![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Central Nervous System
|
CNS - brain and spinal chord
|
|
|
Cerebrum
|
Part of brain, motor control, sensory
|
|
|
Diencephalon
|
part of brain - thalamus and hypothalamus
|
|
|
Thalamus
|
interprets sensations, like temperature and pain
|
|
|
Hypothalamus
|
regulated homeostatic functions (body temp, fluid balance, thirst, urine output, food intake, emotion, and behavioral patterns)
|
|
|
Brain Stem
|
Midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata
|
|
|
Midbrain
|
in brainstem
connecting link |
|
|
Pons
|
in brainstem
contains respiratory centers Lilys help ponds respirate |
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
in brainstem
nerve fibers cross left to right and in reverse influences resp rate, heart rate, vomiting, sneezing, and coughing Waterboy - brings water to players to maintain normal body processes |
|
|
RAS - Reticular activating system
|
in brainstem, responsible for sleep/wake cycles
|
|
|
Cerebellum
|
coordination and balance
BELL = coodinated ballerina |
|
|
Spinal cord
|
Runs through vertebral foramen
Outer: white nerve fibers Inner: gray neuron body cells Protected by bone and meninges |
|
|
Afferent
|
Sensory nerve impulses
Periphery -----> Brain A=absorbed by the brain |
|
|
Efferent
|
Motor nerve impulses
Brain --------> Periphery E=Eject from the brain to the body |
|
|
Dura Mater
|
outer layer of meninges, dense fibrous connective tissue
|
|
|
Arachnoid (arachnoidea) mater
|
Middle layer consisting of very delicate and elastic connective tissue
|
|
|
Pia Mater
|
transparent, delicate connective tissue that contains tiny blood vessels and adheres to surface of brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
epidural space
|
between bone and dura mater, loose connective tissue, blood vessels, and fat
|
|
|
subarachnoid space
|
contains cerebrospinal fluid and large blood vessels
|
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
|
colorless, watery fluid, contains protein, glucose, ions etc.
Cushions and nourishes the brain Lumbar tap or CSF tap to sample |
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
|
all nerve processes connecting to the CNS
|
|
|
Somatic Division
|
Voluntary movements
(Efferent or motor neurons carry impulses from the CNS to the skeletal muscle) |
|
|
Autonomic Division
|
All involuntary functions
(Efferent neurons carry impulses from the CNS to smooth muscle, glands and heart) Sympathetic vs parasymphathetic |
|
|
Sympathetic
|
FIGHT or FLIGHT response (Inc. Heart rate, respiration rate and blood flow)
Sympathetic towards others, adrenaline kicks in to save the day |
|
|
Parasympathetic
|
Quiet activities : digestion, heart rate and return body to normal levels after sympathetic
a Pair of people : couples stay in and calm at home |
|
|
Neuron
|
Nerve Cell
Dendrites --> cell body --> axon |
|
|
Nerve Impulse
|
Generated by action potentials, travel in 1 direction
|
|
|
Saltatory conduction
|
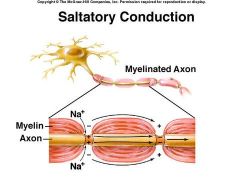
Myelinated (insulative covering) nerve fibers transmit faster than nonmyelinated nerve fibers
myelin = insulative covering for nerve cells interrupted at nodes of Ranvier |
|
|
Neuroglial cells (glial)
|
Connective tissue cells within CNS and PNS, do not transmit impulses but support and protect
|
|
|
Astrocytes
|
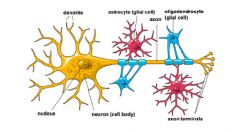
CNS Glial cells - star shaped, most abundant, support nervous tissue, stimulate formation of blood brain barrier
Astro = Many stars in the brain |
|
|
Oligodendrocyte
|
CNS Glial cells - smaller, wrap around axons to form myelin in CNS
|
|
|
Microglia
|
CNS Glial cells - phagocytic cells
|
|
|
Ependymal
|
CNS Glial cells - ciliated, which helps circulate CNS
|
|
|
Schwann cells
|
PNS Glial cells - wrap around axons to form myelin in peripheral nerves
|
|
|
Satellite cells
|
PNS Glial cells - surround cell bodies but function unknown
|
|
|
Reflexes
|
automatic response to stimulus
Impulse transmitted along sensory neuron to spinal chord and synapses with interneuron (3-head neuron reflex) or motor (2-head neuron reflex) Impulse induces effector organ to respond ex: stretch, withdrawal, corneal and papillary light reflexes |

