
Transformational Leader |
|
|
is more focused on the day-to-day operations of a team. They use a system of rewards and punishments to motivate their team to achieve specific goals and meet established standards. emphasize structure and adherence to rules. |
transactional leader |
|
|
characterized by their dedication to serving the needs of their team members and the greater good of the organization. They prioritize the well-being and development of their team and aim to empower others. They often lead through acts of service and humility. |
servant leader |
|
|
characterized by their dedication to serving the needs of their team members and the greater good of the organization. They prioritize the well-being and development of their team and aim to empower others. They often lead through acts of service and humility. |
servant leader |
|
|
possesses a magnetic personality and the ability to inspire and influence others through their charm and charisma. They often have a strong vision and the power to rally others behind their ideas. based on personal appeal and persuasi |
Charismatic Leader: |
|
|
On the other hand, Ms. Caputo notices that the Chief Nurse Executive has a charismatic leadership style. Which of the following behaviors best describes this style? |
Possesses inspirational quality that makes followers get attracted to him and regard him with reverence. |
|
|
ave a magnetic personality that inspires and attracts followers. |
charismatic |
|
|
Certain personal qualities and traits to be associated with success in managerial roles. |
effective communication, emotional intelligence, adaptability, and the ability to motivate and inspire others, |
|
|
She reads about Path-Goal theory. Which of the following behaviors is manifested by the leader who uses this theory? |
Recognizes staff for going beyond expectations by giving them citations. |
|
|
suggests that a leader's role is to assist their followers in achieving their goals and to clarify the path to goal attainment. This can involve providing rewards and recognition when staff members go above and beyond expectations to motivate and reinforce their positive behavior. |
path-goal theory |
|
|
One leadership theory states that “leaders are born and not made,” which refers to which of the following theories? |
trait |
|
|
She came across a theory which states that the leadership style is effective depends on the situation. Which of the following styles best fits a situation when the followers are self-directed, experts, and are matured A. Democraticindividuals? |
Laissez-faire |
|
|
allows self-directed and mature individuals to have a high degree of autonomy and control over their work. It is particularly effective when the followers are capable and experienced in their roles and do not require close supervision. |
Laissez-faire leadership |
|
|
which emphasizes efficiency and productivity in the workplace. |
SCIENTIFIC MANAGEMENT |
|
|
using scientific methods to analyze and optimize work processes to increase efficiency and productivity. This approach often involves breaking down tasks into smaller, specialized components and standardizing work methods. |
Taylor (Frederick Taylor) - Scientific Management: |
|
|
optimizing workflows in a healthcare setting to reduce wait times and improve patient care. |
Scientific Management:(Frederick Taylor) |
|
|
characterized by a hands-off approach where leaders provide minimal guidance or direction to their team. |
Laissez-Faire Leadership: |
|
|
This style is more about leadership than traditional management. leaders trust their team members to make decisions and manage their work independently. |
Laissez-Faire Leadership: |
|
|
when nursing teams are highly skilled and self-motivated, allowing them to work autonomously. However, it may not be suitable in all nursing contexts, especially when close supervision and direction are needed. |
Laissez-Faire Leadership: |
|
|
focuses on the structure and organization of management and administration. |
Max Weber - Bureaucracy: |
|
|
emphasizes a structured hierarchy, clear roles and responsibilities, and standardized procedures in organizations. It is more related to management and organizational structure than leadership. |
Max Weber - Bureaucracy: |
|
|
to ensure clear roles and responsibilities, adherence to protocols, and efficient organizational structures. Nursing administrators may use these principles for effective management of healthcare facilities. |
Max Weber - Bureaucracy: |
|
|
optimize means |
make something as effective, efficient, or functional as possible; enhance; maximize |
|
|
a well known german sociologist, began to study large scale organizations to determine what made some workers more efficient than others. |
max weber |
|
|
VINCE MESSENGER PIC |
Note |
|
|
TEST PAPER GALLER NOTE |
#2 |
|
|
Book note |
Nn |
|
|
Note phone |
Note |
|
|
throughout history, nursing has been required to respond to changing technological and social forces |
nursing management |
|
|
organized nursing services require nurse administrators who are eknowledgeable, skilled, and competent in all aspects of management |
nursing management |
|
|
today's greater emphasis on the business of healthcare, nurse managers are being involved in financial and marketing responsibilities |
nursing management |
|
|
today's healthcare assumes the following areas: (3) |
a.health care organizations are redesigned to meet the chaninging client needs b. there's a shift from episodic care to preventive or restorative care c. home health, long term care, and community mental health are on the rise |
|
|
have an arranged position in the organization, leaders or manager? |
manager |
|
|
have a legitemate source of power due to the delegated authority , leaders or manager? |
manager |
|
|
are expected to carry out specific functions, duties, and responsibilities , leaders or manager? |
manager |
|
|
have a wider variety of roles , leaders or manager? |
leaders |
|
|
emphasize interpersonla relationships, leaders or manager? |
leaders |
|
|
direct the willing followers , leaders or manager? |
leaders |
|
|
Inefficiency: Excessive paperwork and documentation can consume a significant portion of nurses' time.Improvement: |
=Implement electronic health records (EHR) systems to streamline documentation, reducing duplication and enabling easy access to patient information. |
|
|
Inefficiency: Time-consuming medication administration processes. Improvement: |
=Invest in medication dispensing automation systems, barcode scanning, and standardized medication administration procedures to reduce errors and save time. |
|
|
Inefficiency: Ineffective communication during patient handoffs.Improvement: |
=Implement standardized handoff protocols and tools to ensure essential patient information is shared efficiently between shifts. |
|
|
Inefficiency: Wasted time searching for supplies or frequent stockouts. improvements: |
=Adopt a robust supply chain management system, organize supplies logically, and implement just-in-time inventory practices. |
|
|
Inefficiency: Delays in moving patients within the facility.Improvement: |
= Optimize patient transport routes and schedules, use technology for tracking patient movements, and ensure staff availability for timely transfers. |
|
|
Inefficiency: Frequent interruptions during tasks.Improvement: |
= Establish designated "quiet zones" or time blocks for focused work, limit non-essential interruptions, and encourage staff to use communication tools judiciously. |
|
|
Inefficiency: Suboptimal shift schedules leading to burnout and fatigue.Improvement: |
=: Create schedules that consider nurses' preferences and circadian rhythms, and use predictive analytics to optimize staffing levels based on patient needs. |
|
|
where employees' perspectives and contributions are valued, and decisions are made collectively or with input from those directly affected. |
=participatory organization |
|
|
staff nurses are actively engaged in the decision-making process, providing input into planning and changes for their own unit. |
=participatory organization |
|
|
there is an emphasis on involving employees in decision-making and valuing their input. |
=participatory organization |
|
|
The concept of "locus of care" in healthcare refers to the primary or central location where healthcare services are delivered. Traditionally, for many years, _______ hospitals were the primary locus of care, where patients received comprehensive medical treatment for various illnesses and conditions. |
= acute care |
|
|
are expected to beskilled communicators, organizersm and team builders and to be visionary and proactive in preparing for emerging new threats such as domestic terrorism, bilogical warfare, and global pandemics,leaders or managers? |
=managers |
|
|
The theory is that the staff should be nurtured to promote greater leadership competency. |
=peter drucker, participatory organizations |
|
|
According to______, when staff participate in the core functions of management such as planning and changes for their own units, the organization is more effective. |
=peter drucker |
|
|
which gre out of the positive psychology movement (began in the late 1990's), focuses on the development or empowerment of workers strengths as opposed to their weakenesses or areas of needed growth |
=strengths-based leadership |
|
|
strengths-based leadership is part of the development of _____ |
=positive organizational scholarship |
|
|
which focuses on successful performance that exceeds the norm and embodies an orientation toward strengths and developing collective efficacy in organizations. |
=positive organizational scholarship |
|
|
the importane of strengths-based leadership was noted by |
=rath and conchie (2008) |
|
|
the importane of strengths-based leadership was noted by rath and conchie (2008), who completed a review of 30 years of research by the _____ including over 40,000 personal interviews with leaders from around the world and 20,000 interviews with followers to ask why they follow a leader. |
=gallup corporation |
|
|
