![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Explain the monoamine hypothesis of depression
|
deficiency in the amount of or function of cortical and limbic serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine contributes to depression.
**Could be due to homozygous serotonin transporter gene polymorphism |
|
|
According to the monoamine hypothesis, depleting pts of what will cause a relapse of depression if the pt responds to serotnergic or noradrenergic antidepressants?
|
removing Tryptophan and catecholamines
|
|
|
All Available anti-depressants effect the monoamine system, enhancing the synaptic availability of what?
|
Serotonin, NE, or Dopamine.
**this is done via Inc BDNF |
|
|
Will a depressed pt with elevated cortisol levels respond to an Dexamethasone ACTH suppression test?
|
NO, they have chronically elevated CTRH which keeps ACTH high.
**this elevated cortisol causes mood symptoms and cognitive deficits. |
|
|
Glucocorticoid receptors are found in high concentration in the ________ and when cortisol binds, there is a decrease in ____ synthesis
|
Hippocampus, BDNF.
**remember: activation of monoamine rec by antidepressants INC BDNF transcription and downregulate the hyperactive HPA axis |
|
|
List the different classes of Anti-depressants
|
1.Selective Serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
2.Serotonin-NE Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs). 3.TCAs. 4.Serotonin Antagonists. 5.Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. 6.Tetra/Unicyclic Antidepressants. |
|
|
MOA of SSRIs
|
Inhibition of the Serotonin transporter (SERT) located on both pre and post synaptic neurons.
**Dont affect any other receptors |
|
|
List the SSRIs
|
1.Flouxetine**.
2.Sertraline. 3.Citalopram. 4.Paroxetine. 5.Fluvoxamine. 6.Escitalopram. |
|
|
All SSRIs have long half lives, why must a pt be off Flouxetine for > 4weeks before you can give them a MAOI?
|
Still a risk of Serotonin Syndrome since the Active Metabolite is Norfluoxetine which has a 1/2 life of 180hrs.
|
|
|
Which 2 SSRIs cause DISCONTINUATION Syndrome cahracterized by dizziness and paresthesias 1-2 days after stoping the medication? which of these also causes wgt loss?
|
1.Paroxetine (causes both).
2.Sertraline. **Due to their shorter 1/2 life |
|
|
What is major pt complaint on SSRIs?
|
Dec sexual function and interest
|
|
|
Which 2 SSRIs are POTENT CYP2D6 inhibitors requiring you to monitor dosing of other drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 (ex: SNRIs, TCAs)
|
1.Paroxetine.
2.Fluoxetine |
|
|
MOA of SNRIs
|
Bind and inhibit both SERT and NET
|
|
|
List the 3 SNRIs
|
1.Duloxetine (also used for pain).
2.Milnacipran. 3.Venlafaxine. |
|
|
Which SNRI can also be used for Fibromyalgia (which has a strong depression component)
|
Milnacipran
|
|
|
which has a longer 1/2 life, SSRIs or SNRIs (think about for dosing purposes, X/day)? which has more CYP interactions?
|
SSRIs
|
|
|
Since SNRIs also block the reuptake of NE, the cause Inc Noradrenergic SEs like HTN, Inc HR, and Insomnia/agitation (CNS stimulation). Which SNRI is the most cardiotoxic?
|
Venlafaxine
|
|
|
When would you consider using Tricyclic Antidepressants to treat depression? what time of day would you give them?
|
If SSRIs or SNRIs did NOT work.
**Given at night due to sedation |
|
|
List 3 TCADs and their additional use besides depression
|
1.Imipramine: Enuresis.
2.Amitripyline: Post-herpetic Neuralgia, Diabetic neuropathic pain. 3.Clomipramine: OCD. |
|
|
TCADs target every receptor type, what are some Key SEs b/c of this
|
1.Anti-ACh: Dry mouth, constipation.
2.Anti-H: sedation. 3.Anti-adrenergic: orthostatic HTN. 4.Dec sex drive |
|
|
Is the Discontinuation syndrome of TCADs the same as with SNRIs and SSRIs? (dizziness and paresthesia)?
|
NOO, Prominent CHOLINERGIC REBOUND and flu like symptoms
|
|
|
List the 2 Serotonin Antagonists
|
1.Trazodone.
2.Nefazodone. |
|
|
MOA of Trazadone
|
Block 5-HT(2A) receptor.
**Same as LSD |
|
|
Trazadone is BLACK BOXED for what?
|
Hepatotoxicity
|
|
|
MAO(A) will increase what NTs in the neuron? MAO (B) will increase what NTs in the neuron?
|
A:
1.Dopamine. 2.NE. B: 1.Serotonin. 2.Histamine |
|
|
What is ths only MAO Inhbitor used for depression which is an irreversible, nonselective MAO Inhibitor
|
Phenelzine
|
|
|
SEs of Phenelzine
|
1.Orthostatic Hypotension.
