![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Tornadoes |
Rotating cortex of high winds created during a thunderstorm 80% occur in U.S |
|
|
Tornado Alley |
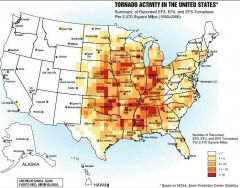
Texas north to Iowa Kansas east to Ohio |
|
|
When do Tornadoes occur? |
Most commonly during spring and summer months |
|
|
Formation (Tornadoes) |
Low-altitude: northward flow of tropical air Mid-altitude: cold, dry air mass High-altitude: jet stream wind moving east |
|
|
Supercell Tornado |
Thunderstorm needs to have large updraft to get tilted by wind shear Most tornados are produced by supercells Only 30% of supercells have tornadoes |
|
|
Wall Cloud |
Markedly lower cloud beneath the main mass of the mesocyclone |
|
|
Final Stages of a Tornado |
Downdrafts interfere with or cut up the energy supply |
|
|
Tornado Outbreaks |
When conditions are correct for one tornado they are correct for multiple tornadoes |
|
|
April 3-4, 1974 (Tornado) |
Conditions aligned - Cold front from Rocky mountains - Low pressure moving east - Humid air from Gulf of Mexico - Strong polar jet - Dry air from the southwest |
|
|
Wisconsin April 2011 (Tornado) |
15 tornadoes Hail Strong winds |
|
|
Fujita Scale |
Based on damage to approximate wind speed |
|
|
EF0 and EF1 |

50% of all tornadoes Rope like appearance Warning time is short |
|
|
EF2 and EF3 |

About 40% of tornadoes Funnel like appearance Fair warning time |
|
|
EF4 and EF5 |

About 10% of tornadoes Wedge shape Good warning time |
|
|
Suction Vortices |
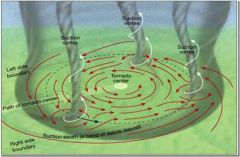
Individual cyclone within a tornado |
|
|
Tornado Wannabes |
Funnel clouds Dust devils Waterspouts |
|
|
Tornado Safety (In a house) |
Lowest floor Center of building Smallest room |
|
|
Tornado Safety (In a car or in the open) |
Get into ditch Drive perpendicular to tornado |
|
|
Tornado Safety (In a large building) |
Outer walls |
|
|
Tornado Watch |
Conditions are favorable for a tornado |
|
|
Tornado Warning |
Tornado has been sighted |
|
|
Tropical Cyclones |
Low pressure system with winds exceeding 119 km/hr Use warm water to energize wind and waves Formation: Sea water over 27℃ Warm, humid unstable air 300 miles from equator Weak upper-level winds |
|
|
Tropical Storm Timeline |
Tropical disturbance Tropical depression (38mph) Tropical storm (73mph) Tropical cyclone |
|
|
Rain Bands |
Intense rain Tornadoes form from here if at all |
|
|
Eyewall and Eye |
As inward-flowing air gets closer to the hurricane center, rotational wind speed increases |
|
|
Hurricane Andrew |
Within the hurricane were small twisting vortices - eddies - Causation behind the change in roof structure |
|
|
Tornadoes in Hurricanes |
Most commonly found on the right-front quadrant in outer rain bands |
|
|
Storm Surge |
Abnormal rise of water generated by a storm |
|
|
Energy Release by Storm |
Needs a heat engine - warm ocean water Hurricanes generate 200 times more energy greater than our worldwide capacity to generate electricity |
|
|
Hurricanes Origins |
Main energy source: latent heat released by condensation Landfall weakens the storm Not associated with fronts The weaker the high-altitude winds means stronger hurricanes Centers are warmer than their surroundings Winds weaken with height Descending air in the center of the storm |
|
|
North Atlantic Hurricanes (When) |
Occur in late summer with warmest ocean temperatures |
|
|
Cape Verde-Type |
Northwest Africa - easterly wave - Disturbances or mage-ripples that develops within the trade winds Blown westward by the trade winds |
|
|
Hurricane Paths |
Difficult to predict - Adjust to other high and low pressure systems - Trade winds - Coriolis effect - Bermuda high |
|
|
Bermuda High |
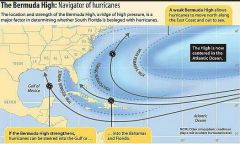
Small: hurricane stay over Atlantic Ocean Large: guides hurricanes toward east coast Moved southward: guides hurricanes into the Caribbean sea and Gulf of Mexico |
|
|
Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico Type |
Originate at the Intertropical Convergence Zone - Daily thunderstorms |
|
|
Notable Storm Surges |
Ike 2008 Katrina 2005 Sandy 2012 |
|
|
Reducing Damages from Hurricanes |
Building codes since 1994 Tied down roofs Wind-borne debris Land-use planning Coastal development restrictions |
|
|
Cyclones and Bangladesh |
In the 20th century, seven of the nine most deadly weather events were cyclones in Bangladesh. - Heavily populated area - Storm surge of 6m would flood 35% of the country - 360 miles of coastline |
|
|
Hyperthermia |
Above 99.5℉ |
|
|
Hypothermia |
Below 95℉ |
|
|
Lake Effect Snow |
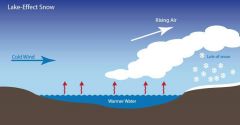
Cold, Dry air moves over warmer water and picks up moisture. Then it rises, freezes and precipitates as snow |
|
|
Wind Chill |
Uses wind speed and temperature |
|
|
Heat Index |
Uses temperature and relative humidity |
|
|
Nor'easters |

