![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is a pathologic finding of babinski's sign?
|
dorsiflexion of the big toe = UMN Lesion
|
|
|
. The student will be able to measure and record visual acuity according to generally agreed upon conventions
|
Eye chart for visual acuity testing. Standard distances are 20 feet for a wall chart and 14 inches for a hand-held card.
Read down to the smallest characters possible or until reaching the 20/20 line, whichever comes first. The acuity is the last line correctly read. say they read like all of the letters but miss 1 or 2 you say 20/20 minus (assuming they read at the 20 20 line) |
|
|
a cut at the optic nerve would cause what visual problem?
|
|
|
|
a cut at the optic chiasm would cause what visual problem?
|
|
|
|
a cut at the right optic tract would cause what visual problem?
|
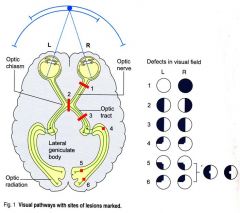
left homonomous hemianopia
|
|
|
right temporal damage could cause what visual damage?
|
4
|
|
|
what system is responsible for constricting the pupil?
|
PNS
|
|
|
please diagram the light reflex pathway...is this PNS or SNS?
|
CN II
pretectal nucleus Edinger Westphal nucleus ciliary ganglion contract pupil (This is PNS) |
|
|
please diagram out the sympathetic pathway for pupilary dilation
|
ipsilateral hypothalamus
synapse at T1 (IML) travel up the sympathetic chain and to the apex of the lung (look out for horners) goes to carotid bifurcation but then sends to the pupil for dilation |
|
|
how can a tumor of the apex of the lung lead to pupil issues?
|
this is horner's syndrome due to a pancoast tumor
you will see a constricted pupil because the sympathetics (which would normally dilate the pupil) stop at the apex of the lung and are disrupted by the tumor |
|
|
pt presents with a droopy eyelid and constricted pupil...
|
ipsilateral sympathetic chain issue--HORNERS
miosis-small pupil ptosis- droppy eyelid |
|
|
please list the primary and secondary action of the extraocular muscles. consider what would happen with a lesion
|
|
|
|
What do CN 6 and 4 do?
|
LR6SO4
LR (lateral rectus) connected to CN 6 SO (superior oblique) connected to CN 4 Remaining EOMs and levator palpebrae connected to CN 3 |
|
|
right lower face is weak, upper face is fine
is this an upper or lower motor neuron problem (o) |
LEFT UPPER MOTOR NEURON
|
|
|
right lower face is weak, upper face is also weak
is this an upper or lower motor neuron problem (o) |
RIGHT LOWER MOTOR NEURON
|
|
|
The student will be able to grade muscular strength according to the MRC (Medical Research Council) scale.
(o) |
|
|
|
You have CN III damage... How will this affect the eye?
|
CN 3 damage → eye looks down and out
-Ptosis, pupillary dilation, loss of accomodation (b/c you are using CN IV, and VI) |
|
|
You have CN VI damage... How will this affect the eye?
|
CN 6 damage → medially directed eye
|
|
|
You have CN IV damage... How will this affect the eye?
|
CN 4 damage → eye drifts upwards causing vertical diplopia
|
|
|
How do the eyes look in a patient with Horner's Syndrome? Where is the lesion?
|
Horner's Syndrome → Ptosis and miosis
• Associated with lesion of spinal cord above T1 (remember, nerve passes through apex of lung where a tumor can compress it) |

