![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
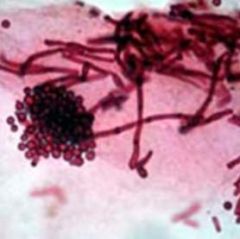
a. What agent causes pityriasis versicolor?
|

i. Malassezia
(On a 10% KOH mount) |
|
|
|
b. What are the symptoms of pityriasis versicolor?
|
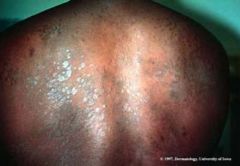
i. Hypo- or hyperpigmented macules due to acid in melanocytes
|

|
|
|
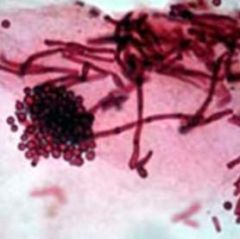
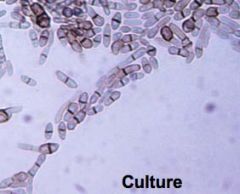
c. How can you ID pityriasis versicolor?
|
i. Spaghetti and meatballs appearance of organisms in skin scrapings
|
|
|
|
a. What agent causes tinea negra?
|
i. Exophiala werneckii
|
|
|
|
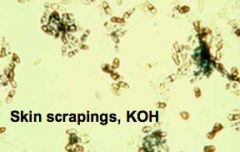
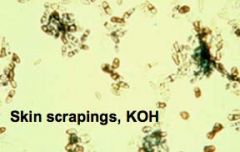
a. What are the symptoms of tinea negra?
|
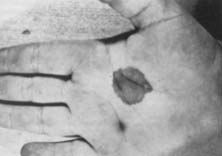
i. Black macules on the skin
|

|
|
|
c. How can you ID tinea negra?
|
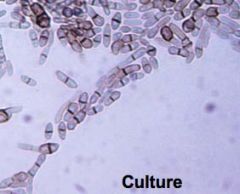
i. 2-celled oval yeast in skin scrapings
|
|
|
|
a. What agent causes black piedra?
|
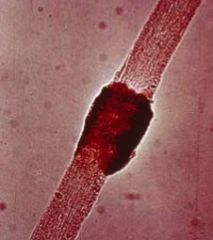
i. PIedraia hortai
|

|
|
|
b. What are the symptoms of black piedra?
|
i. Black nodules on hair shaft
|
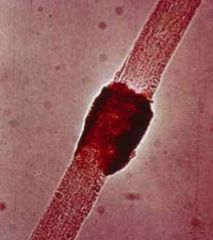
|
|
|
a. What agent causes white piedra?
|
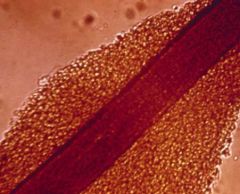
i. Trichosporum beigelli
|
|
|
|
b. What are the symptoms of white piedra?
|
i. Crème-colored nodules on hair shaft
|
|
|
|
a. What is the characteristic presentation of tinea?
|
i. Ringworm lesion
|

|
|
|
b. How can you ID tinea?
|
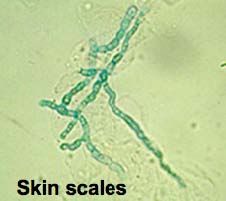
i. Micro- and macroconidia scrapings from lesion
|
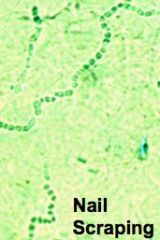
|
|
|
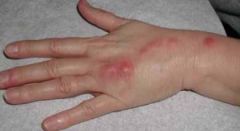
2. What is the most common subcutaneous mycotic disease?
|
a. Sporotrichosis
|
|
|
|
a. What agent causes sporotrichosis/Rose-grower’s disease?
|
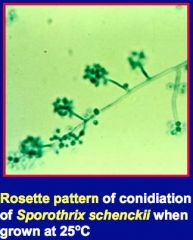
i. Sporothrix schenckii
|

|
|
|
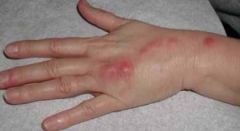
b. What are the symptoms of sporotrichosis?
|
i. Nodules and ulcers along lymphatics at site of inoculation
|
|
|
|
c. How can you ID sporotrichosis?
|
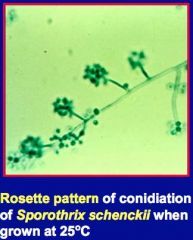
i. Cigar-shaped yeast in tissue exudate
ii. Converts to rosette pattern of conidiation on culture at 25 C |

|
|
|
a. What agent causes chromoblastomycosis?
|
i. Fonsecaea
|

|
|
|
b. What are the symptoms of chromoblastomycosis?
|

i. Warty nodules that progress to cauliflower-like
|

|
|
|
c. How can you ID chromoblastomycosis?
|
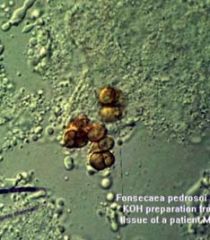
i. Copper-colored spherical yeast called Medlar bodies
|

