![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Anatomy |
The study of internal and external body structures and their physical relationship among other body parts |
|
|
Physiology |
The study of how living organisms perform their functions |
|
|
Gross anatomy |
Gross anatomy can be seen without the use of a microscope |
|
|
Cytology |
The study of the internal structure of the individual cell the simplest units of life |
|
|
Histology |
Is the examination of tissues or groups of specialized cells and cell products that work together to perform a specific function |
|
|
Organs |
Organs are made of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific function |
|
|
Organ System |
A group of organs acting together to perform a specific function |
|
|
Homeostasis |
Means unchanging standing. Refers to the existence of a stable internal environment |
|
|
Autoregulation |
A process that occurs when a cell, tissue, organ, or an organ system adjust in response to some environmental change. For example when oxygen levels decline in a tissue the cells release chemicals that wide and or dialate blood vessels. |
|
|
Extrinsic regulation |
A process that results from the activities of the nervous system or endocrine system. These organ systems detect an environmental change and send either electrical or chemical messengers to adjust many other systems simultaneously. |
|
|
Homeostatic relationship involves what three parts |
Receptor that is sensitive to a particular stimulus or environmental change. A control center which receives and processes that information supplied by the receptor and send out commands. An effector or organ that respond to commands of the control center and who's activity either opposes or enhances stimuli |
|
|
Inregumentar system Organs and funtion |
Skin, Hair, Sweat glands, Nails Protects against environmental hazards helps regulate body temperature, provides sensory information |
|
|
Skeletal system Organs and function |
Organs: bones, cartilage, associated ligaments, bone marrow Functions: provide support and protection for other tissues stores calcium and other minerals forms blood cells |
|
|
Muscular system organs and functions |
Organ: skeletal muscles and associated tendons Functions: provides movement, provides protection and support for other tissues, generates heat that maintains body temperature |
|
|
Nervous system Organs and function |
Organs: brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, sense organs Functions: direct immediate response to stimuli, coordinates or moderate activities of other organ systems, provides and interprets sensory information about external conditions |
|
|
Endocrine system organs and function |
Organs: pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands, gonads, endocrine tissues in other systems Functions: direct long-term changes in the activities of other organ systems, adjust metabolic activity and energy use by the body, controls many structural and functional changes during development |
|
|
Cardiovascular organs and function |
Organs: heart, blood, blood vessels Function: distributes blood cells, water and dissolved materials including nutrients waste products, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Distributes heat and assist in control of body |
|
|
Simple squamous epithelium |
Single layer of flattened cells-simplest of epithelia Allows materials to pass through diffusion and filtration. Secretes lubricant substance in serosae Location: air sacs of lungs, blood vessels, lining of ventral body cavity |
|
|
Simple cuboidal epithelium |
Function: Secretion and absorption
Location: kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface |
|
|
Simple Columnar epithelium |
Description: single layer of tall cells. Some cells bear cilia, may contain mucus secreting goblet cells Function: absorption, Secretion of mucus enzymes. Location: non-cilliated type lines the stomach to the rectum. Ciliated are in the uterine tubes |
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar epithelium |
Description: may contain goblet cells, may have cilia. Single layer of cells with differing height Function: secretes substances, mostly mucus which is propelled by cilia. Location: ciliated in the trachea, non ciliated in men's sperm |
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium |

|
|
|
Stratified cuboidal epithelium |
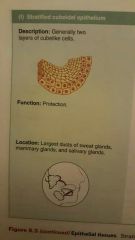
|
|
|
Stratified Columnar epithelium |

|
|
|
4 main types of connective tissue |
Connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood |
|
|
Areolar connective tissue diagram |
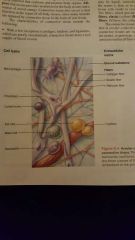
Soft packaging of material that cushions and protects the body. |
|
|
Embryonic connective tissue: Mesenchyme |
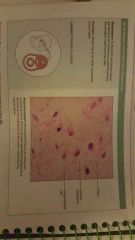
|

