![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
117 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the first step in endotracheal intubation?
|
BSI
Is scene safe? What is the cause of injury or nature of illness? How many patients do you have? Do you need additional resources? Is there trauma or suspected trauma? If so, C-Spine! |
|
|
What is the second step in endotracheal intubation?
|
If patient not breathing, open the airway
|
|
|
How do you open the airway?
|
It depends on if there is trauma or not (Or even suspected trauma)
|
|
|
If there IS trauma or suspected trauma, how do you open the airway?
|
Modified Jaw Thrust
|
|
|
How do you do the modified jaw thrust?
|
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r3ckgEQEE_o&feature=related
|
|
|
If there is NOT trauma or suspected trauma, how do you open the airway?
|
Head tilt, chin lift
|
|
|
How do you do head tilt, chin liftt?
|
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kxfY-f7EV8M&feature=related
|
|
|
What is the third step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Lift up the patient's tongue, and insert a basic airway.
|
|
|
When do you use an oropharyngeal (OPA)?
|
When the patient needs an airway
AND When the patient is unresponsive AND When the patient does NOT have a gag reflex |
|
|
How do you measure an OPA?
|
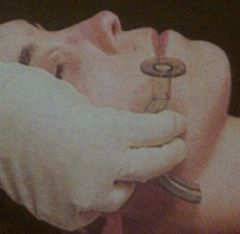
From the FRONT of the teeth to the angle of the jaw
|
|
|
When should you use an NPA?
|
When the patient needs an airway
AND When an OPA can't be used due to clenched teeth, biting, and/or injuries to the upper middle jaw (Maxilla) AND/OR When an OPA cannot be used due to patient's gag reflex |
|
|
Does a patient have to be completely unresponsive to use an NPA?
|
No?
|
|
|
How do you measure an NPA?
|

From the tip of the nose to the earlobe?
|
|
|
How do you insert an NPA?
|
Make sure length is correct
Lubricate with gel, patient's blood, spit, et cetera Insert with the bevel towards the septum, or base of the tonsil |
|
|
When should you NOT use an NPA?
|
Fracture or suspected fracture to the bottom of the skull or middle of the face
|
|
|
How do you insert an OPA?
|
Make sure size is correct
Open patient's mouth using crossed finger technique, and insert the OPA upside down When tip of the OPA touches the soft palate at back of the roof of the mouth, gently turn it 180 degrees and advance until flange is flush with teeth |
|
|
What must you do even after you have inserted an OPA or NPA?
|
Maintain the sniffing position of the airway using "head tilt, chin lift" or "modified jaw thrust" in order to keep it open
|
|
|
What is an alternate way to insert an OPA?
|
Sideways in the corner of the mouth,and then rotated 90 degrees while advancing
|
|
|
What is the preferred way to insert an OPA for infants and children?
|
Tongue depressor is inserted into the mouth until it's tip is at the base of the tongue
Tongue is then pressed down toward the mandible (Lower Jaw), and pressed forward Oropharyngeal is then inserted in it's normal position until the flange is flush with the teeth |
|
|
What is the fourth step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Ventilate immediately using a BVM UNATTACHED to oxygen
|
|
|
What is the fifth step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Ventilate with room air (WTF?)
|
|
|
What is the sixth step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Attach oxygen reservoir to the BVM
|
|
|
What is the SEVENTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Attach the BVM to high flow oxygen
|
|
|
What is high flow oxygen?
|
15 LPM or greater
|
|
|
What is the EIGHTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Ventilate patient at proper volume and rate
|
|
|
What is the proper volume?
|
Enough to make the chest rise and fall?
|
|
|
What is the proper rate?
|
10-12 BPM
|
|
|
In order to give 10 BPM, how often do you give a breath?
|
Every 6 seconds!
|
|
|
In order to give 12 BPM, how often do you give a breath?
|
Every 5 seconds
|
|
|
What is the NINTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Have partner pre-oxygenate/hyperventilate patient
|
|
|
What is preoxygenation/hyperventilation?
|
20-24 BPM
|
|
|
How fast is 20 BPM?
|
1 breath every 3 seconds
|
|
|
What is 24 BPM?
|
1 breath every 2.5 seconds
|
|
|
How long should you preoxygenate/hyperventilate the patient?
|
For at least 30 seconds
|
|
|
What is the TENTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Identify and select proper equipment
|
|
|
What is the ELEVENTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Check equipment
|
|
|
What equipment do you check, and how do you check it?
|
Check the cuff for leaks
Check laryngoscope operation Check bulb tightness |
|
|
What is the TWELFTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Position the patient's head properly
|
|
|
What is the proper head position?
|
Sniffing Position
|
|
|
What is the sniffing position?
|

|
|
|
What is another name for the sniffing position?
|
Sniffing the morning air?