|
|
|
d. Where is chromoblastomycosis usually found?
|
i. Lower limbs
|
|
|
|
a. What agents usually cause mycetoma?
|
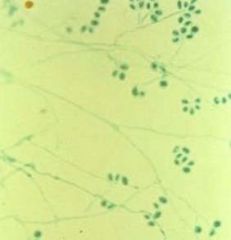
i. Pseudallescheria
ii. Madurella |

|
|
|
b. What are the symptoms of mycetoma?
|
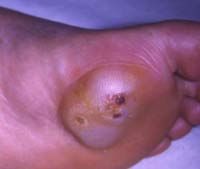
i. Draining sinus tracts at site of inoculation
|

|
|
|
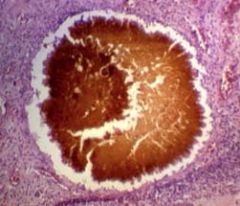
c. How can you ID mycetoma?
|
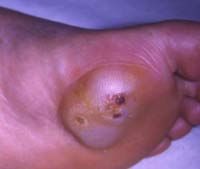
i. White, brown, yellow, or black granules in exudate that are fungal colonies
|
|
|
|
d. What is the name for a mycetoma infection in the foot?
|
i. Madurella foot
|
|
|
|
a. What agents cause mycotic keratitis?
|

i. Fusarium
ii. Candida albicans |

|
|
|
b. How can you differentiate between fusarium and candida albicans?
|

i. Fusarium→ cresecent-shaped macroconidia
ii. C. albicans→ pseudohyphae |

|
|
|
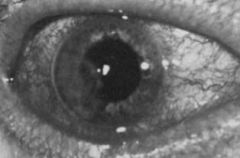
c. What are the symptoms of mycotic keratitis?
|
i. Corneal ulcer
ii. Hypopyon→ pus in anterior chamber |
|
|
|
a. How can you contract histoplasmosis?
|
i. Inhalation of macroconidia from soil at bird and bat roosts
ii. Causes a lung infection |
|
|
|
b. Where do you find macroconidia for histoplasma?
|
i. Major Midwest river valleys
|
|
|
|
c. What is the clinical presentation for histoplasmosis?
|
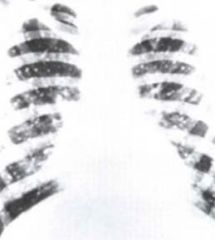
i. Cough, chest pain, dyspnea, hoarseness
ii. Results in acute or chronic progress lug disease with calcifications |
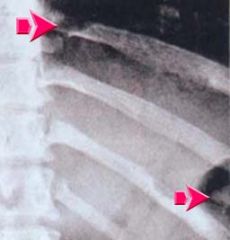
|
|
|
d. How can you ID histoplasmosis?
|
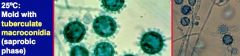
i. “Buckshot picture”
ii. 25 C→ tuberculate macroconidia iii. 37 C→ Small yeast |
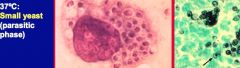
|
|
|
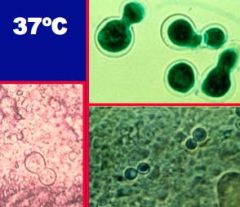
a. What agent causes North American blastomycosis?
|
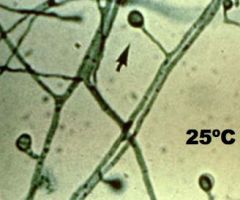
i. Blastomtyces dermatitidis
|
|
|
|
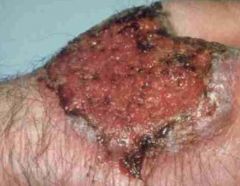
b. What are the symptoms of North American blastomycosis?
|
i. Granulomatous and suppurative lesions of lung with eventual skin lesions
ii. Resembles TB |
|
|
|
c. How can you ID North American blastomycosis?
|
i. Thick-walled yeast with a broad base at 37 C
|

|
|
|
d. Where are you most likely to contract North American blastomycosis?
|
i. Major Midwest river valleys
|
|
|
|
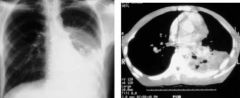
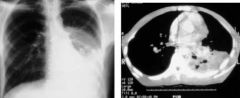
e. What will a CXR look like for North American blastomycosis?
|
i. Mycoplasmic pneumonia
|
|
|
|
a. What agent causes South American blastomycosis?
|
i. Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
|

|
|
|
b. What are the symptoms of South American blastomycosis?
|
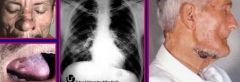
i. Initial lung disease with metastasis to skin and many organs
|

|
|
|
c. How can you ID South American blastomycosis?
|
i. 37 C→ yeast with multiple buds (can look like adenovirus or coronavirus)
|