they found that effective leaders are always investing in strengths but that they consciously and consistently work to use their key strengths to their advantage rather than putting significant effort into being better rounded. |
=rath and conchie (2008) =ambler, 2015 |
|
|
found that the most effective leaders surround themselves with the right people and that they maximize their team, this statement is according to? |
=rath and conchie (2008) =ambler, 2015 |
|
|
this typically requires that leaders create teams that have a balance of strengths in the following 4 leadership domains: (4) |
1. strategic thinking 2. influence 3. relationship building 4. execution |
|
|
effective leaders keep everyone focused on a long term future |
=strategic thinking |
|
|
effective leaders can sell ideas, develop political support, and get people to rally behind a project or an initiative |
=influence |
|
|
effective leaders are able to unite a group of disparate individualsinto a team that works toward a common goal |
=relationship building |
|
|
effective leaders know how to get things done by translating plans into action |
=execution |
|
|
found that the most effective leaders understand their follower's needs |
=rath and conchie (2008)=ambler, 2015 |
|
|
the 4 most common responses about describing what they seek from their leaders |
1. trsut 2. compassion 3. stability 4. hope |
|
|
the concept of level 5 leadership was developed by? |
=jim collins |
|
|
the concept of level 5 leadership was developed b jim collins and published in his classic book, ______ |
=good to great: why some companies make the leap |
|
|
jim collin's level 5 leadership |
1. level 1: highly capable individual 2. contributing team member 3. competent manager 4. effective leader 5. great leader |
|
|
jim collin's level of leadership: where leader makes high quality contributions to their work. posesses useful levels of knowledge and has the talent and skills needed to do a good job |
=level 1: highly capable individual |
|
|
jim collin's level of leadership: where leader is able to galvanize a department or organization to meet performance objectives and achieve a vision |
=level 4: effective leader |
|
|
jim collin's level of leadership: where leader uses knowledge and skills to help their team succeed; works effectively, productively and successfully with other people in their group |
=level 2: contributing team member |
|
|
jim collin's level of leadership: where leader is able to organize a group effectively to achieve specific goals and objectives |
=levle 3: competent manager |
|
|
jim collin's level of leadership: where leader has all of the abilities needed for the other 4 levels, plus a unique blend of humility and will that is required for true greatness |
=level 5: great leader |
|
|
the ability to listen on a deep level and to truly understand |
=servant leader |
|
|
the ability to keep an open mind and hear without judgement |
=servant leader |
|
|
the ability to deal with ambiguity, paradoxes and complex issure |
=servant leader |
|
|
the belief that honestly sharing critical challenges with all parties and asking for their input is more important than personally providing solutions |
=servant leader |
|
|
being clear on goals and good at pointing the direction toward goal achievement without giving orders |
=servant leader |
|
|
the ability to be a servant, helper and teacher first and then a leader |
=servant leader |
|
|
always thinking before reacting |
=servant leader |
|
|
choosing words carefully so as not to damage those being led |
=servant leader |
|
|
the ability to use foresight and intuition |
=servant leader |
|
|
seeing things whole and sensng relationships and connections |
=servant leader |
|
|
they also though demonstrate humility and seek success for the team, rather than for self serving purposes, a core component of another 21st century leadership theory known as? |
=servant leadership |
|
|
although _______ deveoped the idea of servant leadership more than 35 years ago, it continues to greatly influence leadership thinking in the 21st century. |
=greenleaf (1977) |
|
|
noticed that most successful managers lead in a different way from traditional managers |
=greenleaf 1977 |
|
|
servant leaders are more concerned with the needs of other than themselves and lead through their service, statement by? |
1. greenleaf 1977 2. gill, 2015 |
|
|
when national president gets elected by virtue of his being a son of a former president, the people who voted him into office must have this leadership theory in mind: |
= great man theory |
|
|
when the leader is consistently honestm he/she has: |
= personal integrity |
|
|
which type of leadership is shown when the leader is permissive with little or no control |
=laissez-faire |
|
|
the transformational leader possesses the following chracteristics: (3) |
1. identifies common values 2. empowers others 3. is committed |
|
|
the transformational leader possesses the following chracteristics except: |
1. identifies common values 2. empowers others 3. is committed 4. looks at causes answer: 4 |
|
|
the traditional manager, concerned with the day to day operations is called a: |
=transactional leader |
|
|
the tri dimensional leadership effectiveness model was developed by |
=hersey and blanchard |
|
|
when the nurse leader-managers has high concern for people but low regard for production, his/her management style is: |
=country club management |
|
|
Those that play a role in the organization's health and performance |
Stakeholder |
|
|
Example of internal stakeholders |
1. Nurses 2. Dietitians |
|
|
Example of external stakeholders |
Philhealth Public health units |
|
|
A system of symbols and interactions unique to each organization |
Organizational culture |
|
|
It is the way of thinking, behaving and believing that members of a unit have in common |
Organizational culture |
|
|
Organizational effectiveness, to consider: (3) |
1. Size 2. Capability of people 3. Worker commitment |
|
|
In order for the Organization to be effective: (7) |
1. Clearly defined structure 2. Few management levels, shortest chain if command 3. Staff to see their tasks fit into the main task of the organization 4. Enhance communication 5. Facilitate decision making 6. Informal groups encourage to develop a sense of community and belonging 7. Facilitate the development of future leaders
|
|
|
who was regarded as the father of scientific management? |
=federick taylor |
|
|
when the right worker is hired, trained and promoted, this scientific management principle is called |
=scientific personnel system |
|
|
managers and workers would be satisfied if financial rewards were adequate as a result of increased productivity |
=scientific management by frederick taylor |
|
|
, focused on optimizing efficiency through the systematic study of work processes and the use of financial incentives to motivate workers to increase their productivity. |
=scientific management by frederick taylor |
|
|
It emphasized that if workers were rewarded financially based on their increased output, both managers and workers would be satisfied with the results. |
=scientific management by frederick taylor |
|
|
financial incentives would lead to higher productivity and therefore job satisfaction. |
=scientific management by frederick taylor |
|
|
the first to identify the management function was |
=henri fayol |
|
|
which phase of the management process will encompass determining philosophy, goals, objectives, policies, procedures and rules? |
=planning |
|
|
establishing the structure to carry out plans and patient care delivery takes place during |
=organizing |
|
|
motivating the staff, managing conflict, delegating, communicating and facilitating collaboration take place during: |
=directing |
|
|
when the nurse manager is involved in recruitment, interviewing, hiring and orienting staff, she is doing: |
=staffing |
|
|
when the head nurse evaluates the performance of her staff, she is performing |
=controlling |
|
|
the concepts of participatory and humanistic management, emphasizing people rather than machines took place during the |
=human relations era |
|
|
the human relations theory of management was spurred by the |
=hawthorne experiment |
|
|
follows planning |
=organizing, organizational structure |
|
|
second phase of the management process |
=organizing, organizational structure |
|
|
relationships are defined |
=organizing, organizational structure |
|
|
procedures are outlined |
=organizing, organizational structure |
|
|
equipment is readied |
=organizing, organizational structure |
|
|
tasks are assigned |
=organizing, organizational structure |
|
|
establishes a formal structure |
=organizing, organizational structure |
|
|
the way in which a group is formed, its lines of communication, and its means for channeling authority and making decisions |
=organizational structure |
|
|
organizational structure: provides a framework for defining managerial authority,responsibility, and accountability |
=FORMAL STRUCTURE |
|
|
organizational structure: roles and functions are defined and systematically arranged |
=FORMAL STRUCTURE |
|
|
organizational structure: ranks and hierarchy are identified |
=FORMAL STRUCTURE |
|
|
German social scientist |
=max weber |
|
|
Father of Organizational Theory |
=max weber |
|
|
founded the bureaucracy |
=max weber |
|
|
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE: social network of employees |
=informal structure |
|
|
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE: own communication network – grapevine – the heart of the informal organization (Hartzell, 2003-2016) |
=informal structure |
|
|
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE: includes social media sites and electronic communication |
=informal structure |
|
|
CHARACTERISTICS OF BUREAUCRACIES (6) |
1. division of labor 2. hierarchy of authority 3. impersonality of iterpersonal relationships 4. a system of procedures for dealing with work situations 5. a system of rules covering the rights and duties of each position 6. selection for employment and promotion is based on technical competence |
|
|
bureaucracy was popularized during the? |