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the sniffing position?
|
To line up the airway as straight as possible, and make it accessible as possible for insertion of a basic or advanced airway
|
|
|
Is the sniffing position the same for adults and children?
|
No?
|
|
|
Why is the sniffing position different in children and adults?
|
Because children's airways are shorter, and shaped different
|
|
|
What should you do to maintain the sniffing position in a child?
|
Roll up a towel, and put it under their SHOULDERS
|
|
|
What is the pediatric sniffing position?
|

It is similar to the adult sniffing position, but it is accomplished differently because of the difference in size and shape of the anatomies.
|
|
|
What can you do to maintain the sniffing position in an adult?
|
Put a pillow under their neck and part of head?
|
|
|
What is the THIRTEENTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Put the laryngoscope blade into the right side of the patient's mouth (Patient's right), and move the tongue left, up?, and out of the way while gradually advancing the blade
|
|
|
What is the FOURTEENTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Carefully lift up the patient's lower jaw (Mandible) with the laryngoscope
|
|
|
What is the mandible?
|
Lower jaw
|
|
|
What is the FIFTEENTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Insert endotracheal tube to proper depth
|
|
|
What is the proper depth for inserting an endotracheal tube?
|
1-2 cm past vocal cords?
|
|
|
What is the SIXTEENTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Inflate the cuff with the right amount of air
|
|
|
How much air do you put in the cuff of an endotracheal tube?
|
Depends on cuff, but usually 10-15 cc?
|
|
|
When checking the cuff on an endotracheal tube, what must you do?
|
Inflate, and then disconnect the syringe so that you can see if the cuff will stay inflated without the syringe attached to it
|
|
|
What is the SEVENTEENTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Disconnect the syringe
|
|
|
What is the EIGHTEENTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Have partner ventilate the patient
|
|
|
What is the NINETEENTH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Listen to the epigastrium first, then the upper and lower left lung, and then the right lung to see if the endotracheal tube is in the right place
|
|
|
What else must you do to make sure the E.T. is in the right place?
|
Look for rise and fall of the chest
Look for condensation in the tube Attach end tidal CO2 |
|
|
If you hear sounds in the epigastrium, what does that mean?
|
The endotracheal tube is in the esophagus
|
|
|
If the endotracheal tube is in the esophagus, what should you do?
|
Remove it, and start again
|
|
|
If you put air in the stomach, what will happen?
|
The patient will not get oxygen, and there is a good chance they will throw up
|
|
|
If a patient throws up, what may happen?
|
Vomit may go into the lungs, and there is a good chance they will get infected
|
|
|
If you hear lung sounds only on the right side, what does that probably mean?
|
That the tube is in too far, and in the right lung stem
|
|
|
How do you auscultate the lungs?
|
Divide lung into six parts, and ALWAYS start with the back if possible
|
|
|
What is the TWENTIETH step in endotracheal intubation?
|
Securing the endotracheal tube
|
|
|
What size laryngoscope blade should you use?
|
It depends on the size and age of the patient
|
|
|
How do you determine what size laryngoscope blade to use?
|
???
|
|
|
When can/should you not use a stylet?
|
???
|
|
|
When should you use a cuffless endotracheal tube?
|
When intubating a child under twelve
|
|
|
Why must you use uncuffed tubes in children under twelve?
|
Because their airway is smallest below the epiglottis, and if the tube is too big it will put pressure on the mucosal lining around it and cause it's tissue to die
|
|
|
When intubating a child, what must you ALWAYS have?
|
A leak that you can hear...
|
|
|
In a child, if you hear a leak from the endotracheal tube, what does that mean?
|
It shows that the tube is probably not too tight, and will not injure the child's throat
|
|
|
At the beginning of the NREMT endotracheal intubation skill, how long do you have to start ventilating the patient?
|
30 seconds after putting on gloves
|
|
|
During endotracheal intubation, what is the MOST time you should stop ventilations for any reason?
