![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Meissner's Corpuscle
|
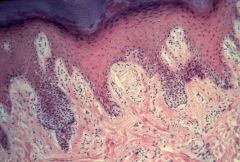
What structure is this?
|
|
|
Pacinian Corpuscle
|
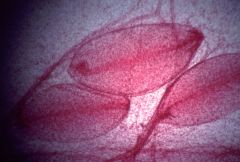
What structure is this?
|
|
|
Pacinian Corpuscle in x-section
|
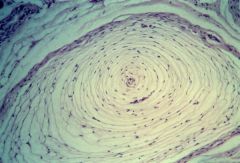
What structure is this?
|
|
|
muscle spindle
|
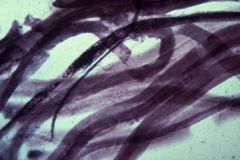
What structure is this?
|
|
|
Golgi tendon organ
|
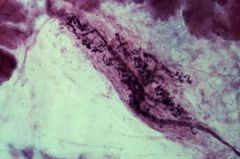
What structure is this?
|
|
|
retina
|
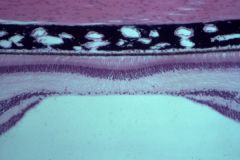
What structure is this?
|
|
|
organ of Corti
|
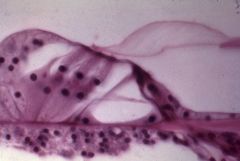
What structure is this?
|
|
|
motor end-plate
|
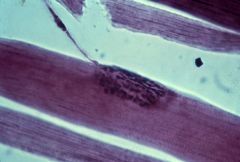
What structure is this?
|
|
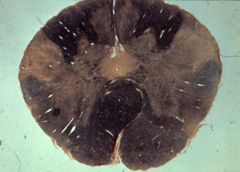
What level is this section and what structures does it contain?
|
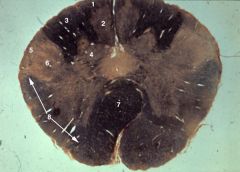
1. Fasciculus gracilis
2. Nucleus gracilis 3. Fasciculus cuneatus 4. Nucleus cuneatus 5. Spinal tract of V 6. Spinal nucleus of V 7. Pyramidal decussation 8. Continuation of the lateral funiculus into the medulla (containing spinocerebellar and spinothalamic pathways) |
|
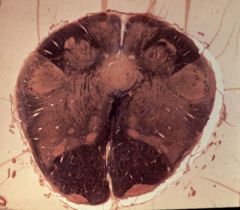
What level is this section and what structures does it contain?
|
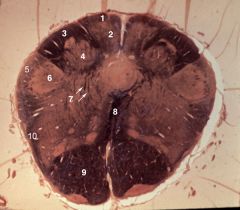
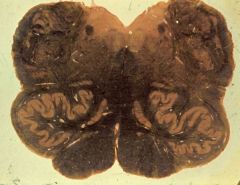
lower medulla (closed)
1. Fasciculus gracilis 2. Nucleus gracilis 3. Fasciculus cuneatus 4. Nucleus cuneatus 5. Spinal tract of V 6. Spinal nucleus of V 7. Internal arcuate fibers 8. Decussation of the medial lemniscus 9. Pyramid 10. Spinothalamic tract |
|
What level is this section and what structures does it contain?
|
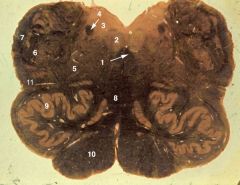
mid-medulla (obex)
1. Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) 2. Hypoglossal nucleus (XII) 3. Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (X) 4. Solitary tract 5. Internal arcuate fibers coursing through the reticular formation 6. Spinal tract and spinal nucleus of V 7. Restiform body (inferior cerebellar peduncle) 8. Medial lemniscus 9. Inferior olivary nucleus 10. Pyramid 11. Spinothalamic tract |
|
What level is this section and what structures does it contain?