=industrial revolution |
|
|
characteristics of bureaucracies: work divided into units or departments |
=division of labor |
|
|
characteristics of bureaucracies: superiors are separated from subordinates |
= HIERARCHY OF AUTHORITY |
|
|
characteristics of bureaucracies: differentiated remuneration |
= HIERARCHY OF AUTHORITY |
|
|
characteristics of bureaucracies: authority is recognized |
= HIERARCHY OF AUTHORITY |
|
|
characteristics of bureaucracies: privileges are allotted |
= HIERARCHY OF AUTHORITY |
|
|
characteristics of bureaucracies: promotions are rewarded |
= HIERARCHY OF AUTHORITY |
|
|
characteristics of bureaucracies: no personal favorites |
=IMPERSONALITY OF INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS |
|
|
COMPONENTS OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE (4) |
1. Relationships and Chain of Command 2. Span of Control 3. Managerial Levels 4. Centrality |
|
|
components of organizational structure: organization chart defines______ relationship within the institution |
=formal |
|
|
components of organizational structure: unbroken solid lines – |
= depict lines of communication and authority |
|
|
components of organizational structure: solid vertical lines [ | ] |
=depict official chain of command |
|
|
components of organizational structure: level of position in the chart |
= signifies power and status |
|
|
components of organizational structure: dotted/broken lines ( - - - |
= represent staff positions, advisory |
|
|
components of organizational structure: unity of command |
▪ vertical solid line ▪ one person/one boss |
|
|
solid horizontal line ( ––– ) |
=represent communication between people of similar responsibility and power but different functions |
|
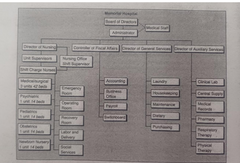
|
organizational chart |
|
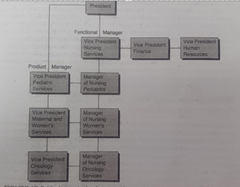
|
matrix organizational structure |
|

|
flattened organizational structure |
|
|
when the nurse leader-managers has high concern for people but low regard for production, his/her management style is: |
country club management |
|
|
In an experiment at a company, they found that when they made the lights dimmer, people actually worked better and got more done (when lighting was reduced, productivity increased). This discovery helped shape the idea that how people feel and work together (human relations) is important in the workplace. What company is this? |
western electric company in Chicago |
|
|
when the nurse leader-manager has high concern for both production and people, his/her management style is |
team management |
|
|
the head nurse seems not to care about her staff nurse's efficiency nor she shows concern for relationship with them. Her management style could be? |
impoverish management |
|
|
when the leader achieves bare minimum for work production and mere getting along with subordinaet, she has: |
middle of the road management |
|
|
the manegerial grd theory was developed by |
blake and mouton |
|
|
mrs. santos, a hospital supervisor observes that mrs. cruz, one of the head nurses in the floor is very competent in her work and demonstrates favorable attitude towards supervision. Mrs. santos's leadership style under the situational leadership model should be: |
delegating |
|
|
when the nursing staff is new to the unit, the most appropriate style can be: |
telling |
|
|
when the nurse leader-manager provides direction and support to her staff, she is using which leadership style? |
selling |
|
|
theory x managers believe that their employees are lazy; theory Y managers think that their employees ennjoy their work and are self motivated. Theory X and Y was developed by: |
douglas mcgregor |
|
|
the concept of bureaucracy was introduced by |
max weber |
|
|
when a leader anticipates the effects of his/her decision, which of the ff roles is assumed? |
risk-taker |
|
|
the leader may not be perfect in his traits but he/she demonstrates professional and ethical behavior behore his/her subordinates, he/she is a: |
role model |
|
|
the aristotelian philosophy that asserts that some people are born to lead belong to: |
great man theory |
|
|
classifying leadership theory that believes leadership behavior generally determined by the relationship between the leader's personality and the specific situation: |
interactional theory |
|
|
people are very complex and highly variable |
assumption of open systems theory |
|
|
people's motivates do not stay constant but change over time |
assumption of open systems theory |
|
|
goals can differ in various situations |
assumption of open systems theory |
|
|
servant leadership was coined by |
greenleaf |
|
|
the assumption that both leaders and followers have the ability to raise each other to higher levels of motivation and morality is |
transformational leader |
|
|
the leader's ability to picture some future state and describe it to the others so they will begin to share the dream is the leader's: |
values |
|
|
focuses on management tasks |
transactional leader |
|
|
is a caretaker |
transactional leader |
|
|
examines causes |
transactional leader |
|
|
transactional leader DO NOT empowers others |
review |
|
|
when managers do coaching and mentoring, they assume which of the following tasks: |
enabling |
|
|
articulate, effective, and enthusiastic sharing of the goals and culture of the organization is: |
mobilizing |
|
|
the skills needed to be on effective leader are dynamic and change constantly in response to a rapidly changing world in which we live. this statement is: true or false |
true |
|
|
the concept of leadershup and management are symbiotic and synergistic |
integrating leadership and management skills |
|
|
every nurse is a leader and manager at some level |
integrating leadership and management skills |
|
|
it is important for nurses to develop skill in leadership roles and management functions |
integrating leadership and management skills |
|
|
when nurse leader managers think long term, they are: |
visionary |
|
|
mrs.z a head nurse of medical floor is capable of coping and resolving conflicting opinion of her staff. she is said to be: |
politically astute |
|
|
management functions include: |
planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling |
|
|
number of people directly reporting to an one manager |
=span of control |
|
|
examples of top level of managers (3) |
1. Chief Nursing Officer 2. Chief Executive Officer 3. Chief Financial Officer |
|
|
Chief Nursing Officer , what level of managers? |
= top level |
|
|
Chief Executive Officer, what level of managers? |
=top level |
|
|
Chief Financial Officer, what level of managers? |
= top level |
|
|
examples of middle level of managers |
1. Unit Supervisor 2. Department Head 3. Director |
|
|
unit supervisor, what level of managers? |
=Middle Level |
|
|
Department Head , what level of managers? |
=Middle Level |
|
|
Director, what level of managers? |
=Middle Level |
|
|
examples of first level of managers: |
1. Charge Nurse 2. Team Leader 3. Primary Nurse |
|
|
Charge Nurse , what level of managers? |
=First Level |
|
|
Team Leader , what level of managers? |
=First Level |
|
|
Primary Nurse, what level of managers? |
=First Level |
|
|
=Look at organization as a whole as well as external influences -Scope of Responsibility, What level |
top level of managers |
|
|
=Focus is on integrating unit-level day-to-day needs with organizational needs |
Scope of Responsibility, middle level of managers |
|
|
=Focus primarily on day to-day needs at unit level |
Scope of Responsibility, first level of managers |
|
|
Primary Planning Focus, top level of managers |
=Strategic Planning |
|
|
Primary Planning Focus, middle level of managers |
=Combination of long and short-range planning |
|
|
=Short-range, operational planning, Primary Planning Focus |
, first level of managers |
|
|
=More often top-down but receives subordinate feedback both directly and via middle-level managers |
top level of managers, Communication Flow |
|
|
middle level of managers, Communication Flow |
=Upward and downward with great centrality |
|
|
first level of managers, Communication Flow |
=More often upward; generally relies on middle-level managers to transmit communication to top level managers |
|
|
where a position falls on the organizational chart (organizational distance) |
=centrality |
|
|
Evaluates the organizational structure frequently to determine if management positions should be eliminated to shorten the chain of command |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Encourages and guides employees to follow the chain of command and counsels employees who do not do so. Management functions or leadership roles |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Supports personnel in advisory (staff) positions |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Models responsibility and accountability for subordinates |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Assists staff to see how their roles are congruent with and complement the organization’s mission, vision, and goals |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Facilitates constructive informal group structure |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Encourages upward communication |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Fosters a positive organizational culture between work groups and subcultures that facilitates shared values and goals |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Promotes participatory decision making and shared governance to empower subordinates. Management functions or leadership roles |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Uses committees to facilitate group goals, not to delay decisions |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Is knowledgeable about the organization’s internal structure, including personal and department authority and responsibilities within that structure |
=Management Functions |
|
|
Facilitates constructive formal group structure |
=Management Functions |
|
|
Provides the staff with an accurate unit organization chart and assists with interpretation |
=Management Functions |
|
|
