![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What's the most common kind of skin cancer?
|
Basal cell carcinoma
|
|
|
What's the rarest kind of cancers?
|
Merkel cell carcinoma
|
|
|
What are risk factors for cutaneous SCC?
|
UV radiation/fair skin
immunosupression Ulcers, scars Environmentla toxins Radiation HPV Genodermatoses |
|
|
What's the most commonly mutated gene in skin cancer?
|
p53
|
|
|
What happens in xeroderma pigmentosum?
|
Inability to repair DNA
Severe skin cancers. |
|
|
What's the distribution of SCC?
|
Where you have the sun!
-Head -Neck -Upper extremities |
|
|
What's the appearance of SCC?
|
Pink papule, nodule, or plaque
Firm to hard Scaling If ulcers, indurated border |
|
|
What cells go awry in cutaneous SCC?
|
Epithelial cells invade the dermis
|
|
|
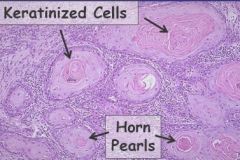
What are features of cutaneous SCC under the scope?
|
Horn Pearls
Variable layers of keratinization If aggressive, mitotic figures and nuclear pleiomorphism |
|
|
What layers of the epidermis give rise to cutaneous SCC?
|
Cornified
Spinous |
|
|
What are the cutaneous precursors of cutaneous SCC?
|
Actinic keratoses
Arsenical keratoses SC in situ Warts |
|
|
What are the properties of an actinic keratoses?
|
Local area of rough, scaly surface; feels like sandpaper
|
|
|
How often does SCC metastasize? Where does it do so at a higher rate?
|
Overall rate: 2-4%, so no.
Risks are higher in places where there's radiation/burn scars or chronic osteomyelitis of the sinus tracts |
|
|
What's the trearment for cutaneous SCC?
|
Surgery!
Cryosurgery Chemo |
|
|
What are risk factors for basal cell carcinoma?
|
UV/fair skin
Immunosupression Arsenic Scars, radiation Genodermatoses -Nevoid basal cell carcionma syndrome |
|
|
What are the different kinds of BCC?
|
Nodular BCC
Superficial Morpheaform |
|
|
What's the appearance of nodular BCC:?
|
Smooth papule with translucent appearance
Telangiectasias Occasional ulceration |
|
|
What is the appearance of superficial BCC?
|
Think, flat, scaly, pink lesions
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a morpheaform BCC?
|
hypopigmented
depressed scar-like |
|
|
What should you do if there's a lesion?
|
Biopsy, always.
|
|
|
What are the features of BCC histologically?
|
Nests of cells in dermis
Resemble epidermal basal cells -Lots of blue cells -Scant cytoplasm -Columnar cells atperiphery Abnormal dermis surrounding it. Palisading |
|
|
What does morpheaform BCC look like?
|
Not like other BCCs
Cells invading the dermis surrounded by fibrotic stroma |
|
|
What's the prognosis of BCC?
|
Very little metastasis
Severe local damage |
|
|
What's the treatment of BCC?
|
Electrodessication and curettage
Excision Cryosurgery Radiation |
|
|
If you have high risk BCC, what do you do?
|
Mohs Micrographic Surgery
|
|
|
What makes a BCC tumor high risk?
|
Large/recurrent
On the face Morpheaform Poorly defined borders Incompletely excised tumors |
|
|
What genes are mutated in BCC?
|
Patched1 gene
|
|
|
What is the function of PTCH1?
|
Receptor for hedgehog proteins
|
|
|
What is the active for SHH in embryogenesis?
|
Turning on of certain TFs that cause differentiation
PTCH, GLII |
|
|
What tumors are associated with SHH?
|
Medulloblastoma
BCCs Rhabdomyosarcoma |
|
|
What kind of drug is good for treating BCC?
|
Vismodegib
Blocker of Smo, which acts in the SHH pathway Doesn't kill the tumors; just decreases the size. YOu've got to be on the drugs all the time. |
|
|
What are the side effects of SHH blockers?
|
Hair loss
Taste loss |
|
|
What's the best treatment for BCC?
|
Surgery!
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for merkel cell carcinoma?
|
Age
UV radiation Immunosupresion |
|
|
What virus can cause MCC?
|
Polyomavirus
|
|
|
What does merkel cell carcinoma look like?
|
Red/blue papule
Hard Shiny Ulceration is rare |
|
|
Where does merkel cell carcinoma occur?
|
Head, neck, extremities
|
|
|
What does merkel cell carcinoma look like under the scope?
|
Small blue cells
Large nodules in dermis High N:C ratio Invasion of nerves, vessels LOTS OF MITOSIS! |
|
|
What's the prognosis of merkel cell carcinoma?
|
Poor if it metastasizes, which it tends to do often.
|

