![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Necrotising enterocolitis |
1/1000 live birth 5%NICU ADMISSIONS 10%full term, 45% VLBW Mean age of onset 12days Mean age of gestation 32weeks Mortality 9-28% |
|
|
Risk factors of NEC |
Prematurity/immaturity of GI tract Enteral feeding Formula feeding Cocaine Toxaemia (mother) Asphyxia Umbilical arterial catheter Congenital heart disease Polycythaemia Sepsis Hypotension Blood transfusion |
|
|
Dx NEC |
1. SISTEMIC SIGNS respiratory distress Apnoea Bradycardia Lethargy Temperature instable Poor feeding Hypotension Poor peripheral perfusion Metabolic acidosis Oliguria Bleeding |
|
|
ABDOMINAL SIGNS OF NEC |
Distension Tenderness Gastric aspirates Vomiting Ileus Blood in the stools Abdominal wall erythema or induration Persistent localized abdominal mass |
|
|
Laboratory features of NEC |
Thrombocytopenia Persistent metabolic acidosis Hyponatremia High lactate Crp raise Blood culture Electrolyte levels, liver, renal function |
|
|
RADIOLOGICAL SIGNS NEC |
Anteroposterior, lateral decubitus Fixed bowel loops Portal or hepatic venous air Pneumatosis intestinalisPortal or hepatic venous airPneumonitisPneumoperitoneum intestinalisPortal or hepatic venous airPneumonitisPneumoperitoneum Pneumonitis Pneumoperitoneum |
|
|
NEC - BELL STAGING CRITERIA |
Stage 1 suspected Stage 2 definite Stage 3 advanced CLINICAL SIGNS&SYMPTOMS ( PNEUMATOSIS RX) ((PNEUMOPERITONEUM AND CRITICAL ILL) |
|
|
Management NEC |
Ventilatory support Monitoring perfusion e blood pressure, give volume and inotrops Metabolic function (Sodium bicarbonate, lactate) Nutrition ( discontinue enteral feeds, nasogastric tube on free drainage, start TPN) INCECTION SCREEN, BROAD SPECTRUM OF ANTIB platelet transfusion, Red Blood trans Oliguria, renal failure (acute tubular necrosis) Neurologic function ( exclude IVH) |
|
|
Rds |
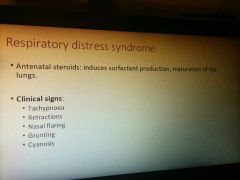
Cxr: low volume lungs with diffuse reticulogranular pattern and air bronchograms |
|
|
Rds MANAGEMENT |

|
|
|
BPD bronchopulmonary dysplasia |
Infant born <32 weeks who remain in oxygen for 28 day MILD: NO SUPPLEMENTAL O2 REQUIREMENT MODERATE: BPD IS A REQUIREMENT OF SUPPLEMENTAL O2 <30% SEVERE: >= 30%02 or CPAP baby >32 weeks with oxy REQUIREMENT for 28 gg |
|
|
BPD MANAGEMENT |
ventilation Small tidal volume to minimize machanical pulmunary injury CO2 55-65 mmhg as long as pH remains in the normal range PEEP between 5-7 cm H20 to minimize atelectasis Mechanical ventilation Small tidal volume to minimize mechanical pulmunary injuryTargeting partial pressure of CO2 55-65 mmhg as long as pH remains in the normal rangePEEP between 5-7 cm H20 to minimize atelectasis Targeting oxygen saturation to avoid hypoxemia and exposure to excess oxygenNUTRITION incrased requesCAREFUL FLUID MANAGEMENTDIURETIC THERAPY for ventilator dependentSYSTEMIC GLUCOCORTICOID therapy for exceptional infantCaffeineVit ALong term follow up by a multidisciplinary team Targeting oxygen saturation to avoid hypoxemia and exposure to excess oxygen Targeting partial pressure of CO2 55-65 mmhg as long as pH remains in the normal rangePEEP between 5-7 cm H20 to minimize atelectasis Targeting oxygen saturation to avoid hypoxemia and exposure to excess oxygenNUTRITION incrased requesCAREFUL FLUID MANAGEMENTDIURETIC THERAPY for ventilator dependentSYSTEMIC GLUCOCORTICOID therapy for exceptional infantCaffeineVit ALong term follow up by a multidisciplinary team
NUTRITION incrased reques
dependent CAREFUL FLUID MANAGEMENTDIURETIC THERAPY for ventilator dependentSYSTEMIC GLUCOCORTICOID therapy for exceptional infantCaffeineVit ALong term follow up by a multidisciplinary team SYSTEMIC GLUCOCORTICOID therapy for exceptional infant DIURETIC THERAPY for ventilator dependentSYSTEMIC GLUCOCORTICOID therapy for exceptional infantCaffeineVit ALong term follow up by a multidisciplinary team Caffeine Vit A Long term follow up by a multidisciplinary team |
|
|
BPD CXR |
Diffuse haziness and a coarse interstitial pattern, which reflect atelectasis , inflammation, pulmonary edema Lung volume: normal/low Areas of atelectasis alternate with areas of gas trapping related to airway obstruction from secretions or bronchiolar injury Severe BPD shows hyperinflation Streaky densities or cystic areas may be prominent (corresponding to fibrotic changes) |