When possible, maintains unity of command. Management functions or leadership roles |
=Management Functions |
|
|
Clarifies unity of command when there is confusion |
=Management Functions |
|
|
Follows appropriate subordinate complaints upward through the chain of command. Management functions or leadership roles |
=Management Functions |
|
|
Establishes an appropriate span of control. Management functions or leadership roles |
=Management Functions |
|
|
Strives to create a constructive organizational culture and positive organizational climate |
=Management Functions |
|
|
Uses the informal organization to meet organizational goals |
=Management Functions |
|
|
Uses committee structure to increase the quality and quantity of work accomplished. Management functions or leadership roles |
=Management Functions |
|
|
Works, as appropriate, to achieve a level of operational excellence befitting an organization that would be eligible for Magnet status or some other recognition of excellence. Management functions or leadership roles |
=Management Functions |
|
|
Continually identifies, analyzes, and promotes stakeholder interests in the organization. Management functions or leadership roles |
=Management Functions |
|
|
types of organizational structures |
1. bureacratic/ line organizations 2. ad hoc design 3. matrix structure 4. flat designs |
|
|
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES: authority and responsibilities are clearly defined |
=Bureaucratic / Line Organizations |
|
|
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES: disadvantage of line and staff organization |
=red tape/ channels |
|
|
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES: usually for projects and disbands when the project is completed |
=Ad Hoc Design |
|
|
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES: focuses on product and function |
= Matrix Structure |
|
|
example of matrix structure |
=product: quality of patient care =function: staff education |
|
|
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES: decentralized and remove hierarchical layers |
=flat designs |
|
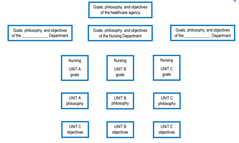
|
sample unit philosophy |
|
|
beliefs that guide societies and organizations behavior |
=values |
|
|
quality having intrinsic worth for a society or an individual and identifies individualism, the pursuit of self-interest, and competition |
=MacPherson, 1987 |
|
|
4 characteristics of a true value by? |
=(McNally, 1980) |
|
|
what are the 4 characteristics of a true value by mcnally 1980 |
1. Freely chosen from among alternatives only after due reflection 2. Must be prized and cherished 3. Must be consciously and consistently repeated 4. Positively affirmed and enacted |
|
|
All nursing staff will recognize the patient’s need for independence and right to privacy and will assess the patient’s level of readiness to learn in relation to his or her illness. |
=sample goals |
|
|
The nursing staff_______ will provide effective patient care relative to patient needs insofar as the hospital and community facilities permit through the use of care plans, individual patient care, and discharge planning, including follow-up contact. |
nursing staff |
|
|
An ongoing effort will be made to create an atmosphere that is conducive to favorable patient and employee morale and that fosters personal growth. |
=sample goals |
|
|
The performance of all employees in the nursing department will be evaluated in a manner that produces growth in the employee and upgrades nursing standards. |
=sample goals |
|
|
All nursing units within County Hospital will work cooperatively with other departments within the hospital to further the mission, philosophy, and goals of the institution. |
=sample goals |
|
|
All nursing units within County Hospital will work cooperatively with other departments within the hospital to further the mission, philosophy, and goals of the institution. |
=sample goals |
|
|
goals should be: |
1. desired results 2. measurable and ambitious 3. realistic |
|
|
“process objectives” VS “outcome objectives” chat gpt |
nn |
|
|
similar to goals but more specific ; specifies how and when the goal is to be accomplished |
=objectives |
|
|
All registered nurses will be proficient in the administration ofintravenous fluids. |
=sample goal |
|
|
All registered nurses will complete Mercy Hospital’s course “IV TherapyCertification” within 1 month of beginning employment. The hospital willbear the cost of this program. |
=sample objectives |
|
|
Registered nurses scoring less than 70% on a comprehensiveexamination in “IV Therapy Certification” must attend the remedial 4-hourcourse “Review of Basic IV Principles” not more than 2 weeks after thecompletion of “IV Therapy Certification.” |
=sample objectives |
|
|
Registered nurses achieving a score of 70% or better on thecomprehensive examination for “IV Therapy Certification” aftercompleting “Review of Basic IV Principles” will be allowed to perform IVtherapy on patients. Individualized plans of remediation will beestablished by the unit manager for employees who fail to achieve thisscore on the examination. |
=sample objectives |
|
|
plans reduced to statement or instructions that direct organizations in the decision making |
=policies |
|
|
derived from the organization’s philosophy, goals, and objectives. ___ are like the rules of the game for an organization. They come from what the organization believes in (philosophy), what it aims to achieve (goals), and the specific things it wants to accomplish (objectives). So, ____ are like the guidelines that help everyone in the organization know what's expected and how things should be done based on the organization's principles and objectives. |
=policies |
|
|
-direct individual behavior toward the organization’s mission and maybe expressed or implied. -are like guidelines that tell people how to behave in a way that supports the goals or mission of the organization. -can be clearly stated (expressed) or understood without being explicitly written down (implied). - - -They help direct individual behavior to align with what the organization is trying to achieve. |
=policies |
|
|
plans that establish customary or acceptable ways of accomplishing a specifictask and delineate a sequence of steps of required action. steps needed to implement a policy. |
=procedures |
|
|
plans that define specific action or non-action |
=rules |
|
|
proactive process |
=planning |
|
|
deliberative process |
=planning |
|
|
considers personal and organizational needs and objectives |
=planning |
|
|
cyclic process |
planning |
|
|
planning is cyclic process: (11) |
1. Unity of goals ❖ Continuous energy ❖ Minimize uncertainty ❖ Focused on the objectives of the organization ❖ Manager’s means of control ❖ Best use of resources ❖ Short- and long-term goals ❖ Leadership skills ❖ Vision and creativity ❖ Flexibility and energy ❖ Precedes all other management functions |
|
|
Assesses the organization’s internal and external environment in forecasting and identifying driving forces and barriers to strategic planning |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Demonstrates visionary, innovative, and creative thinking in organizational and unit planning, thus inspiring proactive rather than reactive planning. Management functions or leadership roles |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Demonstrates visionary, innovative, and creative thinking in organizational and unit planning, thus inspiring proactive rather than reactive planning |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Influences and inspires group members to be actively involved in long-term planning 4. Periodically completes value clarification to increase self-awareness. Management functions or leadership roles |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Encourages subordinates toward value clarification by actively listening and providing feedback |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Communicates and clarifies organizational goals and values to subordinates |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Encourages subordinates to be involved in policy formation, including developing, implementing, and reviewing unit philosophy, goals, objectives, policies, procedures and rules |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Encourages subordinates to be involved in policy formation, including developing, implementing, and reviewing unit philosophy, goals, objectives, policies, procedures and rules. Management functions or leadership roles |
=leadership roles |
|
|
Role models proactive planning methods to subordinates |
=leadership roles |
|
|
considers personal and organizational needs and objectives |
=planning |
|
|
Is knowledgeable regarding legal, political, economic, and social factors affecting healthcare planning |
=management functions |
|
|
Demonstrates knowledge of and uses appropriate techniques in both personal and organizational planning |
=management functions |
|
|
Demonstrates knowledge of and uses appropriate techniques in both personal and organizational planning. Management functions or leadership roles |
=management functions |
|
|
Coordinates unit-level planning to be congruent with organizational goals 5. Periodically assesses unit constraints and assets to determine available resources for planning |
=management functions |
|
|
Develops and articulates a unit philosophy that is congruent with the organizational philosophy |
=management functions |
|
|
Develops and articulates unit goals and objectives that reflect unit philosophy |
=management functions |
|
|
Develops and articulates unit goals and objectives that reflect unit philosophy |
=management functions |
|
|
Develops and articulates unit policies, procedures, and rules that operationalize unit objectives |
=management functions |
|
|
Develops and articulates unit policies, procedures, and rules that operationalize unit objectives. Management functions or leadership roles |
=management functions |
|
|
actively participates in organizational strategic planning, defining, and operationalizing such strategic plans on the unit level |
