![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Neuron |
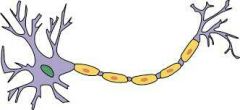
Nerve cell, transmits information throughout the body |
|
|
Dendrites |
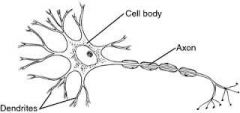
Part of a neuron that receives information from other neurons |
|
|
Axon |
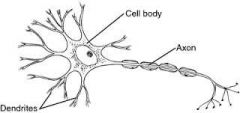
Part of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses |
|
|
Nerve |
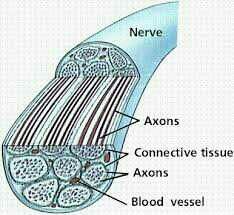
Bundle of neurons |
|
|
Membrane potential |
The difference in electrical charge across a cell membrane |
|
|
Resting potential |
The membrane potential of a neuron at rest |
|
|
Action potential |
Nerve impulse |
|
|
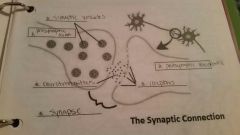
Synapse |
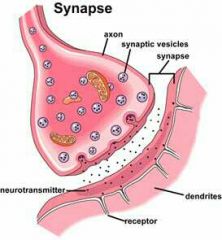
A junction at which a neuron meets another cell |
|
|
Neurotransmitter |
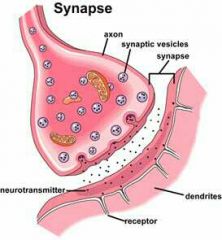
A signal molecule that transmits nerve impulses across synapses |
|
|
Motor neuron |

Carries motor responses from the CNS to muscles, glands and other organs |
|
|
Cerebrum |
Site of capacity for learning, memory perception and intellectual function |
|
|
Central nervous system |
Consists of brain and spinal cord |
|
|
Thalamus |
Relays sensory information |
|
|
Spinal cord |
Dense cable of nervous tissue that runs through the vertebral column |
|
|
Brain |
The body's main processing center |
|
|
Peripheral Nervous system |
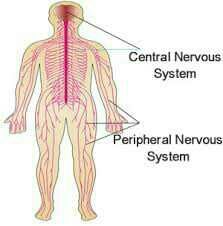
Contains neurons that branch through the body |
|
|
Sensory neuron |

Carries information from sense organs to the CNS |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Regulates breathing, heart rate and endocrine functions |
|
|
Interneurons |
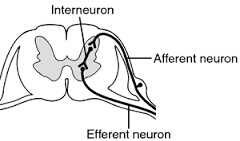
Link neurons to each other |
|
|
Brain stem |
Collection of structures leading down to spinal cord |
|
|
Cerebellum |
Regulates balance, posture and movement |
|
|
Reflex |
A sudden, rapid and involuntary self protective motor response |
|
|

|
|
|
Spinal cord |
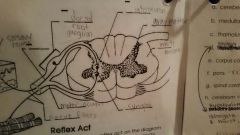
|
|
|
Reflex Arc |
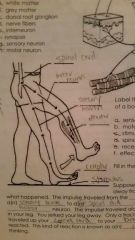
|
|
|
Cerebellum |
Monitors muscle tone and position and coordinates new muscle movement |
|
|
Medulla oblongata |
Regulates vital functions of heart rate, blood pressure, breathing and reflex center for coughing, sneezing, swallowing and vomiting |
|
|
Thalamus |
Relay station that receives sensory nerve impulses from optic nerves and sends them to visual centers in the occipital lobe |
|
|
Pituitary gland |
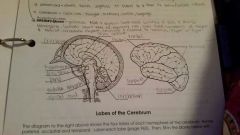
Regulates growth and development of all endocrine glands |
|
|
Corpus callosum |
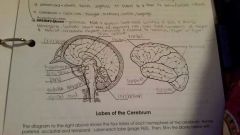
Connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum and allows them to communicate and coordinate their actions |
|
|
Pons |
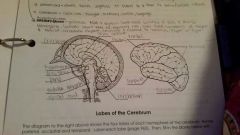
Relays sensory and motor information, role in breathing |
|
|
Spinal cord |
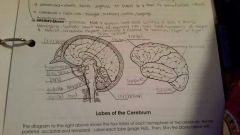
Allows nerve impulses to travel to and from the brain, controls reflexes |
|
|
Cerebrum |
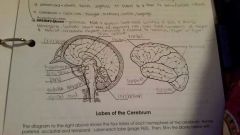
Conscious, thought, memory, senses, language |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
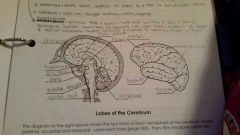
Produces ADH and oxytocin. Coordinates activites of pons and medulla oblongata. Co told heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, body temp, sensations of hunger and thirst, circadian rhythm, emotions and response to emotions and fight or flight response |
|
|
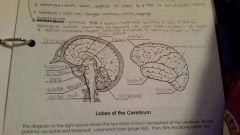
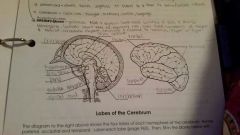
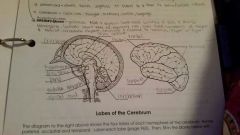
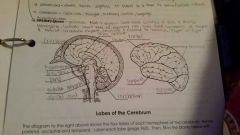
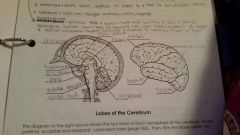
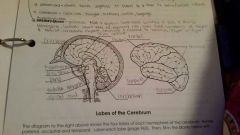
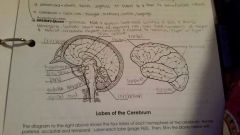
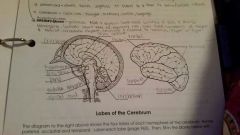
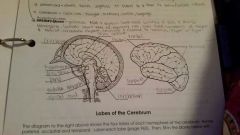
Frontal Lobe |
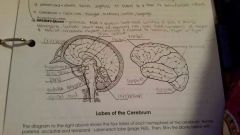
Controls some body movements, reasoning, judgement and emotions |
|
|
Occipital lobe |
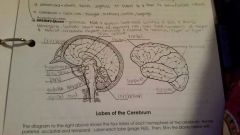
Sense of vision |
|
|
Temporal lobe |
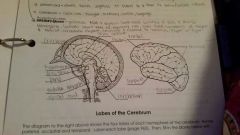
Sense of hearing |
|
|
Parietal |
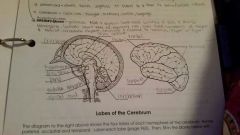
Interprets sensations of pain, pressure, touch, hot and cold |

