![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define periodic vibration. |
The repetition of motion over a certain time. |
|
|
Define frequency. |
Number of complete cycles of vibration in one second. f = 1/T |
|
|
Define tone. |
Sound with definite pitch. |
|
|
Define noise. |
No clear pitch repetition. |
|
|
What is the speed of sound triangle and what are the units? |
c = f x λ c = 345 ms-1 f = Hz λ = m |
|
|
Define transient. |
Time-varying part of sound. |
|
|
Define steady-state. |
Part where sound remains constant. |
|
|
Define Fourier's Theorem. |
Any vibration, however complex, can be analysed into a set of simultaneous sine curve vibrations. |
|
|
What is the harmonic spectrum? |
Spectrum containing frequency components in which the frequencies are whole number multiples of the fundamental frequency. |
|
|
What are the harmonic numbers for the main intervals (e.g octave, major 3rd etc.) |
1:1 - Unison 2:1 - Octave 3:2 - Perfect 5th 4:3 - Perfect 4th 5:4 - Major 3rd 6:5 - Major 6th |
|
|
What is the pitch interval formula? |
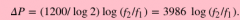
|
|
|
How is sound transmitted? |
Sound travel outwards from a vibrating object in the form of a longitudinal sound wave/ |
|
|
Define reflection. |
When the object is larger than the wavelength and it is reflected. It is high in frequency and pitch. |
|
|
Define diffraction. |
Bending of sound through a blockage when the wavelength is larger than the object. |
|
|
Define constructive interference. |
Same frequency and amplitude arriving in phase. |
|
|
Define destructive interference. |
Arriving 180º out of phase. |
|
|
Define beats. |
Combination of constructive and destructive interferences. |
|
|
Define pitch. |
Mixture of sound heard and sound interpreted by the brain. |
|
|
What is subjective sensation? |
Responding to a particular type of sound vibration. |
|
|
What is fusion? |
Brain combining pure tones into a pitch. Components of dominant region of frequency (500-2000Hz) give particular weights in brain assessing pitch. |
|
|
Define isotropic sound. |
Sound source radiating uniformly in all directions |
|
|
What is the Threshold of audibility? |
Intensity level for just audible sound. |
|
|
Define timbre. |
A steady-state tone that can be described by its waveform or frequency spectrum. Related to physical phenomena of unfolding partials in a spectrum called the spectral envelop. |