|
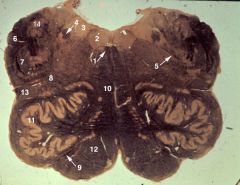
mid-medulla (open)
1. Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) 2. Hypoglossal nucleus (XII) 3. Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (X) 4. Solitary tract 5. Vagal rootlets (X) 6. Restiform body (inferior cerebellar peduncle) 7. Spinal tract of V 8. Location of the nucleus ambiguus (X) within the reticular formation 9. Hypoglossal rootlets (XII) 10. Medial lemniscus 11. Inferior olivary nucleus 12. Pyramid 13. Spinothalamic tract 14. Lateral cuneate nucleus |
|
|
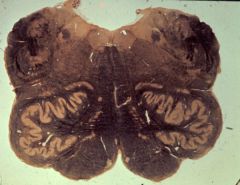
upper medulla
|
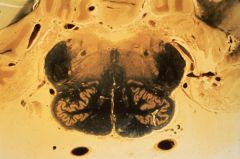
What level is this section?
|
|
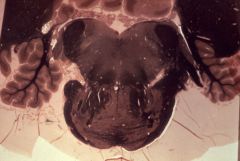
What level is this section and what structures does it contain?
|
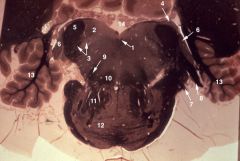
upper medulla (cochlear complex)
|
|
|
deep cerebellar nuclei
|
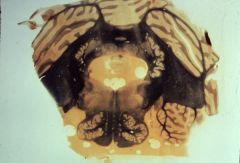
What level is this section?
|
|
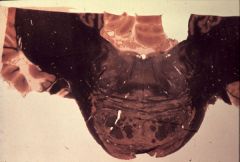
What level is this section and what structures does it contain?
|

lower pons (facial)
1. Abducens nucleus 2. Vestibular nuclei 3. Restiform body (inferior cerebellar peduncle) 4. Abducens rootlets 5. Spinal tract & spinal nucleus of V 6. Facial nerve rootlet (VII) 7. Facial nucleus 8. Central tegmental tract 9. Superior olivary complex 10. Facial nerve (VII) 11. Trapezoid body & media lemniscus 12. Brachium pontis (middle cerebellar peduncle) 13. Pyramidal fasciculi 14. Pontine nuclei 15. Cerebellar vermis 16. Fourth ventricle containing choroid plexus 17. Dentate nucleus of cerebellum 18. Spinothalamic tract |
|
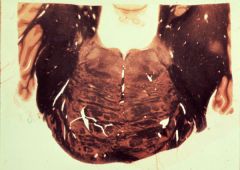
What level is this section and what structures does it contain?
|

mid-pons (trigeminal)
1. Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) 2. Central tegmental tract 3. Superior (chief, main) sensory nucleus of V 4. Motor nucleus of V 5. Superior olivary complex, lateral lemniscus, and spinothalamic tract 6. Medial lemniscus 7. Brachium pontis (middle cerebellar peduncle) 8. Pyramidal fasciculi |
|
|
Nissl-stained spinal cord showing chromatolysis of neurons
|
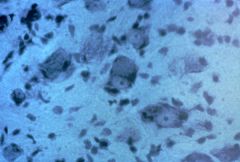
What is this an image of?
|
|
|
electron micrograph of demyelinating axon during recovery from Guillain-Barre disease
|
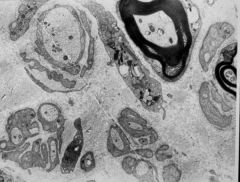
What is this an image of?
|
|
|
teased axon: demyelinating (Guillain-Barre)
|

What ios this an image of?
|
|
|
teased axons: axonopathy
|
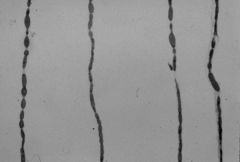
What is this an image of?
|
|
|
H&E -stained normal skeletal muscle (myofibers)
|
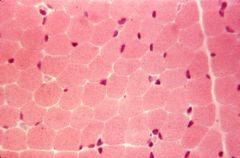
What is this an image of?
|
|
|
H&E stained muscle showing "small group atrophy"
|
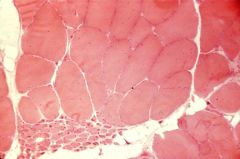
What is this an image of?
|
|
|
muscle fibers, denervated; ATPase staining: fiber-type grouping
|
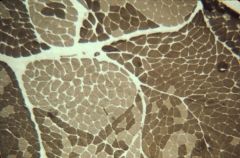
What is this an image of?
