![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
afferent vs efferent
|
afferent: carry nerve impulses from receptors or sense organs towards the central nervous system
efferent: from CNS to target |
|
|
what makes up the brainstem?
|
the midbrain (sup/inf colliculus)
pons medulla |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 lobes of the brain? major functions?
|
frontal: high order processing, planning, etc
parietal: somatosensory temporal: sound Occipital: vision |
|
|
where is broca's area located? (what lobe)
where is Weirnikes area? |
B: Frontal lobe
W: Temporal |
|
|
post central gyrus=?
pre=? |
post central=somatosensory
pre= motor |
|
|
cerebellum function?
|
compare planned motor behavior with actual movement
checks/balances |
|
|
functions of the insular lobe
|
emotions, drives, drug addiction etc
|
|
|
function of the calcarine fissure
|
primary visual processing area
|
|
|
difference btw gray and white matter?
|
gray: cell bodies (and some axons)
white: axons |
|
|
what makes up the basal ganglia?
|
Caudate Nucleus
Putamen Globus Pallidus |
|
|
just list the cranial nerves and their functions
|
* I-Olfactory nerve,
* II-Optic nerve, * III-Oculomotor nerve, * IV-Trochlear nerve/pathic nerve, * V-Trigeminal nerve/dentist nerve * VI-Abducens nerve, * VII-Facial nerve, * VIII-Vestibulocochlear nerve/Auditory nerve, * IX-Glossopharyngeal nerve, * X-Vagus nerve, * XI-Accessory nerve/Spinal accessory nerve and * XII-Hypoglossal nerve. |
|
|
Dorsal horn is associated with what?
Ventral? |
Dorsal: Sensory
Ventral Motor |
|
|
consider the locations of white and gray matter in the spinal cord and brain (which is deep and which is superficial in each)
|
spinal cord: gray matter deep
brain: gray matter superficial |
|
|
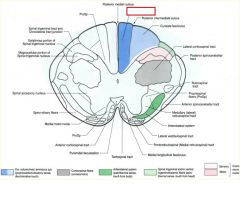
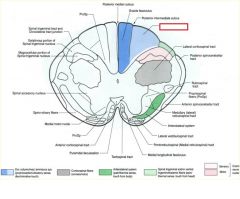
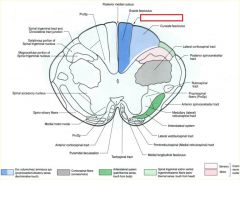
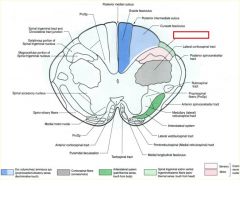
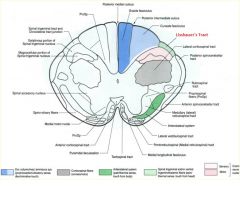
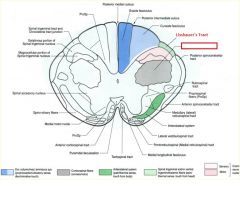
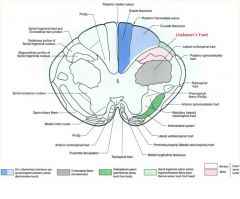
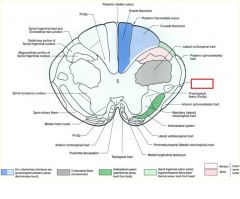
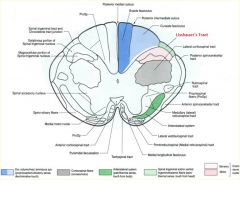
what divides the gracile and cuneate fasciculi?
|
posterior intermediate sulcus
**only seen at T7 and ABOVE*** |
|
|
what is the difference btw the gracile and cuneate fasiculate
|
Gracile: carries axons from lower extremities
cuneate: upper (t6 and up) REMEMBER: Feet in the grass Part of the DCML pathway for sensory info (pressure, vibration, fine touch) |
|
|
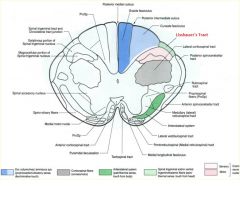
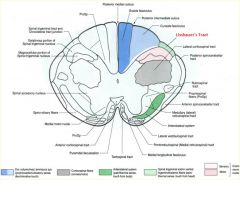
what type of information is carried by the Dorsal column/ medial lemniscus pathway
|
fine touch
proprioception, vibration. |
|
|
lateral corticospinal tract does what?