|
10 seconds?
|
|
|
What is the first critical criteria?
|
BSI
|
|
|
What is the second critical criteria?
|
Not starting ventilations 30 seconds after you put on gloves
Stopping ventilations for greater than 30 seconds for any reason |
|
|
What is the third critical criteria?
|
Not giving high flow oxygen
|
|
|
What is high flow oxygen?
|
15 LPM or greater
|
|
|
What is the fourth critical criteria?
|
Not ventilating the patient at 10-12 BPM
|
|
|
What is the fifth critical criteria?
|
Did not provide adequate volume per breath
|
|
|
What is adequate volume per breath?
|
Enought to make the chest rise and fall?
|
|
|
If you don't give enough air volume in a ventilation more than twice in one minute, what happens?
|
You fail
|
|
|
What is the sixth critical criteria?
|
Not preoxygenating/hyperventilating the patient before you insert the tube and/or suction
|
|
|
What is the seventh critical criteria?
|
Did not intubate in three tries
|
|
|
What is the eighth critical criteria?
|
Using the patient's teeth as a fulcrum
|
|
|
What is the ninth critical criteria?
|
Did not check placement of tube by auscultating over the epigastrium AND bilaterally over each lung
|
|
|
What is the tenth critical criteria?
|
If stylette is used, must NOT go past the end of the endotracheal tube
|
|
|
Where should the end of the stylette be in the endotracheal tube?
|
Above the eyelet?
|
|
|
What is the eleventh critical criteria?
|
Inserting ANY airway in a way that is dangerous to the patient
|
|
|
What is the twelfth critical criteria?
|
Not IMMEDIATELY disconnecting the syringe from the inlet port after inflating the cuff
|
|
|
Suction questions?
|
???
|
|
|
What is a fracture to the bottom of the skull called?
|
Basilar Skull Fracture
|
|
|
What is cricoid pressure?
|

Applying pressure to the cricoid cartilage in order to see the airway when intubating, and can also be used to possibly prevent aspiration
|
|
|
How do you apply cricoid pressure?
|
???
|
|
|
When do you remove the stylet?
|
Immediately after inserting the endotracheal tube?
|
|
|
How do you secure the endotracheal tube?
|
With a tube tamer and/or tape?
|
|
|
How do you secure an endotracheal tube with tape?
|
???
|
|
|
What is 1cc equal to?
|
1 ml
|
|
|
If inserted properly in an adult, where will the endotracheal tube be?
|
21-24cm at the teeth
|
|
|
What can you use to open the mouth before you insert the laryngoscope?
|
Crossed Finger Technique
|
|
|
How do you do the crossed finger technique?
|
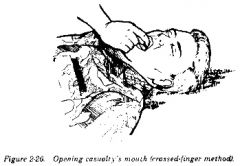
Cross right thumb and index finger to form "X", put thumb on patient's lower front teeth and the index finger on the patient's upper front teeth. Apply crossed finger pressure to open the patient's mouth.
|
|
|
What do you do before you insert the laryngoscope?
|
Open the mouth with the fingers of the right hand, and retract the lips on the teeth or gums to avoid pinching them with the laryngoscope.
|
|
|
How do you apply cricoid pressure?
|
The cricoid cartilage is pushed against the body of the sixth cervical vertebra, mashing the esophagus to block passive vomiting. The technique cannot stop active vomiting.
|
|
|
What is the crossed finger technique?
|
???
|
|
|
What is a basic airway?
|
Oropharengeal
or Nasopharengeal |
|
|
Once you start, how long do you have to start to ventilate the patient?
|
30 SECONDS!!!
|
|
|
Every patient is different, but at what depth is an endotracheal tube usually inserted to in an adult?
|
21-24cm
|
|
|
Every patient is different, but at what depth is an endotracheal tube usually inserted to in an child?
|
???
|
|
|
How long is a centimeter (cm)?
|
???
|
|
|
How much is a "cc"?
|
???
|
|
|
What is the soft palate?
|
???
|
|
|
What is rapid sequence intubation?
|
???
|
|
|
How do you do rapid sequence intubation?
|
???
|
|
|
What is a basic airway?
|
An oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal
|
|
|
How long is one centimeter?
|
??? Show it!
|
|
|
What is another name for cricoid pressure?
|
Sellick's Maneuver
|