=management functions |
|
|
planning modes: (4) |
1. reactive planning 2. inactive planning 3. preactive planning 4. proactive/interactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: planning after a problem exists |
=reactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: response to a crisis |
=reactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: hasty decisions and mistakes |
=reactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: maintains the status quo |
=inactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: maintains conformity |
=inactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: changes occur slowly |
=inactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: future oriented |
=preactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: utilizes technology to accelerate change |
=preactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: plays down experience |
=preactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: considers the past, present, and future in planning |
=proactive/interactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: dynamic |
=proactive/interactive planning |
|
|
planning modes: adaptive |
=proactive/interactive planning |
|
|
the planning hierarchy (triangle) |
top- mission > philosophy > goals > objectives > policies > procedures > rules |
|
|
Brief statement identifying the reason that an organization exists and its future aim or function |
=mission statement |
|
|
Highest planning priority |
=mission statement |
|
|
Influences the organization’s philosophy, goals, objectives, policies, procedures, and rules |
=mission statement |
|
|
"County Hospital is a tertiary care facility and provides comprehensive, holistic care to all state residents who seek treatment. The purpose of County Hospital is to combine high-quality, holistic healthcare with the provision of learning opportunities for students in medicine, nursing, and allied health sciences. Research is encouraged to identify new treatment regimens and to promote high-quality healthcare for generations to come." what type of statement is this? |
=sample mission statement |
|
|
flows from the mission statetment |
=philosophy statement |
|
|
Expresses the values and principles of the organization, type of statement? |
=philosophy statement |
|
|
Organizational philosophy-basis for nursing philosophy at the nursing service and unit level, type of statement |
=philosophy statement |
|
|
Fundamental beliefs about nursing and nursing care |
=nursing service philosophy |
|
|
Quality, quantity, and scope of nursing services |
=nursing service philosophy |
|
|
How the nursing department/unit will meet the organizational goals |
=nursing service philosophy |
|
|
"The board of directors, medical and nursing staff, and administrators of County Hospital believe that human beings are unique, due to different genetic endowments, personal experiences in social and physical environments, and the ability to adapt to biophysical, psychosocial, and spiritual stressors. Thus, each patient is considered a unique individual, with unique needs. Identifying outcomes and goals, setting priorities, prescribing strategy options, and selecting an optimal strategy will be negotiated by the patient, physician, and healthcare team.As unique individuals, patients provide medical, nursing, and allied health students invaluable diverse learning opportunities. Because the board of directors, medical and nursing staff, and administrators believe that the quality of healthcare provided directly reflects the quality of the education of its future healthcare providers, students are welcomed and encouraged to seek out as many learning opportunities as possible. Because high-quality healthcare is defined by and depends on technological advances and scientific discovery, County Hospital encourages research as a means of scientific inquiry." type of statement? |
=sample hospital philosophy |
|
|
The_______ phase of the management process is critical and precedes all othe rfunctions. Without adequate _______, the management process fails. |
= planning |
|
|
______ is a proactive function required of all nurses so that personal and organizational needs and objectives can be met. |
=Planning |
|
|
Plans should be___,__, and ____ |
= specific, simple, and realistic. |
|
|
Because a plan is a guide for action in reaching a goal, it must be ______ and allow for_______ as unexpected events occur. |
=flexible; readjustment |
|
|
The manager should include in the actual planning process all people and_____ that could be affected by the plan. |
= organizational units |
|
|
Good plans have a time for evaluation built into them so there can be a midcourse correction if unexpected events occur. |
review |
|
|
Good plans have a time for evaluation built into them so there can be a midcourse correction if unexpected events occur. In simple terms, having a time for evaluation in good plans is like checking in on your progress to make sure everything is going as expected. It's similar to adjusting your course if something unexpected happens, ensuring you stay on track toward your goals. |
review only |
|
|
Most organizations use many types of plans that form a hierarchy from global to specific.The planning hierarchy in most healthcare institutions includes the elements of ___(7) |
=missionstatement, philosophy, goals, objectives, policies, procedures, and rules. |
|
|
The ______ identifies the reason an organization exists. |
=mission statement |
|
|
The ________ flows from the purpose or mission statement and delineates the set ofvalues and beliefs that guides all organizational actions. |
=philosophy |
|
|
A philosophy that is not or cannot be implemented is ______. |
useless |
|
|
Management functions include determining, implementing, and evaluating the unitphilosophy, but leadership roles require an examination of values by managers and theirsubordinates. |
review |
|
|
include determining, implementing, and evaluating the unitphilosophy, management functions or leadership roles |
Management functions |
|
|
A ____ may be defined as the desired result toward which effort is directed. A _____ is theaim of the philosophy. |
=goal |
|
|
______ are similar to goals because they motivate people to a specific end and areexplicit, measurable, observable or retrievable, and obtainable. ________, however, aremore specific and measurable than goals in that they identify how and when the goal is tobe accomplished. |
=Objectives |
|
|
_______ are plans reduced to statements/instructions that direct an organization in its decision making. |
=policies |
|
|
_______ are plans that have been reduced to a sequence of required actions. |
=Procedures |
|
|
____ are plans that define specific action or nonaction and aregenerally included in policy and procedure statements and describe situations that allowonly one choice of action |
=Rules and regulations |
|
|
All planning must include an evaluation step. Philosophies, goals, objectives, policies,procedures, and the need for rules change with time and require periodic reevaluation andprioritization. When we make plans, it's like setting up a roadmap for what we want to achieve. But, just like roads can change or need fixing, our plans might need to change too. So, after we make plans, we have to regularly check if they're still working well and if anything needs to be adjusted. This helps us stay on the right track and make sure our goals and rules still make sense as things change over time. It's like giving our plans a check-up to keep them effective and up-to-date. |
REVIEW ONLY |
|
|
All planning in the hierarchy must flow from, and be congruent with, planning done athigher levels in the hierarchy. That is, a nursing unit’s goals cannot conflict with the overallphilosophy of the central nursing administration or the mission of the organization. |
nn |
|
|
Plans that involve a long time – usually 3 to 10 years – and are very complex are referredto as long-range or strategic plans. Due to rapidly changing technology, increasinggovernment involvement in healthcare, changing population demographics, and reducedprovider autonomy, healthcare organizations are finding it increasingly difficult toappropriately identify long-term needs and plan accordingly. |
Sure, imagine making big plans for the future, like where to build a city or how to run a healthcare system. These are called long-range or strategic plans and usually cover 3 to 10 years. But things are tricky for healthcare because technology changes fast, the government gets more involved, people's ages and numbers change, and doctors have less say. So, healthcare groups struggle to figure out what they'll need in the long run and plan for it. |
|
|
Managers who are uninformed about the legal, political, economic, and social factorsaffecting healthcare may make strategic planning errors that have disastrous implicationsfor their professional development and the financial viability of the organization. |
**Simple Explanation:**Managers need to know about laws, politics, money matters, and social issues in healthcare. If they don't, they might make big mistakes in planning that can harm their career growth and the organization's financial health. |
|
|
Organizations tend to have one of four planning modes: |
reactive, inactivism, preactivism,or proactive |
|
|
FLASHCARDS |
Nn |
|
|
set the overall direction and provide the resources for a healthcare system to work well |
TOP LEVEL MANAGERS |
|
|
who play a crucial role in organizing how things operate within specific units or departments. |
middle-level managers |
|
|
evaluates periodically the effectiveness of the organizational structure for the delivery of patient care. management functions or leadership roles |
leadership roles |
|
|
determines if adequate resources and support exist before making any changes in the organization of patient care |
leadership roles |
|
|
examines the human element in work redesign and supports personnel during adjustment to change. Management functions or leadership roles |
leadership roles |
|
|
inspires the work group toward a team effort |
