![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Telencephalon |
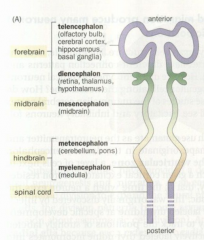
The anterior part of the forebrain, including the olfactory bulb, cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and basal ganglia |
|
|
Diencephalon |
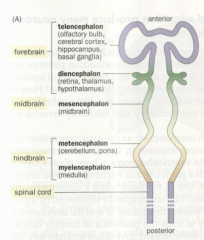
The posterior part of the forebrain, containing the thalamus, hypothalamus, and the retina |
|
|
Mesencephalon |
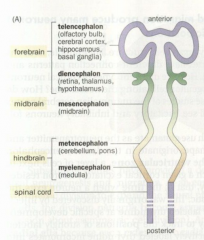
The midbrain |
|
|
Metencephalon |
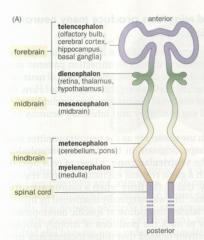
The anterior part of the hindbrain, containing the cerebellum and the pons |
|
|
Mylencephalon |
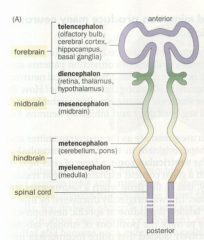
The posterior part of the hindbrain, containing the medulla |
|
|
Cerebral Cortex |
The outer layer of neural tissue in the rostral part of the mammalian brain. It is associated with higher functions, including sensory perception, cognition, and control of voluntary movement |
|
|
Retina |
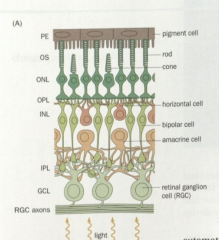
A layered structure at the back of the vertebrate eye made of five major neuronal types (photoreceptors, horizontal cells, bipolar cells amacrine cells, and retinal ganglion cells) and support cells. Collectively, these cells convert light into electrical signals, extract biologically relevant signals from the outputs of photoreceptor, and transmit these signals to the brain |
|
|
Thalamus |
A structure situation between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex through its extensive bidirectional connections with the cortex |