|
somatomotor
|
|
|
what does the anterolateral system (ALS) do?
|
pain
temperature touch (crude) |
|
|
does a 1st, 2nd, or 3rd order neuron cross?
|
2nd will cross
such as the second order neurons from the nucleus cuneatus crossing as internal arcuate fibers in the medulla |
|
|
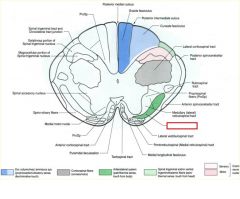
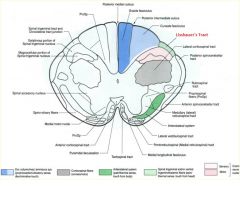
please diagram out the DCML pathway...what info does this carry?
|
|
|
|
please diagram out the Anterior Lateral System, and list what it carries
|
|
|
|
Please diagram out fine touch and vibration of the face
|
|
|
|
please diagram orofacial pain and temp
|
|
|
|
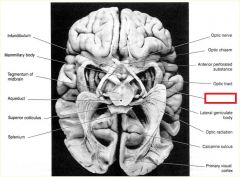
The left optic tract carries info from what visual field?
|
right visual field
|
|
|
What is the job of the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)?
|
visual processing
receives synapse from eyes |
|
|
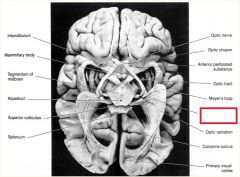
where will superior visual field info end up?
|
inferior calcarine fissure
(remember they also travel inferior in the meyers loop) |
|
|
a pituitary tumor causes pressure on the optic chiasm...what will this lead to?
****TEST |
Bitemporal hemianopia
Will only be able to see info from medial visual fields (peripheral vision lost-->tunnel vision) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
pt falls off their bike and was not wearing a helmet. They now say that they have lost vision just in the very center of each eye...what is going on?
|
Central scotomas
|
|
|
diagram out the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts
|
|
|
|
pt has flaccid paralysis...what is the problem
|
lower motor neuron
|
|
|
pt has spastic paralysis...what is the problem?
|
upper motor neuron
|
|
|
middle cerebral artery damage will lead to issues in what structure
|
face
comes out of sylvian fissure and branches like a tree |
|
|
anterior cerebral artery damage will lead to issues in what structure
|
legs and feet
|
|
|
describe the role of the Direct pathway and the indirect pathway in the basal ganglia
**TEST |
Direct pathway: starting movement
indirect pathway: stopping movement |
|
|
which pathway (direct or indirect) encourages GPm activity...what does this do?
|
INDIRECT
GPm has tonic inhibition of the thalamus (which is always wanting to activate movement...it's like GO GO GO) thus the indirect by activating GPm will stop movement (this is the key thing to remember) note: in the direct pathway, you inhibit GPm so inhibiting the inhibition leads to activity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
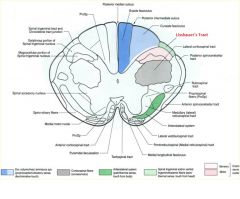
posterior intermediate sulcus is only seen ABOVE T7
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**Meyer's Loop**
-Meyer's Loop can be damaged via stroke in the temporal lobe of the MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY.. This will knock out SUPERIOR VISION **TEST** |
|
|
**Lateral Geniculate Body***
-All optic info passes through here!!! |
|
|
Visual Cortex:
The superior visual field is projected to the ____ portion of the visual cortex ***EXAM*** |
lower portion
|
|
|
Visual Cortex:
The inferior visual field is projected to the ____ portion of the visual cortex ***EXAM*** |
upper portion
|
|
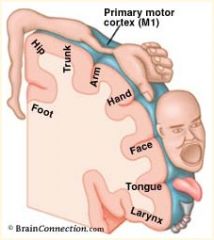
***EXAM***
|
Homunculus:
-Head and face are located more LATERALLY while lower limb is located MEDIALLY on pre and post-central gyrus |

