![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
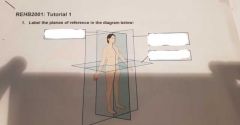
LABEL |
Sagittal, frontal, transverse |
|
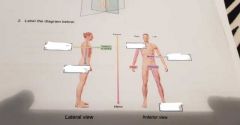
Label |
Posterior, caudal Proximal, lateral, distal |
|

Find the words |
Outer, middle, internal, cerebrum, arachnoid, pia, cerebrospinal fluid, blood vessels |
|
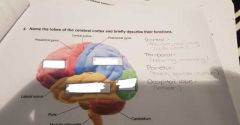
Label and describe |
Red- Frontal, Blue- Parietal, Green- occipital, Yellow- temporal |
|
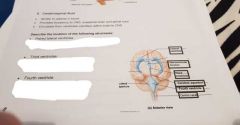
Describe |
1. Located in cerebral hemisphere 2. Midline space slit/ ikn diencephalon 3. Posterial to ponsto cerebellum |
|
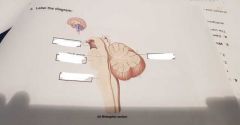
Label |
Midbrain, pons, medulla, cerebellum (other side) |
|
|
What is the function of CNS? |
- receives info about environment around us - communication and processing of sensory info - control and coordination of body (somatic) - involuntary control of body (autonomic) |
|
|
What is afferent nerve fibre? |
Inwards, towards cns |
|
|
What is efferent nerve fibre? |
Outward, away from cns |
|
|
What are neurons? |
Nerve cells or neurons - fundamental units of NS - communicate through generations of action potentials along acon &synapse between neurons |
|
|
What are the functions of neuron? |
Reception, integration, transmission, transfer of information |
|

What is this |
Neuron |
|
|
What is somatic system? |
Somatosensory - conveys all info from skin and musculoskeletal system to brain |
|
|
What is autonomic system? |
Provides bidriectional communication between the brain and smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and gland cells |
|
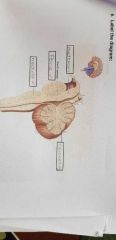
. |
. |
|
|
What does the basal ganglia do? |
Controls motor activity through direct, indirect and hyperdirect pathways |
|
|
What does dopamine do? |
Increase excitability of the direct pathway and decrease excitability of the indirect pathway |
|
|
Structure of cerebellum? |
3 lobes Anterior Posterior Flocculondular |
|
|
Functional regions of cerebellum? |
Vestibulocerebellum - regulates equilibrium Spinocerebellum - connections with spinal cord, coordinates gross limb movement Cerebrocerebellum - coordinates distal limb voluntary movement |

