![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the acute findings of bacterial meningitis?
|
Abrupt onset fever, severe H, stiff neck, photophobia
Rash (purpura) = Neisseria meningititis, N, V Severe = impaired consciousness, delirium, seizures, or other neurological symptoms |
|
|
How do organisms enter to cause meningitis?
|
Enters blood stream via mucous membranes of oropharynx --> Penetrate BBB at choroid plexus --> inflamm on blood side --> spillage into CNS
|
|
|
A microbial load above what indicates pathological meningitis?
|
> 10 ^5
|
|
|
Why are microbes more able to exist in CSF than blood?
|
CSF = less host defenses - low complement and Abs = reduced phagocytosis
|
|
|
Where does N. meningititis enter CSF?
|
At capillaries that make CSF
|
|
|
What are the clinical symptoms of meningitis due to?
|
inflammatory response to meningeal invasion
Pus in sub-arachnoid space may spread over surface of brain, cerebellum, spinal cord --> becomes thick --> blocks foramina and inc CSF pressure --> H and N |
|
|
What causes the severe disease seen with meningitis infection?
|
Neurological deficits caused by dec. in cerebral cortical blood flow
|
|
|
Define Waterhous-Friderichsen Syndrome
|
A Gangrenous condition
|
|
|
A native American without easy access to medical care unfortunately dies from a bacterial meningitis infection that could have been easily treated. What does the pathologist see when he sections the brain of this pt?
|
Yellow-tan exudate of acute bacterial meningitis - obscures sulci
Maybe some transtentorial hernaition |
|
|
Pt has an acute decline in consciousness caused by seizures and a big head because their name is (insert any Fox News caster here). They are started on Abx but fail to improve. Whats your next move?
|
Image because those are the indications for doing so (decline in consciousness presumably caused by seizures and acute hydrocephalus ie big head...and Failure to improve after attempting treatment with Abx
|
|
|
A pt comes in with Limb drift and say they see yellow unicorns in their upper left visual field of view. They can't quite say unicorn, however, and it comes out sounding like "uni-brow". What do you do
|
FIRST = initiate Abx.
Abnormal sensorium, limb drift, Aphrasia and Abnormal visual fields all are symptoms characteristic of a decline in consciousness and this pt needs to be imaged for possible acute meningitis |
|
|
When we take CSF specimen for meninigtis, what do we do with tubes 1, 2, and 3, subsequently?
|
1 = chemical analysis
2 = gram stain and culture 3 = cell count (least contaminated) |
|
|
Whats the defining feature of a bacterial meningitis?
|
inc cell count, esp PMNs
|
|
|
Why is glu low in bacterial meningitis CSF samples?
|
bacteria use it up (note: its also low in Tuberculous and Fungal meningitis)
|
|
|
We can use antigen detection to detect what types of bacterial meningitis?
|
Strep pneumo, N. meningitidis, H. influ, Group B strep, E. coli
- can substitute methylene blue or acridine orange for gram stain for spinal tap |
|
|
Just know these pics
|
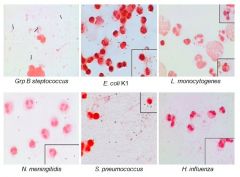
|
|
|
What antibody opsonizes immunoglobulin?
|
IgG2 immunoglobulin on polysaccharide capsule
|
|
|
When does IgG2 immunoglobulin on the polysaccharide capsule of many bacteria that cause meningitis pass the placenta?
|
Only during the last stages of gestation
|
|
|
Whats the empiric tx for Bacterial meningitis?
|
Vancomycin + Ceftaxime or Ceftriaxone + Dexamethazone
Once etiological agent determined, adjust therapy |
|
|
T/F: The antibiotics does not need to penetrate the BBB to have an effect on the meningitis infection
|
FALSE - it must penetrate BBB
|
|
|
A pt with a meningitis infection wants to know how she can protect her 4 and 6 year old kids from the infection. What drug can be used prophylactically in her kids?
|
Rifampin
|
|
|
What are each of the following vaccinated with?
