![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
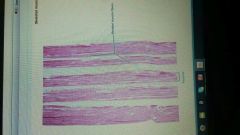
State the tissue type |
Skeletal muscle |
|
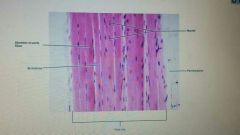
State tissue type |
Skeletal muscle |
|
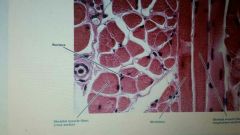
Name tissue type |
Skeletal muscle |
|
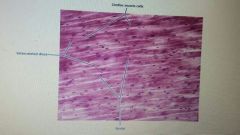
Name tissue type |
Cardiac muscle |
|
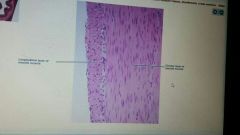
Name tissue type |
Smooth muscle |
|
|
Location of cardiac muscle? |
Walls of the heart |
|
|
Location of Smooth muscle? |
Lines the walls of hollow organs like the bladder and intestines |
|
|
Location of skeletal muscle? |
Attached to the skeleton |
|
|
Function of Cardiac muscle? |
To push blood through arteries and veins |
|
|
Function of Skeletal muscle? |
Produce skeletal movement and maintain body posture and body position and support soft tissue |
|
|
Function of smooth muscle? |
Push fluids through hollow tubes |
|
|
Which muscle tissue(s) is/are involuntary? |
Smooth muscle and Cardiac muscle |
|
|
What muscle tissue is striated? |
Skeletal muscle and Cardiac muscle |
|
|
Spindle-shaped with one nucleus is ____ muscle. |
Smooth |
|
|
____ muscle is thin and branched and has intercalated disks. |
Cardiac |
|
|
____ muscle is large, cylindrical shaped, and Multinucleated |
Skeletal |
|
|
What are the 4 basic properties of all muscle tissue? |
Excitability, contractility, elasticity, extensibility |
|
|
What is excitability |
Able to respond to stimulation |
|
|
What is contractility |
Ability to shorten and create tension |
|
|
What is extensibility |
Ability to contract at multiple lengths of rest and not just all or nothing |
|
|
What is elasticity |
Ability to go back to original shape |