|
|
|
muscle fibers, normal: ATPase staining
|
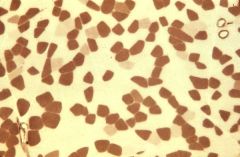
What is this an image of?
|
|
|
Muscle from young male with DMD
A. Fiber splitting and endomysial fibrosis B. Nuclei displaced to the center of the muscle fiber |
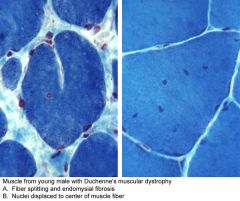
What is this an image of?
|
|
|
muscle myopathy: endomysial fibrosis and fat infiltration
|
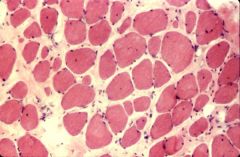
What is this image?
|
|
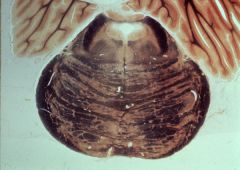
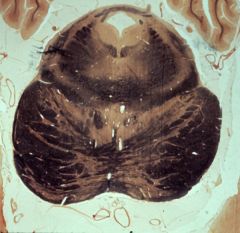
What level is this section and what structures does it display?
|

upper pons (pretgigeminal)
1. Anterior medullary velum 2. Mesencephalic tract (and nucleus) of V 3. Brachium conjunctivum (superior cerebellar peduncle 4. Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) 5. Lateral lemniscus 6. Medial lemniscus 7. Central tegmental tract 8. Pyramidal fasciculi 9. Spinothalamic tract |
|
What level is this section and what structures does it display?
|
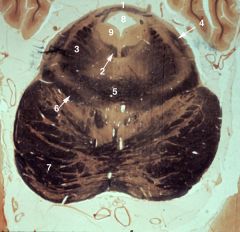
isthmus rhombencephali
1. Trochlear nerve (IV) decussating in the anterior medullary velum and exiting dorsally 2. Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) 3. Brachium conjunctivum (superior cerebellar peduncle) 4. Lateral lemniscus 5. Decussation of the brachium conjunctivum 6. Medial lemniscus 7. Cerebral peduncle 8. Cerebral aqueduct 9. Periaqueductal gray |
|
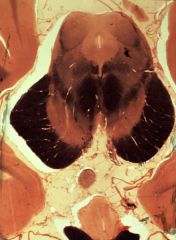
What level is this section and what structures does it display?
|
lower midbrain (inferior colliculus)
1. Trochlear nucleus (IV) 2. Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) 3. Inferior colliculus 4. Central tegmental tract 5. Brachium conjunctivum (superior cerebellar peduncle) 6. Medial lemniscus 7. Substantia nigra 8. Cerebral peduncle 9. Exiting oculomotor nerve (III) 10. Mammillary body 11. Brachium of the inferior colliculus 12. Floor of hypothalamus 13. Uncus |
|
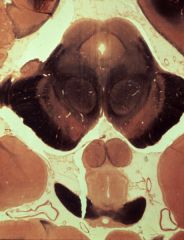
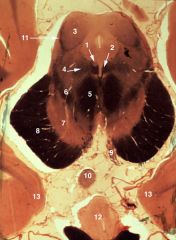
What level is this section and what structures can be identified?
|
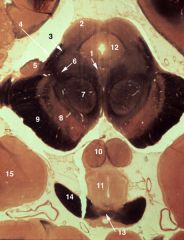
upper midbrain (superior colliculus)
1. Oculomotor nucleus (III) 2. Superior colliculus 3. Spinothalamic tract 4. Brachium of the inferior colliculus 5. Medial geniculate body 6. Medial lemniscus 7. Red nucleus 8. Substantia nigra 9. Cerebral peduncle 10. Mammillary body 11. Hypothalamus 12. Periaqueductal gray 13. Optic chiasm 14. Optic tract 15. Amygdala |
|
|
midbrain-diencephalic junction
|
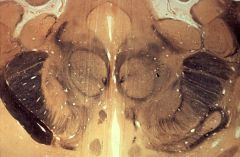
What level is this section?