leadership roles |
|
|
inspires subordinates to achieve higher levels of education, clinical expertise, competency and experience in differentiated practice. Management functions or leadership roles |
leadership roles |
|
|
ensures that chosen nursing care delivery models advance the practice of professional nursing |
leadership roles |
|
|
encourages and supports the use of nursing care delivery models that maximize the abilities of each member on the healthcare team |
leadership roles |
|
|
assures congruence between the organizational mission and philosophy and the patient care delivery system selected for use |
leadership roles |
|
|
assures that the patient and family are the focus of patient care delivery, regardless of which patient care delivery system is used. Management functions or leadership roles |
leadership roles |
|
|
makes changes in work design to facilitate meeting organizational goals. Management functions or leadership roles? |
management functions |
|
|
selects a patient care delivery system that is most appropriate to the needs of the patients being served as well as the expertise of the staffing mix |
management functions |
|
|
uses scientific research and current literature to analyze proposed changes in nursing care delivery models |
management functions |
|
|
uses a patient care delivery system that maximizes human and physical resources as well as time |
management functions |
|
|
uses a patient care delivery system that maximizes human and physical resources as well as time. management functions or leadership roles |
management functions |
|
|
organizes work activities to attain organizational goals. Management functions or leadership roles |
management functions |
|
|
group activities in a manner that facilitates communication and coordinationwithin and between departments . Management functions or leadership roles
|
management functions |
|
|
organizes works so that it is as time and cost effective as possible. Management functions or leadership roles |
management functions |
|
|
idetntifies appropriately cost drivers i high cost, high resource utilization diseases and organizes patient care to address these with efficiency across care settings |
management functions |
|
|
explores opportunities to use case managers, nurse navigators, and clinical nurse leaders (CNLs) to better integrate and coordinate care |
management functions |
|
|
Evaluates Organizational Structure: Periodically checks how well the way patient care is organized is working and makes adjustments as needed. Management functions or leadership roles |
leadership roles |
|
|
Checks Resources Before Changes: Makes sure there are enough resources and support before making any changes to how patient care is organized. Management functions or leadership roles? |
leadership roles |
|
|
Considers Human Element: Looks at how people are affected by changes, supports them during adjustments, and pays attention to the human side of the work. |
leadership roles |
|
|
Considers Human Element: Looks at how people are affected by changes, supports them during adjustments, and pays attention to the human side of the work. Management functions or leadership roles |
leadership roles |
|
|
Promotes Education and Expertise: Encourages subordinates to improve their education, clinical skills, and experience for better patient care.management functions or leadership roles |
leadership roles |
|
|
Advances Nursing Practice: Makes sure the chosen ways of delivering nursing care are helping to improve the overall practice of professional nursing. |
leadership roles |
|
|
Maximizes Team Abilities: Supports and encourages the use of care delivery models that make the most of each team member's abilities. Management functions or leadership roles |
leadership roles |
|
|
Aligns Mission and Philosophy: Ensures that the way patient care is organized matches up with the overall mission and philosophy of the organization. Management functions or leadership roles |
leadership roles |
|
|
Focus on Patient and Family: Makes sure that, no matter the system used, the main focus is always on the patient and their family in delivering care. |
leadership roles |
|
|
traditional patient care delivery methods (5) |
1. total patient care 2. functional nursing 3. team and modular nursing 4. primary nursing 5. case management |
|
|
primary nursing was once called, _____(1) and is now frequently referred to as a (2)_______ |
1. case method nursing 2. professional practice model |
|
|
team nursing is sometimes called _______ |
partners in care or patient service partners |
|
|
the choice of an organiztion model involves ____ (4) to be performed |
1. staff skills 2. availability or resources 3. patient acuity 4. nature of the work |
|
|
Change Work Design for Goals: Adjust how work is done to make sure it helps achieve the organization's overall goals. |
Management functions |
|
|
Choose the Right Patient Care System: Pick a way of delivering patient care that fits the patients' needs and the skills of the staff. |
Management functions |
|
|
Use Research for Changes: Look at scientific research and current information to understand and decide on changes in how nursing care is provided. Management functions or leadership roles |
Management functions |
|
|
Maximize Resources and Time: Use a patient care system that makes the best use of people, equipment, and time. |
Management functions |
|
|
Train and Supervise Non-professional Staff: Make sure staff who aren't professionals are trained and supervised properly when giving care. Management functions or leadership roles |
Management functions |
|
|
Organize Activities for Goals: Arrange tasks in a way that helps the organization reach its goals. |
Management functions |
|
|
Group Activities for Communication: Organize tasks so that communication and coordination are easy within and between different departments. management functions or leadership roles |
Management functions |
|
|
Efficient Work for Time and Cost: Set up work to be as quick and cost-effective as possible. Management functions or leadership roles |
Management functions |
|
|
Address High-Cost Diseases Efficiently: Figure out the most efficient way to organize patient care for diseases that use a lot of resources. |
Management functions |
|
|
Use Coordinators for Better Care: Explore using case managers, nurse navigators, and clinical nurse leaders to make sure care is well-integrated and coordinated. |
Management functions |
|
|
Total Patient Care: Each patient gets care from one nurse who handles everything. |
traditional modes of organizing patient care |
|
|
Functional Nursing: Tasks are divided among different specialists or nurses based on their skills. |
traditional modes of organizing patient care |
|
|
Team and Modular Nursing: Nurses work together in teams, sometimes specialized in certain areas. |
traditional modes of organizing patient care |
|
|
Primary Nursing: One nurse takes the lead and is responsible for the patient's overall care. |
traditional modes of organizing patient care |
|
|
Case Management: Coordination of care, often with a manager overseeing the whole process. |
traditional modes of organizing patient care |
|
|
idea that how people feel and work together |
Human relations |
|

Name the structure |
1. Charge nurse 2.nursing staff 3. Patients 4. Case method or total patient care |
|

|
1. Charge nurse 2. Rn medication, rn treatment nurse, nursing assistants/hygienic care, clerical/housekeeping 3. Patients 4. Functional nursing organization structure
|
|
|
1. Charge nurse 2. Team leader 3. Nursing staff 4. Patients 5. Team nursing organization structre |
|
|
Is the oldest mode of organizing patient care. |
Total patient care |
|
|
Total patient care is sometimes referred to as |
Case method of assignment |
|
|
With ____, Nurses assume total responsibility during their time in duty for meeting all the needs of assigned patients. |
Total patient care |
|
|
Back in the early 1900s, when someone needed nursing care, a nurse would come to their home and take care of everything—cooking, cleaning, and the regular nursing stuff. But when the Great Depression hit in the 1930s, people couldn't afford this anymore. So, they started going to hospitals where private nurses worked. Nurses and students then became the main caregivers in hospitals, and this way of giving complete care continued for a while. |
TOTAL PATIENT CARE NURSING OR CASE METHOD NURSING |
|
|
In some hospitals and home health agencies, they still use a method where one nurse takes care of everything for a patient during their shift. This gives nurses a lot of freedom and responsibility. It's straightforward, but it can lead to different approaches to care if there are different nurses on different shifts. This might confuse the patient. However, this method needs highly skilled and trained staff, which can be more expensive. Some people argue that less trained individuals could do some tasks, making it cheaper. The biggest problem happens when the nurse isn't well-prepared or experienced enough for the job. |
Total patient care or case method nursing |
|
|
Organizations tend to have one of four planning modes: reactive, inactivism, preactivism,or proactive. Leaders should strive to demonstrate a proactive planning style to theirfollowers.Explain in simple terms |
Think of how organizations plan for the future. There are four ways: reacting to things that happen, doing nothing much, planning just a bit ahead, or planning ahead a lot. Good leaders aim to be proactive, meaning they plan ahead and take action before things happen, setting a good example for their team. |
|
|
requires the completion of specific tasks by different nursing personnel |
functional nursing organization |
|
|
typically uses a nurse leader who coordinates team members of varying educational preparation and skill sets in the care of a group of patients. |
team nursing |
|
|
uses mini teams, typically an RN and unlicensed health care workers to provide care to a small group of patients, usually centralized geographically |
modular nursing |
|
|