|
|
|
d. Where are you most likely to contract South American blastomycosis?
|
i. Central and South America
|
|
|
|
i. What are the symptoms of cutaneous blastomycosis?
|
1. Dry, crusted, sharply circumscribed
|

|
|
|
ii. What deficiency puts you most at risk for cutaneous blastomycosis?
|
1. CMI deficiency
|
|
|
|
a. What agent causes coccidioidmycosis?
|
i. Coccidioides immitis
|

|
|
|
b. What are the symptoms of coccidioidmyocis?
|
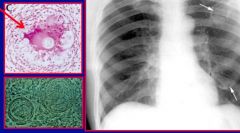
i. Flu-like
ii. Initial pneumonia followed by erythematous skin rash iii. Eventual skin ulcers and abscesses |

|
|
|
c. How can you ID coccidioidmycosis?
|
i. Multinucleate spherule at 37 C→ fungus ball cavity in lung
ii. Septate hypae with arthropsores at 25 C |

|
|
|
d. Where are you most likely to contract coccidioidmycosis?
|
i. SW US, Mexico
|
|
|
|
e. To what areas of the body can coccidioidmycosis? How will it present there?
|
i. Skin and bone
ii. Erythema nodosum iii. Skin lesions iv. Loss of L1-L2 disk space |

|
|
|
a. What agent causes cryptococcosis?
|
i. Cryptococcus neoformans
|

|
|
|
b. What are the symptoms of cryptococcosis?
|
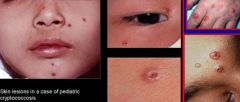
i. Mild lung infection
ii. Skin lesion iii. Meningitis |

|
|
|
c. How can you ID cryptococcosis?
|
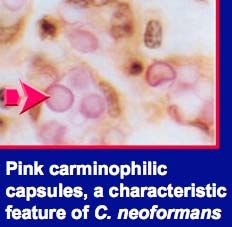
i. Yeast with a large capsule
|

|
|
|
d. What deficiency is associated with cryptococcosis?
|
i. CMI deficiency
|
|
|
|
e. Where are you most likely to contract cryptococcosis?
|
i. Worldwide
ii. Pigeon roosts |
|
|
|
What agent causes pneumocystis pneumonia?
|

Pneumocystis jiroveci
(An atypical fungus, which used to be classified as a protozoan) |
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of pneumocystis pneumonia?
|
asymptomatic, (sub-clinical, latent, 75-90% incidence in kids); AIDS-associated interstitial pneumonia--> 85% of AID patients; malnourished or IC kids
|
|
|
|
How do you ID pneumocystis pneumonia?
|
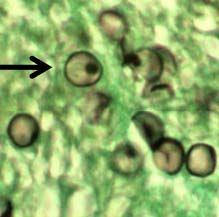
Microscopy of silver or giemsa-stained samples of sputum, bronchial lavage, or lung tissue should show many cysts
|
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of thrush (Candidiasis)?
|

Creamy or cheesy growth at vagina, mouth, moist skin areas; also see endocardidits and GI disease
|

|
|
|
What is the etiological agent of thrush (Candidiasis)?
|

Candida albicans, candida glabrata
|
|
|
|
How can you ID thrush (Candidiasis)?
|

Germ tube formation in serum; chlamydospores on corn meal agar
(Also--> Dimorphic budding yeast, invasive septate hyphae, pseudohyphae in tissues |
|
|
|
Who is most susceptible to contracting thrush (Candidiasis)?
|
Stressed, IC, or those missing normal flora
|
|
|
|
What is the etiological agent of Aspergillosis (allergic bronchopneumonia)?
|
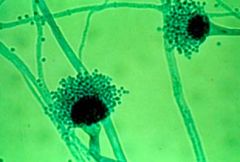
Aspergillus fumigatus
|

|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Aspergillosis (allergic bronchopneumonia)?
|
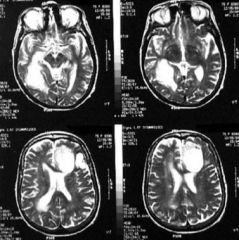
"Fungus Ball" in tissue (paranasal sinus, lung, or brain)
|

|
|
|
How can you ID Aspergillosis (allergic bronchopneumonia)?
|
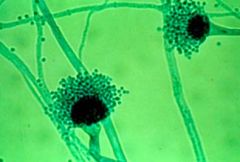
Morphology of asexual fruiting structures
|
|
|
|
How is Aspergillosis (allergic bronchopneumonia) transmission?
|
by inhalation
|
|
|
|
What is the etiological agent of Zygomycosis?
|

Rhizopus, Absidia, and mucor sp.
|
|
|
|
What are the symptoms Zygomycosis?
|
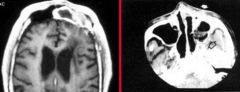
various, associated with diabetes; fungus ball in the eyes, sinuses, lungs, skin, or brain
|

|
|
|
How can you ID Zygomycosis?
|
Morphology of asexual fruiting structure and mycelium
|
|