|
|
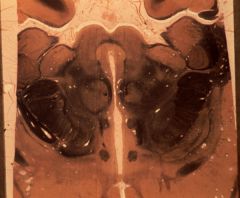
What level is this section and what structures can be identified?
|
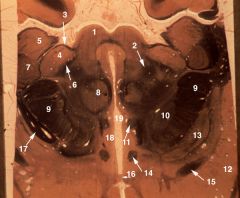
midbrain-diencephalic junction
1. Superior colliculus 2. Medial lemniscus 3. Brachium of the superior colliculus 4. Medial geniculate body 5. Pulvinar 6. Brachium of the inferior colliculus 7. Lateral geniculate body 8. Red nucleus 9. Cerebral peduncle 10. Subthalamic nucleus 11. Mammillothalamic tract 12. Putamen 13. Globus pallidus 14. Fornix 15. Anterior commissure 16. Lamina terminalis 17. Optic tract 18. Hypothalamus 19. Third ventricle |
|
|
caudal diencephalon
|
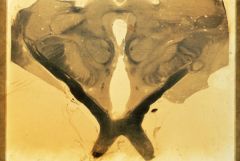
What level is this section?
|
|
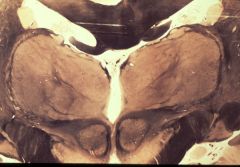
What level is this section and what structures can be identified?
|
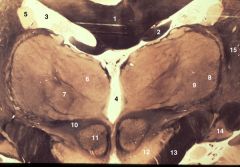
caudal diencephalon
1. Corpus callosum 2. Fornix 3. Lateral ventricle 4. Third ventricle 5. Cardate nucleus (body) 6. Dorsal medial (or medial dorsal) nucleus of thalamus. 7. Intralaminar nuclei of thalamus 8. Ventral postereolateral (VPL) nucleus of thalamus 9. Ventral postereomedial (VPM) nucleus of thalamus 10. Fields of Forel 11. Red nucleus 12. Substantia nigra 13. Cerebral peduncle 14. Lateral genicule nucleus 15. Internal capsule (posterior limb) |
|
|
mid-diencephalon
|
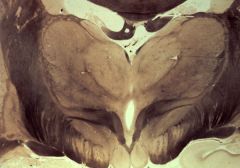
What level is this section?
|
|
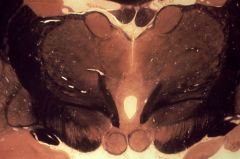
What level is this section and what structures can be identified?
|
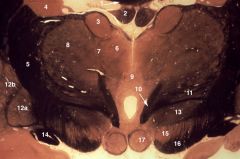
rostral diencephalon
1. Corpus callosum 2. Fornix 3. Anterior nucleus of the thalamus 4. Caudate nucleus 5. Internal capsule 6. Medial mass of the dorsal thalamus 7. Internal medullary lamina 8. Lateral mass of the dorsal thalamus 9. Interthalamic adhesion 10. Mammillothalmic trac 11. Subthalamus (Fields of Forel and zona incerta) 12a. Globus pallidus, internal segment 12b. Globus pallidus, external segment 13. Subthalamic nucleus 14. Optic tract 15. Substantia nigra 16. Cerebral peduncle 17. Mammillary body |
|
|
basal ganglia
|
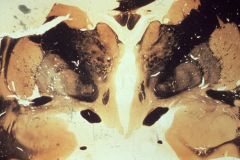
What level is this section?
|
|
|
interventricular foramen
|
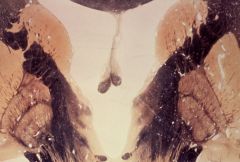
What level is this section?
|
|
|
anterior commissure
|
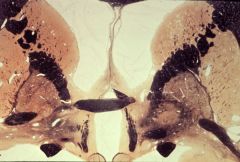
What level is this section?
|
|
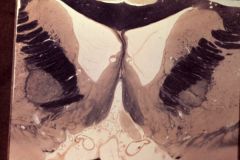
What level is this section and what structures can be identified?