is organized so that one health care provider (typically the RN) has 24 hr responsibility for care planning and coordination |
primary care nursing |
|
|
also provide primary care in the form of PHCTs. These teams typically include, but are not limited to, physicians, nurse practitioners, nurses, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and social workers working collaboratively to deliver coordinated patient care |
interprofessional teams |
|
|
who play a crucial role in organizing how things operate within specific units or departments. What level is this |
middle-level managers |
|
|
*Evaluates Organizational Structure:* Periodically checks how well the way patient care is organized is working and makes adjustments as needed. |
middle-level managers |
|
|
*Evaluates Organizational Structure:* Periodically checks how well the way patient care is organized is working and makes adjustments as needed. What level is this |
middle-level managers |
|
|
*Considers Human Element:* Looks at how people are affected by changes, supports them during adjustments, and pays attention to the human side of the work. What level |
middle-level managers |
|
|
*Inspires Team Effort:* Encourages everyone to work together as a team toward common goals. |
middle-level managers |
|
|
*Promotes Education and Expertise:* Encourages subordinates to improve their education, clinical skills, and experience for better patient care. What level |
middle-level managers |
|
|
*Advances Nursing Practice:* Makes sure the chosen ways of delivering nursing care are helping to improve the overall practice of professional nursing. |
middle-level managers |
|
|
*Maximizes Team Abilities:* Supports and encourages the use of care delivery models that make the most of each team member's abilities. |
middle-level managers |
|
|
*Aligns Mission and Philosophy:* Ensures that the way patient care is organized matches up with the overall mission and philosophy of the organization. What level |
middle-level managers |
|
|
*Focus on Patient and Family:* Makes sure that, no matter the system used, the main focus is always on the patient and their family in delivering care. |
middle-level managers |
|
|
____ is like teamwork to plan, organize, and evaluate care for an individual's health needs. It helps ensure quality care at a reasonable cost. In some cases, instead of focusing on one person, _____ plan care for groups of people with the same health condition, like those with a chronic illness. |
case management |
|
|
steps in staffing |
1. recruitment 2. selection 3. placement 4. indoctrination |
|
|
process of actively searching out or attracting applicants for existing positions. shoudld be an ongoing process. |
recruitment |
|
|
attracting applicants |
recruitment |
|
|
wanting to stay |
retention |
|
|
US RN recruitment cost is |
36,000 to 64, 000 dollars |
|
|
types of interview tools |
1. structure 2. semi-structured 3. unstructured |
|
|
verbal interaction between individuals for a particular purpose |
interviewing |
|
|
Interviewer seeks to obtain enough information to determine applicants ______ for the available position |
sustainability |
|
|
For the applicant to obtain adequate information to or the decision about accepting the job |
interview |
|
|
Interviewer promotes_______ for the organization |
respect & goodwill |
|
|
(Getting People In):* It's about bringing in new folks who want to be nurses. |
recruitment |
|
|
(Keeping Them Happy):* Once we have nurses, we want to make sure they like it and stay. |
retention |
|
|
They want to know if the person being interviewed is right for the job. |
*Interviewer's Goal |
|
|
The person being interviewed wants to decide if they really want the job. |
. *Applicant's Goal: |
|
|
The interviewer also wants to make the company look good and respected. |
Company's Image:* |
|
|
Like a planned script, where everyone gets asked the same questions in the same way. It's organized and fair. |
*Structured Interview:* |
|
|
A bit flexible. There's a plan with some set questions, but the interviewer can also ask follow-up questions based on the conversation. |
*Semi-Structured Interview: |
|
|
It's more like a free-flowing chat. There's no fixed list of questions, and the conversation goes where it naturally goes. |
*Unstructured Interview:* |
|

|
1. physician -charge nurse -health care organizations resources -associate nurse (evenings) -associate nurse (nights)-associate nurse (as needed days) 2. primary nurse/ patient 3. primary nursing structure |
|
|
SEARCH MESSENGER TESTPAPER 1 |
REVIEW ONLY |
|
|
The Aristotelian philosophy that asserts that some people are born to lead belong to? |
Great Man's Theory. |
|
|
Classifying leadership styles into autocratic, democratic, and laissez fair belong to? |
Answer. Behavioral theories. |
|
|
A leadership theory that believes leadership behavior is generally determined by the relationship between the leader's personality and the specific situation. |
Interactional theory. |
|
|
The leader may not be perfect in his traits, but he or she demonstrates professional and ethical behavior before his or her subordinates. He or she is a? |
Answer, role mode |
|
|
A leadership theory that believes leadership behavior is generally determined by the relationship between the leader's personality and the specific situation |
Interactional Theory. |
|
|
People are very complex and highly variable. What is this? |
Open Systems Theory. |
|
|
People's motives do not stay constant but change over time. What is this? |
Open Systems Theory. |
|
|
Goals can differ in various situations. What theory is this? |
Open Systems Theory. |
|
|
Servant Leadership was coined by |
Green Leaf. |
|
|
The assumption that both leaders and followers have the ability to raise each other to higher levels of motivation and morality is |
transformational leader. |
|
|
The leader's ability to picture some future state and describe it to others so they will begin to share the dream is the leader's |
values |
|
|
focuses on management tasks. |
transactional leader. |
|
|
focuses on management tasks. |
transactional leader. |
|
|
examines causes. |
transactional leader. |
|
|
is a caretaker. |
transactional leader. |
|
|
When managers do coaching and mentoring, they assume which of the following tasks? |
Enabling |
|
|
Articulate effective and enthusiastic sharing of the goals and culture of the organization is? |
Communicating |
|
|
The skills needed to be an effective leader are dynamic and change, constantly in response to a rapidly changing world in which we live. This statement is? True or False? |
True |
|
|
A process of choosing from among applicants the best qualified individual for the job? |
Selection |
|
|
Involves verifying applicant's qualifications, history of employment, deciding fitness of the applicant to the organization expectation. |
Selection |
|
|
When a company is picking the best person for a job, that process is called. It includes checking if the applicants have the right qualifications and a good work history. The goal is to see if the person is a good fit for what the organization needs. So, "_______" is like choosing the right person for the job based on their qualifications and how well they match the organization's expectations. |
Selection |
|
|
When employers are looking into an applicant's background, they can ask about the person's current name, previous names they might have used, or if their school records are under a different name. Acceptable inquiries or unacceptable inquiries |
Acceptable Inquiries |
|
|
employers to ask questions about a person's name that might reveal information about their family background, nationality, marital status, or criminal record. Acceptable inquiries or unacceptable inquiries |
Unacceptable inquiries |
|
|
If applicant has worked for the organization under a different name, if school records are under another name, if applicant has another name. Acceptable Inquiries or unacceptable inquiries |
Acceptable Inquiries |
|
|
, inquiries about name that would indicate lineage, national origin, or marital or criminal status. Acceptable Inquiries or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable inquiries |
|
|
Place of Residence and Lengths Resided in City or State. Acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
Acceptable inquiries |
|
|
Former Addresses, Names, or Relationships of People with Whom Applicant Resides, or If Owns or Rents Home. Acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
Unacceptable |
|
|
If Older than 18 Years or Statement that Hire is Subject to Age Requirement, can ask if the Applicant is between 18 years and 70 years. Acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
Acceptable |
|
|
Specific Age or Date of Birth. Acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
Unacceptable |
|
|
can ask for Proof of U.S. Citizenship. Acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
Acceptable |
|
|
ask for Proof of U.S. Citizenship. Acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
Acceptable |
|
|
They can ask about the current place of residence and how long the person has lived in a city or state. Acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
Acceptable |
|
|
They ask about former addresses, names of people the applicant lives with, or if they own or rent their home. Acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
Unacceptable |
|
|
They ask if the person is older than 18 or if being older is necessary for the job. They can also ask if the applicant is between 18 and 70. Acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
Acceptable |
|
|
They ask for the specific age or date of birth. Acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
Unacceptable |
|
|
They ask for proof of U.S. citizenship. acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
Acceptable |
|
|
They ask about the birthplace of the applicant, their spouse, or any relative. Acceptable or unacceptable iniquiries |
UnAcceptable |
|
|
it can be requested for affirmative action but not as employment criteria. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