Winter weather condition involving low-pressure system with center offshore of the Atlantic coasts of the united states and canada |
|
|
March 1993 (nor'easter) |
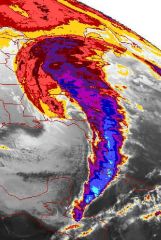
Wind speeds over 100mph 50 tornadoes in Florida |
|
|
Whiteout |
When the sky is non-distinguishable from the ground due to snow |
|
|
Ice storms |
Large volumes of freezing rain - add weight to tree limbs, powerlines and roofs |
|
|
Avalanche (main parts) |
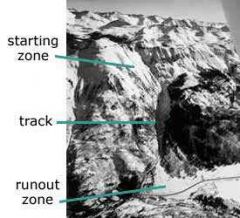
|
|
|
Types of Avalanches |
Loose-powder (flows) Slab (slides) |
|
|
North Ossetia, Russia (Avalanche) |
September 20 2002 Killed more than 100 people |
|
|
Chicago Heat Wave 1995 |
Strong upper-level ridge sat over a slow-moving, hot humid air mass |
|
|
Urban Heat Islands |
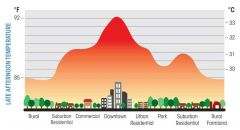
Buildings and streets absorb solar heat all day and release stored heat at night |
|
|
Wildfires |
15% natural cause (lighting) 85% human cause |
|
|
Need for Fire |
Organic material produced by plants is recycled by slow decomposition and rapid burning Necessary for health of some plant communities: germinate seeds, controls parasites, influenced insect behavior |
|
|
The Fire Triangle |

|
|
|
Ladder Fuel |
Understory of slash and shrubs allows fire to spread up into tall trees |
|
|
Preheating |
Water expelled from fuel by nearby flames, drought, hot summer day |
|
|
Pyrolysis |
When the chemical structure of solid wood breaks apart and yields flammable hydrocarbon vapors |
|
|
Flaming Combustion |
Stage of greatest energy release |
|
|
Glowing Combustion |
Wood itself burns slowly, at lower temperatures, without flames |
|
|
Spread of Wildfires |
- Fuel - Wind - Topography |
|
|
Foehn Winds |
When a high pressure air mass spills over a mountain range and descends as a warm, dry wind toward a low pressure zone - Chinooks - Santa Annas - Diablo - North winds - East winds |
|
|
Fire Similarities to Floods |
- Weather, vegetation and topography based - Strongest when atmospheric conditions are extreme - Move across landscape as waves of energy - More turbulent the faster and bigger they are - Described by size and frequency - Understood in recurrece-time events |
|
|
Why are there no hurricanes at the equator? |
There is no coriolis effect |
|
|
What hurricane feature causes the greatest destruction to coastal regions? |
Wind damage |
|
|
What hurricane feature causes the greatest destruction to inland regions? |
Flooding |
|
|
Why is the right hand side of a hurricane (relative to its movement) the most dangerous? |
Because on that side, the wind is moving directly towards the coastline which increases flooding |
|
|
Ways hurricanes can produce damage |
Flooding Tornadoes Storm surge Wind damage |
|
|
Short period comet |
Orbit the sun for less than 200 years |
|
|
Long period comet |
Orbit the sun for more than 200 years |
|
|
Average life span of a species |
4 million years |
|
|
Possible causes of mass extinction |
Plate tectonics - Sea level drop - Sea level rise Continental position and glaciation Volcanic causes - Changes in atmospheric composition Ocean composition causes Extra terrestrial causes - Wild fires, acid rain, tsunami, dust cloud Biologic causes Random extinction Predation and epidemic disease |
|
|
Quaternary extinctions |
Significant extinctions of large-bodies mammals in the last 1.5 million years, during glacial advances and retreats |