|
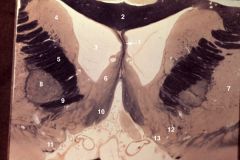
septal region
1. Septum pellucidum 2. Corpus callosum (body) 3. Lateral ventricle (anterior horn) 4. Caudate nucleus (head) 5. Internal capsule (anterior limb) 6. Septal nuclei 7. Putamen 8. Globus pallidus 9. Anterior commissure 10. Diagonal band (of Broca) 11. Anterior perforated substance 12. Nucleus accumbens 13. Nucleus basalis of Meynert |
|
|
frontal region (Kluver Stain)
|
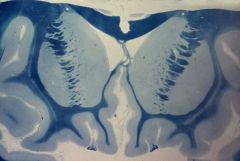
What level is this section?
|
|
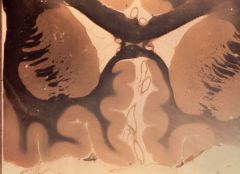
What level is this section and what structures can be identified?
|
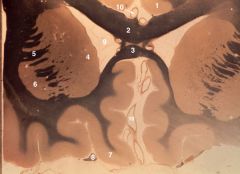
frontal region (Weigert stain)
1. Cingulate gyrus 2. Corpus callosum (body) 3. Corpus callosum (rostrum) 4. Caudate nucleus (head) 5. Internal Capsule (anterior limb) 6. Putamen 7. Gyrus rectus 8. Olfactory tract 9. Lateral ventricle (anterior horn) 10. Anterior cerebral artery |
|

What section is this and what structures can be identified?
|

horizontal section
2. Caudate nucleus (head) 3. Septum pellucidum 4. Lat. vent. (anterior horn) 6. Fornix 7. Interventricular foramen 8. Interthalamic adhesion 9. Thalamus 10. IIIrd Ventricle 11. Posterior commissure 12. Internal capsule (anterior limb) 13. Putamen 14. Internal capsule (genu) 15. Globus pallidus 16. Internal capsule (posterior limb) |
|
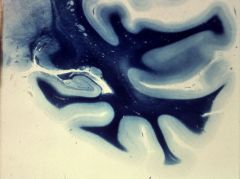
What level is this section and what structures can be identified?
|
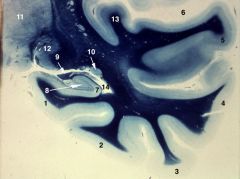
temporal lobe with hippocampus
1. parahippocampal gyrus 2. occipitotemporal (fusiform gyrus) 3. inferior temporal gyrus 4. middle temporal gyrus 5. superior temporal gyrus 6. lateral sulcus (fissure) 7. hippocampus 8. dentate gyrus 9. fornix 10. caudate nucleus (tail) 11. thalamus 12. lateral geniculate nucleus 13. primary auditory cortex 14. lateral ventricle (inferior, or temporal, horn) |
|
|
hypothalamus
|

What level is this section?
|
|
|
cervical enlargement of spinal cord
|
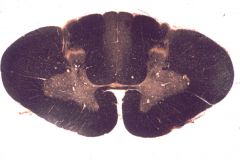
What level is this section?
|
|
|
thoracic spinal cord segment
|
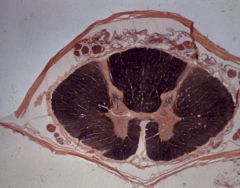
What level is this section?
|
|
|
lumbo-sacral enlargement
|
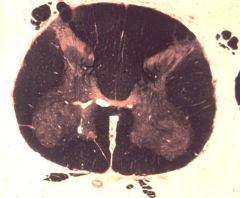
What level is this section?
|
|
|
CT scans of epidural hematoma: axial (left) and coronal (right)
|
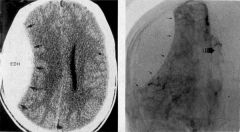
What does this image demonstrate?
|
|
|
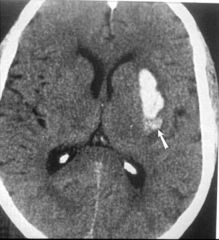
CTscan of brain with left middle cerebral infarct, with (right) and without (left) contrast enhancement
|
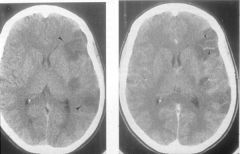
What does this image demonstrate?
|
|
|
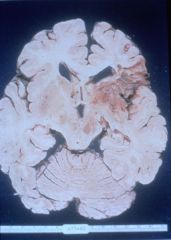
Coronal cut of brain with left middle cerebral artery infarct
|
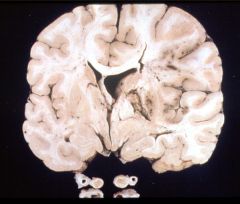
What does this specimen demonstrate?