2.Wgt gain. 3.Dec Sex drive. 4.Inc sedation. 5.Confusion. |
|
|
Describe the discontinuation syndrome from MAO inhibitors
|
Delirium-like: psychosis, excitement, confusion.
|
|
|
Phenelzine and MAOIs will cause Serotonin Syndrome (Coma, HTN, Tachycardia, and myoclonus, and tremor) with which Anti-depressant drug classes
|
1.SSRIs.
2.SNRIs. 3.TCADs. 4.Meperidine. **All need to be discontinued 2 weeks prior to MAOI use, Fluoxetine needs to be 4-5 weeks prior. |
|
|
MAOI (Phenelzine) inhibit the breakdown of _____ in the GI tract which leads to ______ ___ and __. What foods should be avoided?
|
Tyramine,
Elevated BP & MI. **Foods that contain Tyramine: 1.Aged Cheese. 2.Tap beer. 3.Soy. |
|
|
What SE should you be worried about in your pt taking Phenelzine that also does METH?
|
HTN
|
|
|
Which 2 drugs might you switch your pt to if they complained about sexual SEs?
|
1.Bupropion.
2.Mirtazapine (a2 Antagonist on presynaptic terminal) |
|
|
What is Unique about the Bupropion elmination?
|
it is BIPHASIC:
1st: lasts 1 hr. 2nd: lasts 14hrs. |
|
|
Which unclassified antidepressant can cause parkinson syndrome?
|
Amoxapine: (has D2 blocking activity
|
|
|
1st line Depression
|
SSRIs.
**Also SNRIs, Bupropion, Mirtazapine |
|
|
What drug is also used to treat seasonal depression as well as smoking cessation?
|
Bupropion.
|
|
|
Over doses are common method of suicide with TCADs, what should be given to reverse the fatal arrhythmias?
|
NaHCO3-.
**Over doses are also seen with MAOIs |
|
|
ALL Anti-depressants are BLACK BOXED for what?
|
Inc risk of Suicidality in pts < 25 y/o
|
|
|
Which Anti-depressant is Category D? why?
|
Paroxetine: Inc risk for cardiac septal defects in the first trimester
|
|
|
when is permanent maintainence therapy suggested for depressed pts?
|
when patient has 2+ serious major depressive episodes in the last 5 years or 3+ in a lifetime
|
|
|
Tx for Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
|
1.Flouxetine.
2.Sertraline |
|
|
Which SSRI is also useful in Tx of BULEMIA
|
Fluoxetine
|
|
|
Which Anti-depressant is used in treating obesity
|
Bupropion
|
|
|
What Anti-depressant can be used to treat hot flashes (Vasomotor symptoms in menopause)?
|
Desvenlafaxine
|
|
|
St. John Wort is used to treat depression, however, you should be worried about what?
|
it can cause drug drug interactions b/c it induces CYP3A4
|
|
|
Tx for Bipolar
|
1.Manic Phase: Lithium, Valproate, Carbamazepine.
2.Bipolar depression: Atypical anti-psychotic |
|
|
What drugs can BLOCK the renal clearance of Lithium?
|
1.Thiazide Diuretics.
2.NSAIDS |
|
|
Lithium has a narrow therapeutic window, what main SE should you be worried about? what would you tx it with?
|
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (polyuria, Polydipsia).
**treat with amiloride |
|
|
What nerve growth factor is critical in the regulation of neural plasticity, resilience, and neurogenesis?
|
brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
evidence points to depression may be due to loss of neurotrophic support |
|
|
What's some other key things about BDNF?
|
Stress and pain are associated in a drop in BDNF levels
-this leads to specific areas of atrophic structural changes, specifically the hippocampus, medial frontal cortex, and anterior cingulate Chronic activation of Monoamine receptors increase BDNF transcription |
|
|
What's some other neuroendocrine factors with depression?
|
abnormalities in the HPA Axis
elevated cortisol levels non-suppression of ACTH with dexamethasone test Chronically elevate CRH 25% have thyroid dysregulation |
|
|
Tell me about SSRI's
|
Primary action is the inhibition of the serotonin transporter (SERT).
Most commonly used, with *Fluoxetine* as the prototype |
|
|
How do SSRI's inhibit the SERT?
|
Causes an allosteric conformational change in the transporter, so technically not blocking it.
