![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Muscle tissue |
Contraction; movement of body; change in shape and size internal organs. |
|
|
How do muscle cell contract? |
Sliding movement between actin and myosin (contraction) What are |
|
|
What are the muscle cells made up of? |
Myofilaments |
|
|
Two types of myofilaments |
Thick filaments: composed of myosin II; one structure Thin filaments: composed of actin (G-actin and F-actin); troponin and tropomyosin; 3 structures |
|
|
What are long cylindrical structures of muscle tissue called? |
Muscle fibers |
|
|
Cell membrane |
Sarcolemma |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Sarcoplasm |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Sarcosome |
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
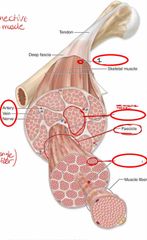
Front (Term) |
1) Epimysium: separates/enclose the fascicles |
|
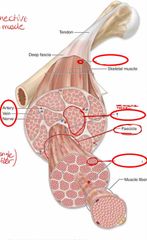
Front (Term) |
Perimysium: surround each fascicle or bundle |
|
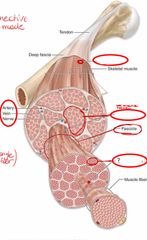
Front (Term) |
Endomysium: surrounds a single muscle fiber |
|
|
Myoblast |
Fusion of individual muscle cells. |
|
|
Characteristic of a muscle fiber |
Multinucleated syncytium |
|
|
What is so special about satellite cells? |
Limited regeneration of muscle fiber. |
|
|
What is an important feature of skeletal muscle? |
Striation and voluntary movement. |
|
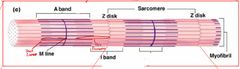
Front (Term) |
A-band: form myosin filaments and overlapping of myosin and actin filaments M-line: myosin filaments are attached I-band= where actin filaments are formed Z-disc: actin filaments are attached Sacromere: area between two z-disks |
|
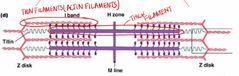
Front (Term) |
H-zone: myosin filaments only |
|
|
What happens when muscles contract? |
Sacromere (z-line) shortens No change in actin or myosin H-zone and I-band shortens Myofilaments don’t change length |
|
|
What is t-tubule and significance? |
Passage that allows deeper access to muscle fibers and causes depolarization. |
|
|
What is a triad? |
A complex that includes T tubule and 2 terminal cisternae |
|
|
Describe the depolarization event in skeletal muscle fibers |
Sarcoplasmic reticulum form terminal cisternae that serves as a reservoir for Calcium which is where muscle contraction come into play |
|
|
What are types of skeletal muscle fibers? |
Type I (oxidative): slow contraction; a lot of myoglobin; red muscle; less chance of fatigue Type IIa (fast oxidative glycolytic): fast contraction; less myoglobin; white muscle; less chance of fatigue Type IIb (fast glycolytic): fast contraction; less myoglobin; white muscle; fatigue easily |
|
|
Cardiac muscle |
Striated involuntary contraction; each cardiomyocyte are highly branched with its own nucleus; attached by intercalated discs |
|
|
Smooth muscle |
No striation involuntary contraction; actin and myosin are present but not in form of striation; actin is attached to dense bodies (z-line) |
|
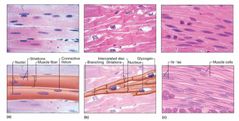
Front (Term) |
A) Skeletal muscle B) Cardiac muscle C) Smooth muscle |