|
|
|
evolution of cortical infarct: a. normal; b. acute neuronal ischemic change; c. neutrophil infiltration; d. macrophage infiltration
|
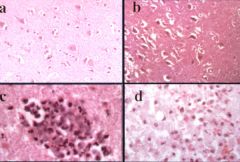
What does this series of photomicrographs demonstrate?
|
|
|
photomicrograph of hemorrhagic infarct in brain
|
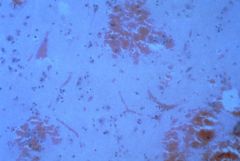
What is this an image of?
|
|
|
brain slice showing "older" infarct
|
What does this specimen demonstrate?
|
|
|
Photomicrographs of a resolving cerebral infarct, showing a cavity formed by liquifactive necrosis with reactive astrocytes in the wall (left) and residual macrophages within the cavity (right).
|
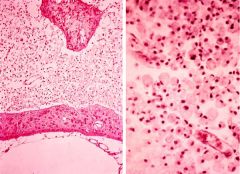
What does this image demonstrate?
|
|
|
CT scan of brain from hypertensive patient with intracerebral hemorrage
|
What does this image demonstrate?
|
|
|
CN VI
|
Abducens
caudal pons ipsilateral rectus |
|
|
CN XI
|
spinal accessory
anterior horn medulla to C5 sternocleidomastoid and trapezius |
|
|
Amygdala
|
anteromedial temporal lobe
just beneath uncus core of the major limbic scircuits with hippocampus |
|
|
Angular Gyrus
|
Language fx
|
|
|
ansa lenticularis
|
projection from globus pallidus to thalamus
|
|
|
anterior cerebral artery
|
supplies orbital cortex and medial surface of frontal and parietal lobes
|
|
|
anterior commissure
|
connects temporal cortices
|
|
|
anterior corticospinal tract
|
smaller than lateral corticospinal tract
end on axial motor neurons |
|
|
anterolateral system
|
spinothalamic tract and associated fibers carrying pain and temperature to thalamus and reticular formation
|
|
|
aqueduct of sylvius
|
connects third and fourth ventricles
|
|
|
area postrema
|
hole in the bbb near the obex
|
|
|
babinski's
|
damage to corticospinal tract
|
|
|
basal ganglia
|
striatum
globus pallidus substancia nigra subthalamic nucleus |
|
|
nucleus basalis
|
cholinergic neurons in substancia inominata
|
|
|
brachium of inferior colliculis
|
auditory fibers from inferior colliculus to medial geniculate nucleus
|
|
|
brachium of superior colliculus
|
retinal afferents passing over medial geniculate nucleus to bypass lateral geniculate nucleus to project to superior colliculus
|
|
|
Broca's area
|
language function center usually in the left inferior frontal gyrus
|
|
|
brodmann's areas
|
46 divisions of neocortex
|
|
|
c fibers
|
unmyelinated PNS axons including nociceptor fibers
|
|
|
calcarine sulcus
|
temporal to occipital lobe
visual cortex brodman's area 17 |
|
|
catecholamines
|
neurotransmitters synthesized from tyrosine
dopamine norepinepherine epinepherine |
|
|
cerebellar cortex
|
molecular layer
purkinje cells granule cells |
|
|
flocullonodular lobe
|
flocullus and nodulus associated with vestibular system and eye movements
|
|
|
cerebral peduncle
|
tightly packed corticospinal, corticobulbar and corticopontine tracts
|
|
|
cingulate gyrus
|
upper part of limbic lobe
|
|
|
clark's nucleus
|
nucleus dorsalis
T1-L3 posterior spinocerebellar tract with stretch and mechanoreceptor info |
|
|
corticobulbar tract
|
corticospinal tract for cranial nerve nuclei
|
|
|
corticopontine tract
|
cortex to basal pons to contralateralt cerecellar hemispheres via middle CP
|
|
|
corticospinal tract
|
principal pathway for skilled volitional movements
|
|
|
cuneate tubercle
|
dorsolateral midmedulla overlying cuneate nucleus
|
|
|
delta fibers
|
thinly myelinated sensory fibers including fast pain
|
|
|
dentate nucleus
|
largest and most lateral cerebellar nuclei
afferents form superior CP ending in thalamus |
|
|
diencephalon
|
pineal
habenula thalamus subthalamic nucleus retina and optic nerve/tract hypothalamus neurohypophisis |
|
|
dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
|
ascending and descending fibers running through periaquaductal and perventricula grey matter