, all questions about race are prohibited, acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
, all questions about race, acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
questions relating to arrests or conviction of a crime. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
relatives employed in organization, names and addresses of parents if the applicant is a minor. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
questions about who the applicant lives with or the number of dependents. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
Employers ask about race for affirmative action purposes, but not as a basis for hiring. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
All questions about race, in general, are not allowed. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
Employers can inquire about actual convictions related to the ability to perform the job. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
They shouldn't ask about arrests or general questions about a person's criminal history. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
Employers can ask if any relatives work in the same organization. For minors, they can ask for the names and addresses of parents. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
They shouldn't ask about who the applicant lives with or details about the number of dependents. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
This is a traditional setup with clear hierarchies, like a pyramid. Each level reports to the one above, creating a structured chain of command. |
Bureaucratic/Line Organizations: |
|
|
This is more flexible and temporary. It's like assembling a team for a specific project, and once the project is done, the team might disband. |
*Ad Hoc Design:* |
|
|
It's a mix of different structures. People often report to both a functional manager and a project manager, allowing for more collaboration across different parts of the organization. |
*Matrix Structure |
|
|
These have fewer levels of hierarchy, making the organization more horizontal. It often promotes faster decision-making and open communication. |
*Flat Designs:* |
|
|
a leader applying the____ |
Path-Goal theory |
|
|
________1. is like making plans for the near future, focusing on day-to-day activities._______,2. such as team leaders or supervisors, is primarily involved in this type of planning. They focus on the immediate tasks and activities to ensure things run smoothly on a daily basis. It's about organizing and managing the routine operations to meet short-term goals. |
1. Short-range, operational planning 2. The first level of managers |
|
|
ask about who the applicant lives with or details about the number of dependents. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
This is not really planning at all. It's being passive and not actively making plans for the future. |
*Inactive Planning:* |
|
|
This is preparing in advance. You're getting ready for potential events and making plans before they actually happen. |
Preactive Planning: |
|
|
* This is being ahead of the game. You're not just getting ready; you're actively shaping the future by making plans and adjusting them as needed. |
*Proactive/Interactive Planning |
|
|
LVN stands for |
licensed vocational nurses |
|
|
LPN stands for |
licensed practical nurses |
|
|
During World War II, there was a huge demand for nurses, leading to a shortage. To cope, less skilled workers were trained for specific tasks, like checking blood pressure or administering medication. Instead of one nurse caring for a patient, tasks were divided among different personnel. Registered Nurses (RNs) became more like managers, overseeing care provided by others. This method, called _______, helped manage the shortage by assigning specific tasks to different workers. |
functional nursing |
|
|
means doing things in a way that meets our needs today without harming the ability of future generations to meet their needs. It's about using resources wisely, not wasting, and taking care of the environment so that it stays healthy for a long time. |
sustainability |
|
|
This is like searching for new team members. It involves finding and attracting people who might be a good fit for the job. |
Recruitment |
|
|
Once you have potential team members, this step is about choosing the best ones. It involves evaluating and picking the right people for the job. |
Selection |
|
|
After selecting the right people, this is about putting them in the right positions or roles within the organization. |
Placement |
|
|
This is like the orientation phase. It involves introducing new team members to the organization's way of doing things, its culture, and making them feel part of the team. |
Indoctrination |
|
|
name and address of a person to be notified. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
, name and address of a relative to be notified. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
professional organizations. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
requesting a list of all memberships. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
, professional or character reference. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
religious references. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
all applicants can be asked if they are able to carry out the physical demands of the job. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
employers must be prepared to justify any mental or physical requirements. Specific questions regarding handicaps are forbidden. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
statement that a photograph may be required after employment. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
a photograph be taken before interview or hiring. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
if necessary to perform job, languages applicants speaks, reads, or writes. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
about birthplace, native language, ancestry, date of arrival in the United States, or native language. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
You can ask for the name and address of a person to be notified in case of an emergency. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
* Asking for the name and address of a relative for emergency notification is not allowed. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
* It's okay to ask about professional organizations. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
Don't ask for a list of all memberships in organizations. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
You can ask for professional or character references. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
Asking for religious references is not allowed. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
You can ask if applicants are physically able to handle the job's demands. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
Employers should not ask specific questions about disabilities unless they can justify them for the job. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
You can say that a photograph may be required after employment. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
Requiring a photograph before an interview or hiring is not allowed. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
If needed for the job, you can ask about the languages an applicant speaks, reads, or writes. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
Asking about birthplace, native language, ancestry, date of arrival in the United States, or native language is not allowed.acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
You can ask about academic, vocational, or professional education, schools attended, and language abilities. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
Asking about the racial or religious affiliation of a school or the specific dates of schooling is not allowed. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
You can inquire about sex only if it's a genuine requirement for the job, but this is interpreted narrowly by the courts. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
Asking about sex on an application or using it as a factor for hiring decisions is not allowed. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
No inquiries about credit rating are allowed. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
Questions about car or home ownership are also not permitted. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
unacceptable |
|
|
You can notify applicants that misstatements or omissions of facts may lead to dismissal. acceptable or unacceptable inquiries |
acceptable |
|
|
require an examination of values by managers and theirsubordinates. management functions or leadership roles |
leadership roles |
|
|
See each employee as unique, motivated by different things. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Understand and align with the team's values, rewarding accordingly. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Foster engagement and emotional commitment to organizational goals. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Listen to understand needs and prevent dissatisfaction. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Project a positive and empowering image. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Encourage personal growth by pushing employees to challenge themselves. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Support mentoring and coaching relationships. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Create a supportive environment for discouraged individuals. management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Be genuine, not just automatic, in giving praise. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Develop a philosophy valuing each employee and promoting success. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Show belief in your team's ability to achieve organizational goals. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |
|
|
Stay self-aware and motivated to lead by example. Management functions or leadership roles |
Leadership roles |