Young kids, Young adult, elderly |
Young kids = conjugate Hib, 7 valent S. pneumo, and N. meningitidis
Young Adult = Conjugate vaccine with N. meningitidis and W135 polysaccharide vaccine when entering military or college Elderly = S. pneumo (Pneumovax) |
|
|
****TEST questions: Whats the difference between Polysaccharide (= T cell independent) and Conjugate (=T cell dependent) vaccine?
|
Conjugate is conjugated to a strong immunogenic protein that causes it to be picked up by antigen presenting cell = presents it to TH2 cell = undergoes activation - releases interleukins and chemokines
SO ANSWER IS: Presents it to B cells --> produces MEMORY B Cells Produces a better IgG = stronger and binds better |
|
|
Whats the most important characteristic between these two features of conjugate vaccines (=T cell dependent)?
Presents it to B cells --> produces MEMORY B Cells Produces a better IgG = stronger and binds better |
Produces a better IgG
|
|
|
Just to beat this to the ground re-state the characteristic of T cell-dependent Ab production (ie conjugate)
|
Protein Ag
IgG high affinity Adequate memory (T cell independent = Polysaccharide Ag, IgM Ab, Lack of memory response, Little boosting achieved) |
|
|
What bacterial diseases can manifest as chronic meningitis?
|
Tuberculosis, Syphilis, Lyme disease, Cryptococcosis, Coccidiomycosis, Histoplasmosis
|
|
|
What causes Tuberculosis meningitis and how does it occur?
|
Rupture of superficial infective focus in subarachnoid space --> mycobacterium tuberculosis infection --> ocular palsies (50% of cases)
|
|
|
What causes Syphilis meningitis?
|
Treponema pallidum
|
|
|
Lymphocytic pleocytosis in CSF. Dx?
|
Tuberculosis meningitis
|
|
|
VDRL (=Venereal disease research lab test) on CSF is positive, so you confirm with an FTA. Dx?
|
Syphilis meningitis
|
|
|
What causes Lyme meningitis?
|
Borrelia Burgdorferi
|
|
|
Whats a major clue you have been infected with Borrelia burgdorferi that caused your meningitis?
|
Multiple erythema migrans
Neurological symptoms in 1/3 of untreated cases |
|
|
Lab for Borrelia burgdorferi meningitis?
|
>80% mononuclear cells, H > 5 days, cranial neuritis = cranial nerve palsy or neuritis
|
|
|
Pt presents with erythema migrans and Lab results for a pt show 85% mononuclear cells. Tx?
|
Think Borrelia burgdorferi. Tx = Ceftriaxone
|
|
|
***TEST Define Brain Abcess
|
A focal infection of brain parenchyma that causes specific focal deficits
Contiguous infection of (paranasal sinuses, middle ear, or mastoids) frequently caused by mixed facultative and anaerobic bact. |
|
|
How does a brain abcess often present?
|
Usually starts as a septic emboli, trauma or surgery case where staph a. spreads hematogenously
|
|
|
How do we Dx brain abcess caused by staph a.?
|
CT or MRI
Note - this is prob the test question - DO NOT DO A LUMBAR PUNCTURE - its contraindicated. |
|
|
Pt post-Sx comes in with brain abcess which you know b/c you're not a dummy and did a CT then MRI to confirm (NOT a lumbar puncture). How do you tx this pt?
|
Drain abcess and give approproate Abx
|
|
|
A pt has an amoeba which is eating her brain. (ie primary amoebic meningoencephalitis) What stages infected her?
|
Naegleria fowleri Flagellated or trophozoite can both enter nose and penetrate nasal mucosa, migrating to brain via olefactory n.
|
|
|
A female preggo is bitten by a pig, mouse, sheep, and her cat crapped on her pillow which she didn't wash. What stage of the infective organism does it change into once it has infected her with the cyst form?
|
Think Toxoplasma --> Cyst infects then transforms into Tachyzoites
|