connects hypothalamus to reticular formation and preganglionic autonomic neurons |
|
|
dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
|
parasympathetic efferent nucleus in rostral medulla for thoracic and abdominal viscera
|
|
|
edinger-westphal nucleus
|
efferent neurons for direct and consensual pupillary light reflexes near midline of oculomotor nucleus
|
|
|
entorhinal cortex
|
cortex in anterior parahippocampal gyrus
major source of afferents to hippocampus |
|
|
epithalamus
|
dicephalon that includes pineal gland and habenula
|
|
|
CN VII
|
facial nerve
emerges anterolaterally at pontomedullary junction |
|
|
Facial Nucleus
|
LMN in caudal pons with axons looping around the abducens nuclei
|
|
|
Fasciculus cuneatus
|
tactile and proprioception from the arm to the nucleus cuneatus
|
|
|
Fasciculus gracilis
|
tactile and proprioception from the leg and terminating in the nucleus gracilis
|
|
|
fastigial nucles
|
most medial deep cerebellar nucleus projecting to vestibular nucleus and reticular formation
|
|
|
fornix
|
paired fiber bundle with hippocampal efferents
|
|
|
globus pallidus
|
wedge shaped basal ganglia nucleus medial to putamen
recieves input from striatum and subthalamic with the external segment going to the subthalamic nucleus and the internal segment going to the thalamus internal segment |
|
|
habenula
|
dorsomedial mound on caudal thalamus derived from embryonic diencephalon
|
|
|
dentate gyrus
|
subdivision of the hippocampal formation with afferents from entorhinal; cortex and efferents to hippocampal pyramidal cells
|
|
|
histamine
|
monoamine neurotransmitter used by hypothalamus in sleep wake cycles. also can promote sensitization in nociceptors.
|
|
|
CNXII
|
hypoglossal nerve emerging from preolivary sulcus in rostral medulla
|
|
|
hypoglossal nucleus
|
LMN innervating ipsilateral tongue muscles located near the midline of rostral medulla
|
|
|
hypoglossal trigone
|
elevation in floor of fourth ventricle formed by the hypoglossal nucleus
|
|
|
Anterior hypothalamus
|
includes suprachiasmatic, supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei
innervates neurohypophysis |
|
|
Posterior hypothalamus
|
includes mammillary and posterior nuclei and projects to the thalamus and tegmentum
|
|
|
tuberal hypothalamus
|
includes dorsomedial, ventromedial and arcuate nuclei
secretes releasing and inhibitory factors into the pituitary portal system |
|
|
inferior cerebellar peduncle
|
input to cerebellum
receives contralateral ovilary fibers and other ipsilateral cerebellar afferents |
|
|
inferior colliculus
|
caudal midbrain
relays auditory info from lateral mensicus to the medial geniculate nucleus via the inferior brachium |
|
|
inferior frontal gyrus
|
opercular and triangular parts form broca's area (language fx)
|
|
|
inferior olivary nucleus
|
efferents form climbing fibers that enter contralateral cerebellum via inferior cerbellar peduncle
|
|
|
infundibulum
|
pituitary stalk connecting median emminence of hypothalamus to posterior pituitary
|
|
|
internal arcuate fibers
|
decussating fibers in the medulla made of either posterior column fibers forming the medial lemniscus or olivocerebellar fibers
|
|
|
anterior limb internal capsule
|
connects thalamus to prefrontal cortex
|
|
|
genu of internal capsule
|
connects thalamus to motor/premotor cortex
|
|
|
posterior limb of internal capsule
|
connects thalamus to motor and somatosensory cortex as well as desending corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts
|
|
|
retrolenticular internal capsule
|
connect thalamus and association cortex as well as upper part of optic radiations
|
|
|
sublenticular internal capsule
|
to and from temp-oral cortex including auditory radiation and lower part of optic radiation
|