At therapeutic doses, only about 80% of the transporters activity is inhibited |
|
|
Which SSRI's are potent CYP2D6 inhibitors?
|
Paroxetine and Fluoxetine
|
|
|
Which SSRI is a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor?
|
Fluvoxamine
|
|
|
What should be the concern about giving SSRI's and MAOI's together?
|
Serotonin Syndrome
|
|
|
Tell me about SNRI's
|
bind both SERT and Norepinephrine transporter (NET)
**MAJOR USE IN PAIN DISORDERS, like fibromyalgia and neuropathies**-----> Milnacipran for fibromyalgia |
|
|
SNRI Pharmacodynamics
|
Velnlafaxine is a weak inhibitor of NET
Deslvenlafaxine, Duloxetine, and milnaciprain are balanced inhibitors of SERT and NET SNRI's have a greater affinity for SERT than NET |
|
|
What are the adverse noradrenergic FX of SNRI's?
|
increased BP, HR, and CNS activation (insomnia, anxiety, agitation)
also has a discontinuation syndrome |
|
|
Which of the SNRI/SSRI's has the most cardiac toxicity?
|
Venlafaxine
|
|
|
Tell me about Tricyclic Antidepressant/TCA's/TCAD's
|
was originally the primary class of antidepressants until SSRI's were introduced. They treat depression unresponsive to SSRI's, SNRI's, pain conditions, enuresis, and insomnia.
Loss of popularity due to poor tolerability, difficult to use, and lethal OD's |
|
|
Which TCA has serotonin effects?
|
Imipramine
|
|
|
TCA's and receptor FX (know the red)
|
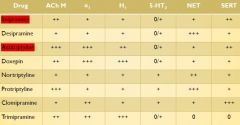
|
|
|
TCA Pharmacodynamics (know the red)
|
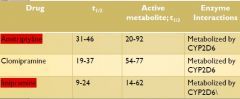
|
|
|
TCA's most concerning AFx?
|
Potent antimuscarinic FX, with dry mouth, constipation, etc. (anti-DUMBBELS)
More common with amitriptyline and imipramine |
|
|
Be aware that TCA levels are elevated when other drugs inhibit CYP2D6 and can also have additive FX with other drugs metabolized by CYP2D6
|
...just know it.
|
|
|
What are the two 5HT2 antagonists?
|
Trazodone and nefazodone (no longer used)
|
|
|
how do the 5HT2 antagonists work?
|
blockade of the 5HT2a receptors, the same target for LSD and mescaline.
|
|
|
Why is Nefazodone no longer prescribed?
|
hepatotoxicity, leading to lethal hepatic failure.
|
|
|
Drug Interactions of 5HT2 antagonists?
|
Nefazodone inhibits CYP3A4, but trazodone is a CYP3A4 substrate (inhibitors increase it's concentration
|
|
|
Tell me about MAOI's
|
target the A and B receptors non-selectively. Some structurally resemble amphetamines, and cause a CNS stimulation.
They are classified by specificity to A or B, and whether they are irreversible or reversible |
|
|
What's the main MAOI to know that is irreversible AND Non-selective?
|
Phenelzine
|
|
|
What's the difference between MAO receptor A vs B?
|
A is in dopamine and NE neurons, and are found in the brain, gut, placenta, and liver.
B is in serotonin and histamine neurons, in the brain, liver, and platelets. Both metabolize tryptamine and dopamine |
|
|
What are some AFx of MAOI's?
|
Most common is orthostatic hypotension and weight gain
Blocks metabolism of tyramine Sudden discontinuation causes delirium |
|
|
What's important SFx of Phenelzine?
|
High rate of sexual FX (anorgasmia)
More sedation Confusion at higher doses |
|
|
What's the triad of Serotonin Syndrome FX with MAOI's?
|
cognitive, autonomic, and somatic FX
or the 3C's-> coma, cardiac, and clonus |
|
|
be aware that most serotonergic antidepressants need to be D/c'd for at least 2 wks prior to starting an MAOI
|
know it.
|
|
|
What are the drug choices for the following clinical situations:
Pain Treatment of OCD Smoking |
Pain-----> TCA's and SNRI's
Treatment of OCD------> SSRI's and clomipramine Smoking------> bupropion and nortriptyline |
|
|
What drug class often used for suicidal overdose?
|
TCA's---> cause fatal arrhythmias, BP changes, and anticholinergic FX
Antidote is Sodium Bicarb |
|
|
What's the hangup on giving antidepressants to patients under 25?
|
Increased risk of suicidality
|
|
|
What pregnancy categories are the antidepressants?
|
Most are Category C, but Paroxetine causes cardiac septal defects-------> Category D
|
|
|
What is Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder, and how is it treated?
|
During the late luteal phase of every cycle, with anxiety, depressed mood, irritability, insomnia, and fatigue
Treat with fluoxetine and sertraline |
|
|
What does St. John's Wort induce?
|
CYP3A4-> lots of drug interactions
|
|
|
Review the Bipolar slides at the end of the Affective Disorders lecture (~ slide 70 and on)
Adverse SFx of Lithium? |
Thyroid fxn decreased
nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus edema CI'd in sick-sinus syndrome TOXIC in pregnancy----> Ebstein's Anomaly (lethargic, cyanosis, poor suck and Moro reflexes, hepatomegaly) |

